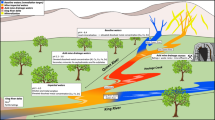
Abstract
The increasing urbanization, along with tourism, has posed a major threat to the Kumaun Himalayan Lakes, Uttarakhand, India. The total metal concentration in the water, interstitial water, and sediments along with the metal fractionation studies were carried out to understand the remobilization of the trace metals from the sediments of the lakes. The high concentration of the metals in the water column of the lakes generally decreases with depth and the metals release from the sediment is mainly due to the prevalence of anoxic condition at the sediment–water interface and sediment column. The sediment shows that metals Fe and Cr are derived from detrital source, whereas Co, Ni, and Zn are derived mainly from the organic matter dissolution. The sparse correlation of the trace metals with Ti shows most of the metals have chiefly re-precipitated from the water column. The metals speciation studies also supports that metals experience a high rate of anoxic dissolution and their precipitation onto the sediments are determined by the sediment composition and organic matter content. The high concentration of manganese in the interstitial water in the lakes indicates dissolution of organic matter. The released manganese is adsorbed/precipitated as carbonate phase (Nainital Lake) and oxide pahse (in other lakes). The study shows that the trace metals are regenerated from the sediments due to oxyhydroxide dissolution and organic matter decomposition.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, M. B., Tripathi, R. D., Rai, U. N., Pal, A., & Singh, S. P. (1999). Physico-chemical characteristics and pollution level of Lake Nainital (U.P., India): Role of macrophytes and phytoplankton in biomonitoring and phytoremediation of toxic metal ions. Chemosphere, 39, 2171–2182.
Bhat, M. I., & Ahmad, T. (1987). Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Bhowali–Bhimtal volcanics, Kumaun Lesser Himalayas. Geosciences Journal, 3, 51–68.
Boyle, J. (2001). Redox remobilzation and the heavy metal record in Lake sediments: A modelling approach. Journal of Paleolimnology, 26, 423–431.
Bruland, K. W., & Lohan, M. C. (2003). Controls of trace metals in seawater. In H. Elderfield (Vol. Ed.), Treatise on geochemistry 6: The oceans and marine geochemistry, (1st ed., pp. 23–57). UK: Elsevier Pergamon.
Callender, E. (2004). Heavy metals in the environment—historical trends. In B. S. Lollar, (Vol. Ed.), Treatise on geochemistry 9: Environmantal geochemistry, (1st Ed., pp. 585–643). UK: Elsevier Pergamon.
Calvert, S. E., & Pederson, T. F. (1993). Geochemistry of recent oxic and anoxic marine sediments: implications for the geological record. Marine Geology, 113, 67–88.
Canfield, D. E., Thamdrup, B., & Hansen, J. W. (1993). The anaerobic degradation of organic matter in Danish coastal sediments: Iron reduction, manganese reduction, and sulfate reduction. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 57, 3867–3883.
Carroll, S., O’Day, P. A., Esser, B., & Randall, S. (2002). Speciation and fate of trace metals in estuarine sediments, under reduced and oxidized conditions, Seaplane Lagoon, Alameda Naval Air Station (USA). Geochemical Transactions, 3, 81–101.
Chakrapani, G. J. (2002). Water and sediment geochemistry of major Kumaun Himalayan lakes, India. Environmental Geology, 43, 99–107.
Choudhary, P. (2008). Characterisation of organic matter in sediments of Kumaun Himalayan Lakes, (p. 110). Ph.D Thesis, Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, India.
Choudhary, P., Routh, J., Chakrapani, G. J., & Kumar, B. (2009). Biogeochemical Records of Paleoenvironmental Changes in Nainital Lake, Kumaun Himalayasa, India. Journal of Paleolimnology, 42, 571–586.
Das, B. K. (2005). Environmental pollution impact on water and sediments of Kumaun lakes, Lesser Himalaya, India: A comparative study. Environmental Geology, 49, 230–239.
Das, B. K., Singh, M., & van Grieken, R. (1995). The elemental chemistry of sediments in the Nainital Lake, Kumaun Himalaya, India. Science of the Total Environment, 168, 85–90.
Davison, W. (1993). Iron and manganese in lakes. Earth-Science Review, 34, 119–163.
Forstner, U., & Wittmann, G. T. W. (1983). Metal pollution in the aquatic environment, (2nd Revised Edition, p. 486). Springer Verlag.
