Abstract
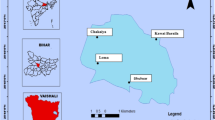
Aqaba Gulf is an economically important marine environment in Egypt. Its coastal area was subjected to anthropogenic impact of urbanization and economic development during the last decades. The study was oriented to investigate the distribution as well as assess the heavy metal pollution status (Fe, Mn, Zn, Ni, Co, Cr, Cu, and Cd) in its surface sediment. Large heavy metals fluctuations were detected along the studied area. The results pointed out to the highly significant correlations among Fe, Cu, Ni, and Co heavy metals and their similar lithogenic origin beside their input sources. The sediment quality was performed by using the geo-accumulation index (I geo) and different sediment criteria guidelines; China State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision (CSBTS), and Canadian guidelines. Among the studied heavy metals, Cd was the only metal that showed moderate pollution for I geo as well as it exceeded the primary and the secondary criteria of CSBTS and the threshold effect level of the Canadian guidelines (TEL). On the other hand, the other heavy metals were within the natural background levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Halim, A. M., Abol-Khair, E. M., Fahmy, M. A., & Shridah, M. A. (2007). Environmental assessment on the Aqaba Gulf coastal waters; Egypt. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 33(1), 1–14.
Abelson, A., Shteinman, B., Fine, M., & Kaganovsky, S. (1999). Mass transport from pollution sources to remote coral reefs in Eilat (Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 38, 25–29.
Abu-Hilal, A. H. (1985). Phosphate pollution in the Jordan Gulf of Aqaba. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 16, 281–285.
Abu-Hilal, A. H. (1987). Distribution of trace elements in near shore surface sediments from the Gulf of Aqaba (Red Sea), Jordan. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 18, 190–193.
Abu-Hilal, A. H., & Al-Najjar, T. (2004). Litter pollution on the Jordanian shores of the Gulf of Aqaba (Red Sea). Marine Environmental Research, 58, 39–63.
Adefem, O. S., Olaofe, O., & Asaolu, S. S. (2007). Seasonal variation in heavy metal distribution in the sediment of major dams in Ekiti-State, Pakistan. Journal of Nutrition, 6(6), 705–707.
Ahmed, M. H. M. (1996). An environmental impact assessment of pollution on the Arabian Gulf (p. 114). Ph.D. Thesis. Egypt: University of Alexandria.
Al-Horani, F. A., Al-Rousan, S. A., Al-Zibdeh, M., & Khalaf, M. A. (2006). The status of coral reefs on the Jordanian coast of the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Zoology in the Middle East, 38, 99–110.
Al-Ouran, N. (2005). Environmental assessment, documentation and spatial modeling of heavy metal pollution along the Jordan Gulf of Aqaba using coral reefs as environmental indicator (p. 152). Ph.D. Thesis. Germany: Universität Würzburg.
Al-Rousan, S. A., Al-Shloul, R. N., Al-Horani, F. A., & Abu-Hilal, A. H. (2007). Heavy metal contents in growth bands of Porites corals: Record of anthropogenic and human developments from the Jordanian Gulf of Aqaba. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 54, 1912–1922.
Anonymous (2002). Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life. CCME Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, Canada (cited from L. Rojas de Astudillo, I. Chang Yen and I. Bekele (2005): Heavy metals in sediments, mussels and oysters from Trinidad and Venezuela, Rev. Biol. Trop. (Int. J. Trop. Biol. 53 (1), 41–53)).
Badran, M. I., & Foster, P. (1998). Environmental quality of the Jordanian coastal waters of the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 1, 75–89.
Birth, G. (2003). A scheme for assessing human impacts on coastal aquatic environments using sediments. In C. D. Woodcoffe & R. A. Furness (Eds.), Coastal GIS.
Breckenridge, R. P., & Crockett, A. B. (1995). Determination of background concentrations of inorganics in soils and sediments at hazardous waste sites. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Engineering Forum Issue, EPA /540/S-96/500.
CASE NUMBER: 380. Case mnemonic: Aqaba Case Name: Aqaba, Trade and Environtment. http://www1.american.edu/projects/mandala/TED/aqaba.htm.
