Abstract
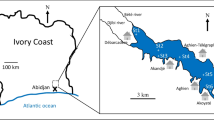
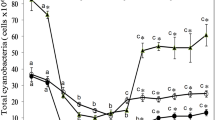
Cyanobacteria dominance and cyanotoxin production can become major threats to humans and aquatic life, especially in warm shallow lakes, which are often dominated by cyanobacteria. This study investigates the occurrence and distribution of microcystins (MCYST) in water, cell-bound and in the tissues of the commercial mugilid Liza sp. in the largest, coastal, Spanish Mediterranean lake (Albufera of Valencia). This is the first report concerning microcystin accumulation in tissues of mugilid fish species. Considerable amounts of microcystins were found in the water and seston, which correlated with development of Microcystis aeruginosa populations in the lake. The MCYST concentrations found in Lake Albufera (mean 1.7 and 17 μg/L and maximum 16 and 120 μg/L in water and seston, respectively) exceeded by one to two orders of magnitude the guideline levels proposed by the World Health Organization and were higher than that reported in other lakes of the Mediterranean zone. The presence of MCYST was found in all the fishes studied and accumulated differently among tissues of the commercial species Liza sp. Toxin accumulation in fish tissues showed that although the target organ for MCYST was the liver, high concentrations of microcystins were also found in other analysed tissues (liver>intestine>gills>muscle). Human tolerable daily intake for microcystins is assessed relative to the WHO guidelines, and potential toxicological risks for humans, wildlife and related ecosystems of the lake are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albay, M., Akcaalan, R., Tufekci, H., Metcalf, J., Beattie, K., & Codd, G. (2003). Depth profiles of cyanobacterial hepatotoxins (microcystins) in three Turkish freshwater lakes. Hydrobiologia, 505, 89–95.
Andersen, R. J., Luu, H., Chen, D. Z. X., Holmes, C. F. B., Kent, M. L., Le Blanc, M., et al. (1993). Chemical and biological evidence links microcystins to salmon “netpen liver disease”. Toxicon, 31, 1315–1323.
APHA. (1992). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Beveridge, M. C. M., Baird, D. J., Rahmatullah, S. M., Lawton, L. A., Beatie, K. A., & Codd, G. A. (1993). Grazing rates on toxic and non-toxic strains of cyanobacteria by Hypophthalmichthys molitrix and Oreochromis niloticus. Journal of Fish Biology, 43, 901–907.
Beklioglu, M., Romo, S., Kagalou, I., Quintana, X., & Bécares, E. (2007). State of the art in the functioning of shallow Mediterranean lakes: Workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia, 584, 317–326.
Blanco, S., & Romo, S. (2006). Ictiofauna del lago de la Albufera de Valencia: Evolución histórica y situación actual. Boletín Real Sociedad Espa nola Historia Natural (Sección Biología.), 101, 45–56.
Blanco, S., Romo, S., Villena, M. J., & Martínez, S. (2003). Fish communities and food web interactions in six shallow Mediterranean lakes. Hydrobiologia, 506, 473–480.
Bradt, S., & Villena, M. J. (2002). Detection of microcystins in the coastal lagoon La Albufera de Valencia, Spain by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Limnetica, 20, 187–196.
Briand, J., Robillot, C., Quiblier-Lloberas, C., & Bernard, C. (2002). A perennial bloom of Planktothrix agardhii (Cyanobacteria) in a shallow eutrophic French lake: Limnological and microcystin production studies. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, 153, 605–622.
Bury, N., Flik, G., Eddy, F., & Codd, G. (1996). The effects of cyanobacteria and the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin-LR on Ca2 + transport and Na + /K + -ATPase in Tilapia gills. Journal of Experimental Biology, 199, 1319–1326.
Carbis, C. R., Rawlin, G. T., Grant, P., Mitchell, G. F., Anderson, J. W., & McCauley, I. (1997). A study of feral carp, Cyprinus carpio L., exposed to Microcystis aeruginosa at lake Mokoan, Australia, and possible implications for fish health. Journal of Fish Deseases, 20, 81–91.