Gambrell, R. P., Wiesepepe, J. B., Patrick, W. H., Jr., & Duff, M. C. (1991). The effects of pH, redox and salinity on metal release from a contaminated sediment. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 57, 359–367.
Guo, T., DeLaune, R. D., & Patrick, W. H., Jr. (1997). The influence of sediment redox chemistry on chemically active forms of arsenic, cadmium, chromium, and zinc in estuarine sediment. Environmental International, 23, 305–316.
Gupta, P. K., & Pant, M. C. (1989). Sediment chemistry of Lake Bhimtal, UP, India. International Review of Hydrobiologia, 74, 679–687.
Irabien, M. J., & Velasco, F. (1999). Heavy metals in Oka river sediments (Urdaibai National Biosphere Reserve, northern Spain): Lithogenic and anthropogenic effects. Environmental Geology, 37, 54–63.
Jacobs, L., Emerson, S., & Skei, J. (1985). Partitioning and transport of metals across the O2/H2S Interface in a permenantly anoxic basin: Framvaren Fjord, Norway. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 49, 1433–1444.
Jain, C. K., Malik, D. S., & Yadav, R. (2007). Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of Lake Nainital, Uttaranchal, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-006-9383-6.
Koretsky, C. M., Haas, J. R., Miller, D., & Ndenga, N. T. (2006). Seasonal variations in pore water and sediment geochemistry of littoral lake sediments (Asylum Lake, MI, USA). Geochemical Transactions, 7. doi:10.1186/1467-4886-7-11.
Kotlia, B. S., Bhalla, M. S., Sharma, C., Rajagopalan, G., Ramesh, R., Chauhan, M. S., et al. (2000). Palaeoclimatic conditions in the upper Pleistocene and Holocene Bhimtal–Naukuchiatal lake basin in south-central Kumaun, North India. Palaeogeograpgy Palaeoclimatology and Palaeoecology, 130, 307–321.
Leleyter, L., & Probst, J. L. (1999). A new sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particular trace elements in river sediments. International Journal of Environmental and Analytical Chemistry, 73, 109–128.
Lovley, D. R. (1995). Microbial reduction of iron and manganese, and other metals. In D. L. Sparks (Ed.), Advances in agronomy, (pp. 175–230). New York: Academic.
Morel, F. M. M., & Price, N. M. (2003). The biogeochemical cycles of trace metals in the ocean. Science, 300, 944–947.
Mortimer, R. J. G., & Rae, J. E. (2000). Metal speciation (C, Zn, Pb, Cd) and organic matter in oxic to suboxic salt marsh sediments, Severn Estuary, Southeastern Britain. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40, 377–386.
Muller, G. (1979). Schwermetalle in den sedimenten des rheins—Veranderungen seit. Umschau, 79, 778–783 (original in German language).
Nachiappan, P. R., Kumar, B., Saravanakumar, U., Jacob, N., Sharma, S., Joseph, T. B., et al. (2000). Estimation of sub-surface components in the water balance of lake Nainital (Kumaun Himalaya, India) using environmental isotopes. Proceedings of International Conference on Integrated Water resources Management for Sustainable Development, New Delhi, 239–254.
Panda, D., Subramanian, V., & Panigrahy, R. C. (1995). Geochemical fractionation of heavy metals in Chilka Lake (east coast of India)—a tropical coastal lagoon. Environmental Geology, 26, 199–210.
Pant, M. C., Sharma, A. P., & Sharma, P. C. (1980). Evidence for the increased eutrophication of lake Nainital as a result of human interference. Environmental Pollution (Series B), 1, 149–161.
Pauwels, H., Foucher, J.-C., & Kloppmann, W. (2000). Denitrifiaction and mixing in a schist aquifer: influence on water chemistry and isotopes. Chemical Geology, 168, 307–324.
Purushothaman, P. (2009). Nutrients and heavy metals in Kumaun Himalayan Lakes, India, Ph.D thesis, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, India.
Purushothaman, P., Soren, A., & Chakrapani, G. J. (2008). Phosphorous fractionation in Nainital Lake. Himalayan Geology, 29, 73–79.
Schneider, R. R., Price, B., Muller, P. J., Kroon, D., & Alexander, I. (1997). Monsoon related variations in Zaire (Congo) sediment load and influence of fluvial silicate supply on marine productivity in the east equatorial Atlantic during the last 200,000 years. Paleoceanography, 12, 463–481.
Scholz, F., & Newmann, T. (2007). Trace element diagenesis in pyrite-rich sediments of the Achterwasser lagoon, SW Baltic Sea. Marine Chemistry, 107, 516–532.