CSBTS (China State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision) (2002). The People’s Republic of China national standards GB 18668–2002—marine sediment quality (p. 10).
Draz, S. E. O., Youssef, D. H., & El-Siad, G. F. (2009). Sedimentological characterisrics and distribution of fluoride in granulometric fractions of subsurface sediments in Suez and Aqaba gulf, Egypt. Journal of Egyptian Academic Society for Environmental Development D-Environmental Studies, 10(1), 73–91.
El-Sikaily, A. (2008). Assessment of some heavy metals pollution in the sediments along the Egyptian Mediterranean Coast. Egyptian Journal ofAquatic Research, 34(3), 58–71.
Förstner, U., & Wittmann, G. T. W. (1979). Metal pollution in the aquatic environment (2nd ed.). Berlin: Springer.
Förstner, U., & Wittmann, G. T. W. (1981). In U. Förstner & G. T. W. Wittmann (Eds.), Metal pollution in the aquatic environment (2nd Revised ed., p. 486). Berlin: Springer.
Förstner, U., & Wittmann, G. T. W. (1983). Metal pollution in the aquatic environment. Berlin: Springer.
Greaney, K. M. (2005). An assessment of heavy metal contamination in the marine sediments of Las Perlas Archipelago, Gulf of Panama (p. 109). M.Sc. thesis. Edinburgh: School of Life Sciences, Heriot-Watt University.
Guevara, R., Rizzo, A., & Sanchez, R. (2005). Heavy metal inputs in northern Patagonia lakes from short sediment core analysis. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 265(3), 481–493.
Hashim, S. A., Mahasei, A. M., & Al-Saad, G. (1994). Variation of trace metal concentration in seawater and pearl oyster Pinctada radiate from Bahrin, Arabian Gulf. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 28, 370–373.
Hawkins, J. P., & Roberts, C. N. (1994). The growth of coastal tourism in the Red Sea: Present and future effects on coral reefs. Ambio, 23, 503–508.
Hoepner, T. (1999). A procedure for environmental impact assessments (EIA) for seawater desalination plants. Desalination, 124, 1–12.
Jonathan, M. V., & Mohan, V. R. (2003). Heavy metals in sediments of the inner shelf off the Gulf of Mannar, South East Coast of India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 46, 258–268.
Khalaf, M. A., & Kochzius, M. (2002). Changes in trophic community structure of shore fishes at an industrial sites in the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 239, 287–299.
Kloke, A., Sauerbeck, D. R., & Vetter, H. (1984). The contamination of plants and soils with heavy metals and the transport of metals in terrestrial food chains. In J. O. Nriagu (Ed.), Changing metal cycles and human health (pp. 113–141). Berlin: Springer.
Knutson, A. B., Klerks, P. L., & Levinton, J. S. (1987). The fate of metal contaminated sediments in Foundry Cove, New York. Environmental Pollution, 45, 291–304.
Korte, F. (1983). Eco-toxicology of cadmium: General overview. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 7, 3–8.
Lattemann, S., & Höpner, T. (2008). Environmental impact and impact assessment of seawater desalination. Desalination, 220, 1–15.
Leopold, E. N., Jung, M. C., Auguste, O., Ngatcha, N., Georges, E., & Lape, M. (2008). Metals pollution in freshly deposited sediments from river Mingoa, main tributary to the Municipal lake of Yaounde, Cameroon. Geoscience Journal, 12(4), 337–347.
Lin, S., & Chen, C. M. (1996). Spatial variations of heavy metals in the east China Sea continental shelf surface sediments. Chemistry and Ecology, 13, 77–91.
Long, E. R., MacDonald, D. D., Smith, S. L., & Calder, F. D. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environment & Management, 19, 81–97.
Long, E. R., Hameedi, M. J., Sloane, G. M., & Read, L. B. (2002). Chemical contamination, toxicity, and benthic community indices in sediments of the lower Miami River and adjoining portions of Biscayne Bay, Florida. Estuaries, 25(4A), 622–637.
