Abstract
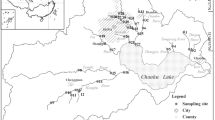
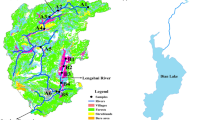
Sediment phosphorus (P) fractions and sorption characteristics and P release from intact sediment cores of Baiyangdian Lake in North China in spring 2009 were investigated. Results of chemical fractionation showed that total P (TP) content in sediment ranged from 443 to 611 mg kg − 1. Of the P fractions including inorganic P (IP) and organic P (OP), IP was a dominant component of TP and present in the form of P bounded to calcium (Ca–P) while the bioavailable P content bounded to Al, Fe, and Mn oxides and hydroxides (Fe/Al–P) varied from 14 to 102 mg kg − 1. The batch experiments showed that the sediments had appreciable maximum P adsorption capacity from 141.86 to 377.37 mg kg − 1. However, the zero P equilibrium concentration (C\(_{{\rm eq}}^{0})\) in most sampling sites was larger than the P concentration in water column. Accordingly, the sediments from those sampling sites would release P into the overlying water at the positive P flux rates as a P release source. Significant positive correlation between P flux rates and Fe/Al–P revealed that the sediment P release would mainly originate from the bioavailable P fraction. It is evident that the inherent phosphorus present in lake sediments would be a major threat to the water quality and ecosystem reservation in Baiyangdian lake.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christophoridis, C., & Fytianos, K. (2006). Conditions affecting the release of phosphorus from surface lake sediments. Journal of Environmental Quality, 35(4), 1181–1192.
Ditoro, D. M. (2001). Sediment Flux Modeling. New York: Wiley.
Ellen, L. P., & Joselito, M. A. (2001). Evaluation of iron-phosphate as a source of internal lake phosphorus loadings. The Science of the Total Environment, 266(1–3), 87–93.
Gale, P. M., & Reddy, K. R. (1994). Phosphorus retention by wetland soils used for treated wastewater disposal. Journal of Environmental Quality, 23, 370–377.
Gao, L., Zhou, J. M., Yang, H., & Chen, J. (2005). Phosphorus fractions in sediment profiles and their potential contributions to eutrophication in Dianchi Lake. Environmental Geology, 48(7), 835–844.
Golterman, H. L. (2004). The Chemistry of Phosphate and Nitrogen Compounds in Sediments (pp. 57–59). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.
Hupfer, M., & Lewandowski, J. (2008). Oxygen controls the phosphorus release from lake sediments—A long-lasting paradigm in limnology. International Review of Hydrobiology, 93(4–5), 415–432.
Jensen, H. S., & Andersen, F. (1992a). Importance of temperature, nitrate, and pH for phosphate release from aerobic sediments of four shallow, eutrophic lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 37(3), 577–589.
Jensen, H. S., Kristensen, P., Jeppesen, E., & Skytthe, A. (1992b). Iron: phosphorus ratio in surface sediment as an indicator of phosphate release from aerobic sediments in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia, 235–236(1), 731–743.
Jin, X. C., Wang, S. R., Bu, Q. Y., & Wu, F. C. (2006a). Laboratory experiments on phosphorous release from the sediments of 9 lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze river region, China. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 176(1–4), 233–251.
Jin, X. C., Wang, S. R., Pang, Y., & Wu, F. C. (2006b). Phosphorus fractions and the effect of pH on the phosphorus release of the sediments from different trophic areas in Taihu Lake, China. Environmental Pollution, 139(2), 288–295.
Kaiserli, A., Voutsa, D., & Samara, C. (2002). Phosphorus fractionation in lake sediments—Lakes Volvi and Koronia, N. Greece. Chemosphere, 46, 1147–1155.
Kim, L. H., Choi, E., & Stenstrom, M. K. (2003). Sediment characteristics, phosphorus types and phosphorus release rates between river and lake sediments. Chemosphere, 50(1), 53–61.
Lai, D. Y., & Lam, K. C. (2008). Phosphorus retention and release by sediments in the eutrophic Mai Po Marshes, Hong Kong. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 57(6–12), 349–356.
Mesnage, B., & Picot, V. (1995). The distribution of phosphate in sediments and its relation with eutrophication of a Mediterranean Coastal Lagoon. Hydrobiologia, 297(1), 29–41.
Pant, H. K., & Reddy, K. R. (2001). Phosphorus sorption characteristics of estuarine sediments under different redox conditions. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30, 1474–1480.
Reddy, K. R., Diaz, O. A., Scinto, L. J., & Agami, M. (1995). Phosphorus dynamics in selected wetlands and streams of the Lake Okeechobee Basin. Ecological Engineering, 5(2–3), 183–207.
Richardson, C. J. (1985). Mechanisms controlling phosphorus retention capacity in freshwater wetlands. Science, 228(4706), 1424–1427.
Ruban, V., & Demare, D. (1998). Sediment phosphorus and internal phosphate flux in the hydroelectric reservoir of Bort-les-Orgues, France. Hydrobiologia, 3373/3374, 349–359.
Ruban, V., Brigault, S., Demare, D., & Philippe, A. M. (1999a). Selection and evaluation of sequential extraction procedures for the determination of phosphorus forms in lake sediment. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 1, 51–56.
Ruban, V., Brigault, S., Demare, D., & Philippe, A. M. (1999b). An investigation of the origin and mobility of phosphorus in freshwater sediments from Bort-Les-Orgues Reservoir, France. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 1, 403–407.
Ruban, V., Lopezsanchez, J. F., Papdo, P., Rauret, G., Muntau, H., & Quevauviller, P. (2001). Development of a harmonised phosphorus extraction procedure and certification of a sediment reference material. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 3, 121–125.
Sallade, Y. E., & Sims, J. T. (1997). Phosphorus transformations in the sediments of delaware’s agricultural drainageways: I Phosphorus forms and sorption. Journal of Environmental Quality, 26, 1571–1579.
SEPA (State Environmental Protection Administration of China) (2002). Monitor and analysis method of water and wastewater. Beijing: Chinese Environmental Science.
Søndergaard, M., Jensen, P. J., & Jeppesen, E. (2001). Retention and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow, eutrophic lakes. Scientific World Journal, 1, 427–442.
Søndergaard, M., Jensen, P. J., & Jeppesen, E. (2003). Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia, 506–509, 135–145.
Sun, S. J., Huang, S. L., Sun, X. M., & Wen, W. (2009). Phosphorus fractions and its release in the sediments of Haihe River, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences-China, 21(3), 291–295.
Wang, S. R., Jin, X. C., Pang, Y., Zhao, H. C., Zhou, X. N., & Wu, F. C. (2005). Phosphorus fractions and phosphate sorption characteristics in relation to the sediment compositions of shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River region, China. Journal of Colloid And Interface Science, 289(2), 339–346.
Zhou, A. M., Tang, H. X., & Wang, D. S. (2005). Phosphorus adsorption on natural sediments: Modeling and effects of pH and sediment composition. Water Research, 39(7), 1245–1254.
Zhu, G. W., Wang, F., Gao, G., & Zhang, Y. L. (2008). Variability of phosphorus concentration in large, shallow and eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Water Environment Research, 80(9), 832–839.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, L., Yang, Z. & Liu, X. Phosphorus fractions, sorption characteristics, and its release in the sediments of Baiyangdian Lake, China. Environ Monit Assess 179, 335–345 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1740-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1740-9