Schwientek, M., Einsiedl, F., Stichler, W., Stogbauer, A., Strauss, H., & Maloszewski, P. (2008). Evidence for denitrifiaction regulated by pyrite oxidation in heterogeneous porous groundwater system. Chemical Geology. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.06.005.
Singh, S. P., & Gopal, B. (2002). Integrated management of water resources of Lake Nainital and its watershed: An Environmental Economics Approach, (p. 162). Mumbai, India: EERC, Indira Gandhi Institute for Developmental Research.
Sparks, D. L. (2005). Toxic metals in the environment: The role of surface. Elements, 1, 193–197.
Sprenger, M., & McIntosh, A. (1989). Relationship between concentrations of aluminum, cadmium, lead, and zinc in water, sediments, and aquatic macrophytes in six acidic lakes. Archives of Environmental Contaminant and Toxicology, 18, 225–231.
Staelens, N., Parkpian, P., & Polprasert, C. (2000). Assessment of metal speciation evolution in sewage sludge dewatered in vertical flow reed beds using a sequential extraction scheme. Chemical Speciation and Bioavailability, 12, 97–107.
Stumm, W., & Morgan, J. J. (1996). Aquatic chemistry: Chemical equilibria and rates in natural waters, (3rd Ed., p. 1022). Canada: Wiley.
Szymanowska, A., Samecka-Cymerman, A., & Kempers, A. J. (1999). Heavy metals in three lakes in West Poland. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 43, 21–29.
Tack, F. M., & Verloo, M. G. (1995). Chemical speciation and fractionation in soil and sediment heavy metal analysis: A review. International Journal of Environmental Chemistry, 59, 225–238.
Taylor, S. R., & Mclennan, S. M. (1985). The continental crust: Its composition and evolution, (p. 312). Oxford: Blackwell.
Tessier, A., Rapin, F., & Carignan, R. (1985). Trace metals in oxic lake sediments: Possible adsorption on to iron oxyhydroxides. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 49, 183–194.
Tessier, A., Fortin, D., Belzile, N., DeVitre, R. R., & Leppard, G. G. (1996). Metal sorption to diagenetic iron and manganese oxyhydroxides and associated organic matter: Narrowing the gap between field and laboratory measurements. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60, 387–404.
Tribovillard, N., Algeo, T. J., Lyons, T., & Riboulleau, A. (2006). Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: An update. Chemical Geology, 232, 12–32.
Turekian, K. K., & Wedepohl, K. H. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 72, 175–192.
Valdiya, K. S. (1988). Geology and natural environment of Nainital Hills, Kumaun Himalaya, (p. 155). Nainital, India: Gyanodaya Prakashan.
van Griethuysen, C., Luitwieler, M., Joziasse, J., & Koelmans, A. A. (2005). Temporal variation of trace metal geochemistry in floodplain lake sediment subject to dynamic hydrological conditions. Environmental Pollution, 137, 281–294.
Wang, S. X., Zhang, S. Z., & Shan, X. Q. (2003). Fractionation of heavy metals in different particle size sediments and its relationship with heavy metal pollution. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination Toxicology, 71, 873–880.
Warren, L. A., & Haack, E. A. (2001). Biogeochemical controls on metal behaviour in freshwater environments. Earth-Science Reviews, 54, 261–320.
Yu, K. C., Tsai, L. J., Chen, S. H., & Ho, S. T. (2001). Chemical binding of heavy metals in anoxic river sediments. Water Research, 35, 4086–4094.
Zabel, M., Schneider, R. R., Wagner, T., Adegbie, A. T., de Vries, U., & Kolonic, S. (2001). Late Quaternary climate changes in central Africa as inferred from terrigenous input to the Niger Fan. Quaternary Research, 56, 207–217.
Zhai, M., Kampunzu, H. A. B., Modisi, M. P., & Totolo, O (2003). Distribution of heavy metals in Gaborone urban soils (Botswana) and its relationship to soil pollution and bedrock composition. Environmental Geology, 45, 171–180.
Acknowledgement
We thank MoEF, India for funding the project. P.P specially acknowledges MoEF, CSIR India for support through fellowship. We also thank Ravi, Yadav, and Vijay for their help in the field and lab.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Purushothaman, P., Chakrapani, G.J. Trace metals biogeochemistry of Kumaun Himalayan Lakes, Uttarakhand, India. Environ Monit Assess 184, 2947–2965 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2163-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2163-y