Macias-Zanora, J. V., Villaesusa-Celaya, J. A., Munoz-Barbosa, A., & Gold-Bouchot, G. (1999). Trace metals in sediment cores from the Campeche Shelf, Gulf of Mexico. Environmental Pollution, 104, 69–77.
Manasrah, R., Badran, M., Lass, H. U., & Fennel, W. (2004). Circulation and winter-deep water formation in the northern Red Sea. Oceanologica, 46, 5–23.
Mil-Homens, M., Stevens, R. L., Abrantes, F., & Cato, I. (2006). Heavy metal assessment for surface sediments from three areas of the Portuguese continental shelf. Continental Shelf Research, 26, 1184–1205.
Muller, G. (1979). Heavy metals in the sediment of the Rhine—Changes seity, 1971. Umsch Wiss Tech, 79, 778–783.
Muller, G. (1981). The heavy metal pollution of the sediments of Neckars and its tributary: A stocktaking. Chemiker-Zeitung, 105, 157–164.
Okbah, M. A., Mahmoud, T. H., & El-Deek, M. S. (1999). Nutrient salts concentrations in the Gulf of Aqaba and Northern Red Sea. Bulletin of the National Institute of Oceanography and Fisheries, 25, 103–116.
Okbah, M. A., Shata, M. A., & Shriadah, M. M. A. (2005). Geochemical forms of trace metals in mangrove sediments-Red Sea (Egypt). Chemistry and Ecology, 21(1), 23–36.
Oregioni, B., & Aston, S. R. (1984). IAEA Monaco Laboratory, internal report (cited from reference methods in pollution studies no.38, UNEP, 1986).
Riegl, B., & Velimirov, B. (1991). How many damaged corals in the Red Sea reef systems? A quantitative survey. Hydrobiologia, 216/217, 249–256.
Ruilian, Y., Xing, Y., Yuanhui, Z., Gongren, H., & Xianglin, T. (2008). Heavy metal pollution in intertidal sediments from Quanzhou Bay, China. Journal of Environmental Science, 20, 664–669.
Saad, M. A. H., & Ahdy, H. H. H. (2006). Speciation of heavy metals in Lake Mariut core sediments. In Proc. 7 th internat. conf. geochem., Fac. Sci., Alex. Univ., Egypt (Vol. 3, pp. 73–86).
Saleh, S. M. K. (2006). Environmental assessment of heavy metals pollution in bottom sediments from the Gulf of Aden, Yemen (p. 235). Ph.D. thesis. Egypt: Alexandria University.
Shridah, M. A., Okbah, M. A., & El-Deek, M. S. (2004). Trace metals in the water columns of the Red Sea and Gulf of Aqaba, Egypt. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 153, 115–124.
Smith, I. C., & Carson, B. L. (1981). Trace metals in the environment. Ann Arbor: Ann Arbor Science Publishers.
Walker, D. I., & Ormond, R. F. G. (1982). Coral death from sewage and phosphate pollution at Aqaba, Red Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 13, 21–25.
Wang, F., & Chen, J. S. (2000). Relation of sediment characteristics to trace metal concentration: A statistical study. Water Research, 34, 694–698.
Wolfe, D. A., Long, E. R., & Thursby, G. B. (1996). Sediment toxicity in the Hudson-Raritan Estuary: Distribution and correlations with chemical contamination. Estuaries, 19(4), 901–912.
Youssef, D. H., & Abbas, M. M. (2005). Concentrations of some heavy metals in surficial sediments of Abu-Qir Bay, during 2004. Journal of Egyptian Academic Society for Environmental Development D-Environmental Studies, 6(3), 45–61.
Youssef, D. H., & El-Said, G. F. (2010). Comparative study between the levels of some heavy metals in the sediments of two Egyptian contaminated environments. Chemistry and Ecology, 26(3), 183–195.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Youssef, D.H., El-Said, G.F. Assessment of some heavy metals in surface sediments of the Aqaba Gulf, Egypt. Environ Monit Assess 180, 229–242 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1784-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1784-x