Abstract
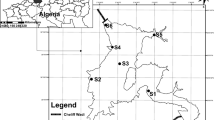
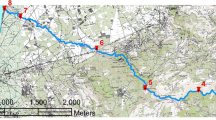
The paper presents water-quality evaluation based on an 8-year monitoring programme in the Gdansk Municipality region, on the Southern coast of the Baltic Sea. The studies were carried out from 2000 to 2007 by surface water analysis at 15 various sites within eight watercourses. Sampling sites included rather urbanized or developed lands, farming fields and non-polluted city recreational areas such as parks and forests. Most of the watercourses were sampled monthly at two locations, one within the upper course of the watercourse and the other near its mouth. In all samples, eight parameters of water quality were determined: total suspended solids, dissolved oxygen, water temperature, oxygen saturation, 5-day biochemical oxygen demand, chemical oxygen demand, total phosphorus and total nitrogen concentration. Interpretation of the obtained results revealed that examination of those basic physicochemical parameters permits to discriminate initially watercourses with respect to level of water contamination. During the research, a large dataset was obtained and it was described by both basic statistical parameters and chemometric method of cluster analysis. The paper presents relations between analysed parameters and influence of land exploitation mode on water quality and describes variation of the results both in space and time.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
Almeida, C. A., Quintar, S., Gonzalez, P., & Mallea, M. A. (2007). Influence of urbanization and tourist activities on the water quality of the Potrero de los Funes River (San Luis–Argentina). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 133, 459–465.
APHA (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water & wastewater (21st ed.). Washington. D.C: American Public Health Association.
Astel, A., Tsakovski, S., Barbieri, P., & Simeonov, V. (2007). Comparison of self-organizing maps classification approach with cluster and principal components analysis for large environmental data sets. Water Research, 41(19), 4566–4578.
Brogueira, M. J., & Cabeçadas, G. (2006). Identification of similar environmental areas in Tagus estuary by using multivariate anlysis. Ecological Indicators, 6(3), 508–515.
Chang, H. (2005). Spatial and temporal variations of water quality in the Han River and its tributaries, Seoul, Korea, 1993–2002. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 161, 267–284.
Dojlido, J. (1987). Chemia wody (chemistry of water). Warsaw: Arkady.
Dz. U. Nr 162, poz. 1008 (2008). Rozporządzenie Ministra Środowiska z dnia 20 sierpnia 2008 roku w sprawie sposobu klasyfikacji stanu jednolitych części wód powierzchniowych (Regulation of the Polish Minister of Environment of 20 August 2008 on the classification of the surface water bodies), 8654–8681. http://static1.money.pl/d/akty_prawne/pdf/DU/2008/162/DU20081621008.pdf. Accessed 20 March 2010.
Ekpo, N. M., & Inyang, L. E. D. (2000). Radioactivity, physical and chemical parameters of underground and surface waters in Qua Iboe River estuary, Nigeria. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 60, 47–55.
Giridharan, L., Venugopal, T., & Jayaprakash, M. (2009). Assessment of water quality using chemometric tools: A case study of river Cooum, South India. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 56, 654–669.
Goncharuk, V. V. (2008). A new concept of supplying the population with a quality drinking water. Journal of Water Chemistry and Technology, 30, 129–136.
Hill, Y., & Lewicki, P. (2006). Statistics, methods and applications: A comprehensive reference for science, industry, and data mining. Tulsa: StatSoft.
Holt, M. S. (2000). Sources of chemical contaminants and routes into the freshwater environment. Food Chemistry and Toxicology, 38, S21–S27.
Kannel, P. R., Lee, S., Kanel, S. R., & Khan, S. P. (2007). Chemometric application in classification and assessment of monitoring locations of an urban river system. Analytica Chimica Acta, 582, 390–399.
Marengo, E., Gennaro, M. C., Giacosa, D., Abrigo, C., Saini, G., & Avignone, M. T. (1995). How chemometrics can helpfully assist in evaluating environmental data. Lagoon water. Analytica Chimica Acta, 317, 53–63.
Ocampo-Duque, W., Ferré-Huguet, N., Domingo, J. L., & Schuhmacher, M. (2006). Assessing water quality in rivers with fuzzy inference systems: A case study. Environment International, 32(6), 733–742.
Olajire, A. A., & Imeokparia, F. E. (2001). Water quality assessment of Osun River: Studies on inorganic nutrients. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 69, 17–28.
Otto, M. (1999). Chemometrics: Statistics and computer application in analytical chemistry. New York: Wiley.
Petraccia, L., Liberati, G., Masciullo, S. G., Grassi, M., & Fraioli, A. (2006). Water, mineral waters and health. Clinical Nutrition, 25, 377–385.
Reghunath, R., Sreedhara Murthy, T. R., & Raghavan, B. R. (2002). The utility of multivariate statistical techniques in hydrogeochemical studies: An example from Karnataka, India. Water Research, 36, 2437–2442.
Reisenhofer, E., Adami, G., & Barbieri, P. (1998). Using chemical and physical parameters to define the quality of karstic freshwaters (Timavo River, North-Eastern Italy): A chemometric approach. Water Research, 32, 1193–1203.
Simeonov, V., Sarbu, C., Massart, D. L., & Tsakovski, S. (2001). Danube River water data modelling by multivariate data analysis. Mikrochimica Acta, 137, 243–248.
Simeonov, V., Stratis, J. A., Samara, C., Zachariadis, G., Voutsa, D., Anthemidis, A., et al. (2003). Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Research, 37, 4119–4124.
Van Leeuwen, F. X. R. (2000). Safe drinking water: The toxicologist’s approach. Food Chemistry and Toxicology, 38, S51–S58.
Vega, M., Pardo, R., Barrado, E., & Debán, L. (1998). Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Research, 32, 3581–3592.
WFD (2000). Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32000L0060:EN:NOT. Accessed 20 March 2010.
Xia, X., Yang, Z., Wang, R., & Meng, L. (2005). Contamination of oxygen-consuming organics in the Yellow River of China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 110, 185–202.
Yunus, A. J. M., & Nakagoshi, N. (2004). Effects of seasonality on streamflow and water quality of the Pinang River in Penang Island, Malaysia. Chinese Geographical Science, 14, 153–161.
Zhang, Y., Guo, F., Meng, W., & Wang, X.-Q. (2009). Water quality assessment and source identification of Daliao river basin using multivariate statistical methods. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 152, 105–121.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Cieszynska, M., Wesolowski, M., Bartoszewicz, M. et al. Application of physicochemical data for water-quality assessment of watercourses in the Gdansk Municipality (South Baltic coast). Environ Monit Assess 184, 2017–2029 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2096-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2096-5