Cazenave, J., Wunderlin, D. A., Bistoni, M. A., Ame, M. V., Krause, E., Pflugmacher, S., et al. (2005). Uptake, tissue distribution and accumulation of Microcystin-RR in Corydoras paleatus, Jenynsia multidentata and Odontesthes bonariensis. Aquatic Toxicology, 75, 178–190.
Chorus, I. (2001). Cyanotoxins: Occurrence, Causes, Consequences. Berlin: Springer.
Chorus, I., & Bartram, J. (1999). (Eds.), Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water. A guide to public health consequences, monitoring and management (p. 416). London: E & FN Spon, WHO.
Cook, C., Vardaka, E., & Lanaras, T. (2004). Toxic cyanobacteria in Greek freshwaters, 1997–2000: Occurrence, toxicity and impacts in the Mediterranean region. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 32, 107–124.
Crush, J. R., Briggs, L. R., Sprosen, J. M., & Nichols, S. N. (2008). Effect of irrigation with lake water containing microcystins on microcystin content and growth of ryegrass. Clover, Rape, and Lettuce. Environmental Toxicology, 23, 246–252.
Ernst, B., Hitzfeld, B., & Dietrich, D. (2001). Presence of Planktothrix sp. and cyanobacterial toxins in Lake Ammersee, Germany and their impact on whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus L.). Environmental Toxicology, 16, 483–488.
Falconer, I., Bartram, J., Chorus, I., Kuiper-Goodman, T., Utkilen, H., Burch, M., et al. (1999). Safe levels and practices. In I. Chorus & J. Bartam (Eds.), Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water. A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management (pp. 155–178). London: E & FN Spon.
Fastner, J., Flieger, I., & Neumann, U. (1998). Optimised extraction of microcystins from field samples: A comparison of different solvents and procedures. Water Research, 32, 3177–3181.
Fisher, W., & Dietrich, D. (2000). Pathological and biochemical characterization of MC-induced hepatopancreas and kidney damage in carp (Cyprinus carpio). Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 16, 73–81.
Gaete, V., Caenelo, E., Lagos, N., & Zambrano, F. (1994). Inhibitory effects of Microcystis aeruginosa toxin on ion pumps of the gill of freshwater fish. Toxicon, 82, 121–127.
Gkelis, S., Harjunpa, V., Lanaras, T., & Sivonen, K. (2005). Diversity of hepatotoxic microcystins and bioactive anabaenopeptins in cyanobacterial blooms from Greek freshwaters. Environmental Toxicology, 20, 249–256.
Gkelis, S., Lanaras, T., & Sivonen, K. (2006). The presence of microcystins and other cyanobacterial bioactive peptides in aquatic fauna collected from Greek freshwaters. Aquatic Toxicology, 78, 32–41.
Hillebrand, H., Urselen, C., Kirschtel, D., Pollingher, U., & Zohary, T. (1999). Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. Journal of Phycology, 35, 403–424.
Huisman, J., Matthijs, H., & Visser, P. (2005). Harmful Cyanobacteria. The Netherlands: Springer.
Jones, G. J., & Orr, P. T. (1994). Release and degradation of microcystin following algicide treatment of a Microcystis aeruginosa bloom in a recreational lake, as determined by HPLC and protein phosphatase inhibition assay. Water Research, 28, 871–876.
Kardinaal, W., & Visser, P. (2005). Dynamics of cyanobacterial toxins. Sources of variability in microcystin concentrations. In J. Huisman, H. Matthijs, P. Visser (Eds.), Harmful cyanobacteria (pp. 41–64). The Netherlands: Springer.
Kagalou, I., Papadimitriou, T., Bacopoulos, V., & Leonardos, I. (2008). Assessment of microcystins in lake water and the omnivorous fish (Carassius gibelio, Bloch) in Lake Pamvotis (Greece) containing dense cyanobacterial bloom. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 137, 185–195.
Keshavanath, P., Beveridge, M. C. M., Baird, D. J., Lawton, L. A., Nimmo, A., & Codd, G. A. (1994). The functional grazing response of a phytoplanktivorous fish Oreochromis niloticus to mixtures of toxic and non-toxic strains of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Journal of Fish Biology, 45, 123–129.
Klaassen, C., & Watkins, B. (1984). Mechanisms of bile formation, hepatic uptake, and biliary excretion. Pharmacological Reviews, 36, 1–67.
