Abstract
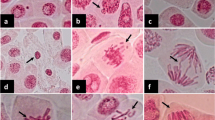
Plant-based bioassays have recently gained remarkable popularity among the toxicological/eco-toxicological assessment procedures. The reasons for their wide use are comparative simplicity, sensitivity, and cost-effectiveness as well as a good correlation with other toxicity tests. The present study describes the use of two plant bioassays, Allium cepa test and seed germination test in the evaluation of the toxicity/genotoxicity of industrial waste water and river water and standardization with the commonly occurring pollutants in Indian waters namely heavy metals and phenolics. Both tests were standardized to suit the Indian conditions, and the local varieties were used. Both bioassays responded significantly with the test range of heavy metals and phenolics. The toxicity of heavy metals was in the order of Cu > Ni > Cd in both the tests whereas 2,4-dinitrophenol was the most toxic among the phenolic compounds. Cabbage, millet, and cucumber, respectively, were found to be the most sensitive in the seed germination test for the test heavy metals and phenols. Significant amounts of chromosomal abnormalities including bridges, stickiness, and fragmentations were recorded with both the industrial waste water and the XAD concentrated river water samples by A. cepa test.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (APHA). (1998). In L. S. Clesceri, A. E. Greenberg, & A. D. Eaton (Eds.), Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington: APHA.
Brusick, D. J., & Young, R. R. (1981). IERL-RTP procedures manual: Level 1 environmental assessment biological test. EPA-600/8-81-024. Washington: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Constantin, M. J., & Owens, E. T. (1982). Introduction and perspectives of plant genetic and cytogenetic assays. A report of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Gene-Tox Programme. Mutation Research, 99, 1–12.
Dutka, B. J. (1996). Bioassays-summary of the 18 years work, NWRI, Canada Water Tox Workshop, Theme Paper, IDRC, Canada.
Fatima, R. A., & Ahmad, M. (2005). Certain antioxidant enzymes of Allium cepa as biomarkers for the detection of toxic heavy metals in wastewater. Science of the Total Environment, 346, 256–273.
Fatima, R. A., & Ahmad, M. (2006a). Allium cepa derived EROD as a potential biomarker for the presence of certain pesticides in water. Chemosphere, 62, 527–537.
Fatima, R. A., & Ahmad, M. (2006b). Genotoxicity of industrial wastewaters obtained from two different pollution sources in northern India: A comparison of three bioassays. Mutation Research, 609, 81–91.
Fiskesjo, G. (1988). The Allium test-an alternative in environmental studies: The relative toxicity of metal ions. Mutation Research, 197, 243–260.
Fiskesjo, G. (1993). The Allium test in wastewater monitoring. Environmental Toxicology and Water Quality, 8, 291–298.
Fletcher, J. S., Muhitch, M. J., Vann, D. R., McFarlance, J. C., & Benenati, F. E. (1985). Review: Phytotoxdatabase evaluation of surrogate plant species recommended by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 4, 523–532.
Gentile, J. M., Wanger, E. D., & Plewa, J. M. J. (1977). The detection of weak recombinogenic activities in the herbicides alachlor and propachlor using a plant activation assay. Mutation Research, 48, 113–116.
Gopalan, H. N. (1999). Ecosystem health and human well being: The mission of the international programme on plant bioassays. Mutation Research, 426, 99–102.
Grant, W. F. (1978). Chromosome aberrations in plants as a monitoring system. Environmental Health Perspectives, 27, 37–43.
ISGE (1990). Integrated study of Ganga Ecosystem between Kachla to Kannauj, Ganga Project Report. New Delhi: Department of Environment and Forests, Government of India, Report no: 21.
Kincl, S. V., Stegnar, P., Lovka, M., & Toman, M. J. (1996). The evaluation of waste, surface and ground water quality using the Allium test procedure. Mutation Research, 368, 171–179.
Levan, A. (1951). Chemically induced chromosome reactions in Allium cepa and Vicia faba. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology, 16, 233–243.
Liang, J. C. (1983). Cytogenetics and public health-assess for environmental mutagens. Cancer Bulletin, 35, 138–143.
Ma, T. H. (1999). The International Programme on plant bioassays and the report of the follow-up study after the hands-on workshop in China. Mutation Research, 426, 103–106.
Maila, M. P., & Cloete, T. A. (2002). Germination of Lepidium sativum as a method to evaluate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) removal from contaminated soil. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 50, 107–113.
Malik, A., & Ahmad, M. (1995). Genotoxicity of some waste waters of India. Environmental Toxicology and Water Quality, 10, 287–293.