Kosten, S., Huszar, V., Bécares, E., Costa, L., van Donk, E., Hansson, L.-A., et al. (2011). Warmer Climate Boosts Cyanobacterial Dominance in Lakes. Global Change Biology. in press.
Kotak, B. G., Lam, A. K., Prepas, E. E., Hrudey, S. E., & Kenefick, S. L. (1995). Variability of the hepatotoxin, microcystin-LR, in hypereutrophic drinking water lakes. Journal of Phycology, 31, 248–263.
Kotak, B. G., Zurawell, R., Prepas, E., & Holmes, C. (1996). Microcystin-LR concentration in aquatic food web compartments from lakes of varying trophic status. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 53, 1974–1985.
Kuiper-Goodman, T., Falconer, I., & Fitzgerald, J. (1999). Human health aspects. In I. Chorus, & J. Bartram (Eds.), Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water—A Guide to Their Public Health, Consequences, Monitoring and Management (pp. 113–153). London: E and FN Spon.
Kurmayer, R., Dittmann, E., Fastner, J., & Chorus, I. (2002). Diversity of microcystin genes within a population of the toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis spp. in Lake Wannsee (Berlin, Germany). Microbial Ecology, 43, 107–118.
Lam, A. K. Y., Fedorak, P. M., & Prepas, E. (1995). Biotransformation of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin-LR, as determined by HPLC and protein phosphatase bioassay. Environmental Science and Technology, 29, 242–246.
Lindholm, T., Vesterkvist, P., Spoof, L., Lundberg-Niinistö, C., & Meriluoto, J. (2003). Microcystin occurrence in lakes in Åland, SW Finland. Hydrobiology, 505, 129–138.
MacKintosh, C., Beattie, K. A., Klumpp, S., Cohen, P., & Codd, G. A. (1990). Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Letters, 264, 187–192.
Magalhães, V. F., Soares, R., & Azevedo, S. (2001). Microcystin contamination in fish from the Jacarepaguaa^ Lagoon (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil): Ecological implication and human health risk. Toxicon, 39, 1077–1085.
Malbrouck, C., & Kestemont P. (2006). Effects of microcystins on fish. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 25, 72–86.
McElhiney, J., Lawton, L. A., & Leifert, C. (2001). Investigations into the inhibitory effects of microcystins on plant growth, and the toxicity of plant tissues following exposure. Toxicon, 39, 1411–1420.
Mohamed, Z. A., Carmichael, W. W., & Hussein, A. A. (2003). Estimation of microcystins in the freshwater fish Oreochromis niloticus in an Egyptian fish farm containing a Microcystis bloom. Environmental Toxicology, 18, 137–141.
Nasri, H., Bouaïcha, N., & Kaid-Harche, M. (2007). A new morphospecies of Microcystis sp. forming bloom in the Cheffia dam (Algeria): Seasonal variation of microcystin concentrations in raw water and their removal in a full-scale treatment plant. Environmental Toxicology, 22, 347–356.
Ouahid, Y., & Fernández, F. (2009). Typing of toxinogenic Microcystis from environmental samples by multiplex PCR. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 85, 405–412.
Papadimitriou, T., Kagalou, I., Bacopoulos, V., & Leonardos, I. (2009). Accumulation of microcystins in water and fish tissues: An estimation of risks associated with microcystins in most of the Greek lakes. Environmental Toxicology. doi:10.1002/tox.
Reynolds, C. S. (1997). Vegetation process in the pelagic: A model for ecosystem theory. In O. Kinne (Ed.), Oldendorf (pp. 1–371). Excellence in Ecology ECI. Oldendorf/Luhe: Ecology Institute.
Romo, S., & Miracle, R. (1993). Long-term periodicity of Planktothrix agardhii, Pseudanabaena galeata and Geitlerinema sp. in a shallow hypertrophic lagoon, the Albufera of Valencia (Spain). Archiv für Hydrobiologie, 26, 469–486.
Romo, S., Miracle, R., Villena, M. J., Rueda, J., Ferriol, C., & Vicente, E. (2004). Mesocosm experiments on nutrient and fish effects on shallow lake food webs in a Mediterranean climate. Freshwater Biology, 49, 1593–1607.
Romo, S., Villena, M. J., Sahuquillo, M., Soria, J., Giménez, M., Alfonso, T., et al. (2005). Response of a shallow Mediterranean lake to nutrient diversion: Does it follow similar patterns as northern shallow lakes? Freshwater Biology, 50, 1706–1717.
Romo, S., García-Murcia, A., Villena, M. J., Sánchez, V., & Ballester, A. (2008). Tendencias del fitoplancton en el lago de la Albufera de Valencia e implicaciones para su ecología, gestión y recuperación. Limnetica, 27, 11–28.
Sahin, A., Tencalla, F. G., Dietrich, D. R., & Naegeli, H. (1996). Bilary excretion of biochemically active cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) hepatotoxins in ?sh. Toxicology, 106, 123–130.
Smith, J. L., & Haney, J. F. (2006). Foodweb transfer, accumulation, and depuration of microcystins, a cyanobacterial toxin, in pumpkinseed sun?sh (Lepomis gibbosus). Toxicon, 48, 580–589.
Soares, R., Magalhaes, V., & Azevedo, S. (2004). Accumulation and depuration of microcystins (cyanobacteria hepatotoxins) in Tilapia rendalli (Cichlidae) under laboratory conditions. Aquatic Toxicology, 70, 1–10.
Tencalla, F. G, & Dietrich, D. (1997). Biochemical characterization of microcystin toxicity in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Toxicon, 35, 583–595.
Tencalla, F. G., Dietrich, D. R., & Schlatter, C. (1994). Toxicity of Microcystis aeruginosa peptide toxin to yearling rainbow trout (Oncorhyunchus mykiss). Aquatic Toxicology, 30, 215–224.
Ueno, Y., Nagata, S., Tsutsumi, T., Hasegawa, A., Yoshida, F., Suttajit, M., et al. (1996). Survey of microcystins in environmental water by a highly sensitive immunoassay based on monoclonal antibody. Natural Toxins, 4, 271–276.
Vasconcelos, V., Sivonen, K., Evans, W., Carmichael, W. W., & Namikoshi, M. (1996). Hepatotoxic microcystin diversity in cyanobacterial blooms collected in Portuguese freshwaters. Water Research, 30, 2377–2384.
Villena, M. J., & Romo, S. (2003). Temporal changes of cyanobacteria in the largest coastal Spanish Lake. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, 109/148, 593–608.
Visser, P., Ibelings, B., Mur, L., & Walsby, A. (2005). The ecophysiology of the harmful cyanobacterium Microcystis. Features explaining its success and measures for its control. In J. Huisman, H. Matthijs, P. Visser P. (Eds.), Harmful cyanobacteria (pp. 109–142). The Netherlands: Springer.
WHO (2003). Guidelines for safe recreational water environments. Coastal and Freshwaters. WHO Document.
Xie, L., Xie, P., Guo, L., Li, L., Miyabara, Y., & Park, H. D. (2005). Organ distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in freshwater fish at different trophic levels from the eutrophic Lake Chaohu, China. Environmental Toxicology, 20, 293–300.
Xu, L., Lam, P. K. S., Chen, J., Zhang, Y., & Harada, K. (2000). Comparative study on in vitro inhibition of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) and mouse protein phosphatases by microcystins. Environmental Toxicology, 15, 71–75.
Zhang, X., Xie, P., Hao, L., Guo, N., Gong, Y., & Hu, X. (2006). Effects of the phytoplanktivorous silver carp (Hypophthalmichtys molitrixon) on plankton and the hepatotoxic microcystins in an ecosystem experiment in a eutrophic lake, Lake Shichahai in Beijing. Aquaculture, 257, 173–186.
Zhao, M., Xie, S., Zhu, X., Yang, Y., Gan, N., & Song, L. (2005). Effect of inclusion of blue-green algae meal on growth and accumulation of microcystins in gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 22, 72–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romo, S., Fernández, F., Ouahid, Y. et al. Assessment of microcystins in lake water and fish (Mugilidae, Liza sp.) in the largest Spanish coastal lake. Environ Monit Assess 184, 939–949 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2011-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2011-0