Menn, J. J. (1978). Comparative aspects of pesticide metabolism in plants and animals. Environmental Health Perspectives, 27, 113–124.
Merdelsohn, M. I. (1982). Extrapolation of mutagenicity testing to the human. In R. R. Flock, & A. Hollaender (Eds.), Genetic toxicology (pp. 113–116). New York: Planum.
Nielsen, M. H., & Rank, J. (1994). Screening of toxicity and genotoxicity in wastewater by the use of Allium test. Hereditas, 121, 244–254.
Nilan, R. A., & Vig, B. K. (1976). Plant test systems for detection of chemical mutagens. In A. Holleander (Eds.), Chemical mutagens, principles and methods for their detection (pp. 143–170). New York: Plenum.
Radić, S., Stipanic̆ev, D., Vujc̆ić, V., Rajc̆ić, M. M., Širac, S., & Pevalek-Kozlina, B. (2010). The evaluation of surface and wastewater genotoxicity using the Allium cepa test. Science of the Total Environment, 408, 1228–1233.
Rank, J., & Nielsen, M. H. (1993). A modified Allium test as a tool in the screening of genotoxicity of complex mixtures. Hereditas, 118, 49–53.
Rank, J., & Nielsen, M. H. (1994). Evaluation of the Allium anaphase- telophase test in relation to genotoxicity screening of industrial wastewater. Mutation Research, 312, 17–24.
Rank, J., & Nielsen, M. H. (1997). Allium cepa anaphase telophase root tip chromosome aberration assay on N-methyl-N-nitrosourea, maleic hydrazide, sodium azide and ethyl methanesulfonate. Mutation Research, 390, 121–127.
Rank, J., & Nielsen, M. H. (1998). Genotoxicity testing of wastewater using the Allium cepa anaphase-telophase chromosome aberration assay. Mutation Research, 418, 113–119.
Ratsch, H. C. (1983). Interlaboratory root elongation testing of toxic substance on selected plant species, EPA-600/33-83-051. Connallis: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Ratsch, H. C., & Johndro, D. (1986). Comparative toxicity of six test chemicals to lettuce using two root elongation test methods. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 6, 267–276.
Rehana, Z., Malik, A., & Ahmad, M. (1995). Mutagenic activity of the Ganges water with special reference to the pesticide pollution in the river between Kachla to Kannauj (U.P.). Mutation Research, 343, 137–144.
Rehana, Z., Malik, A., & Ahmad, M. (1996). Genotoxicity of Ganges water at Narora (U.P.) India. Mutation Research, 367, 187–193.
Repetto, G., Jos, A., Hazen, M. J., Molero, M. L., del Paso, A., Solguero, M., et al. (2001). A test battery for the ecotoxicological evaluation of pentachlorophenol. Toxicology In vitro, 15, 503–509.
Smaka-Kincl, V., Stegnar, P., Lovka, M., & Toman, M. J. (1996). The evaluation of waste, surface and ground water quality using the Allium test procedure. Mutation Research, 368, 171–179.
Tabrez, S., & Ahmad, M. (2009a). Effect of waste water intake on antioxidant and marker enzymes of tissue damage in rat tissues: Implications for the use of biochemical markers. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 47(10), 2465–2478.
Tabrez, S., & Ahmad, M. (2009b). Some enzymatic/non enzymatic antioxidants as potential stress biomarkers of trichloroethylene, heavy metal mixture and ethyl alcohol in rat tissues. Environmental Toxicology. doi:10.1002/tox.20548.
Tamura, R., Fukuzadi, N., Hirano, Y., & Muzuhima, Y. (1985). Evaluation of mercury contamination using plant leaves and humus as indicators. Chemosphere, 14, 1687–1693.
Tsuda, S., Murakami, M., Matusaka, N., Kano, K., Taniguchi, K., & Sasaki, Y. F. (2001). DNA damage induced by red food dyes orally administered to pregnant and male mice. Toxicological Sciences, 61, 92–99.
Wang, W. C. (1986). Comparative toxicology of phenolic compounds using root elongation method. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 5(10), 891–896.
Wang, W. (1987). Root elongation method for toxicity testing of organic and inorganic pollutants. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 6, 409–419.
Wilcox, P., & Williamson, S. (1986). Mutagenic activity of concentrated drinking water samples. Environ Health Prospect, 69, 141–150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siddiqui, A.H., Tabrez, S. & Ahmad, M. Validation of plant based bioassays for the toxicity testing of Indian waters. Environ Monit Assess 179, 241–253 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1732-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1732-9