Abstract
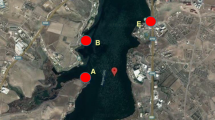
Dilek National Park in Western Turkey is a protected habitat for several endangered and threatened species. In an attempt to protect the endangered species, the park was classified as a World Heritage Preserve. Even with this change, the animal and flora variety are still at risk from previous metal contamination. Water samples were collected 10 cm below the water surface and sediment from 0–30 and 30–60 cm depth. Inorganic elements were found in all sediment samples. Sodium had the highest aqueous concentration (10,312 mg/L), while Cu, Fe, Mn, and Zn were present at levels significantly lower than the chronic exposure criteria. Zn was the least prevalent (0.4 mg/kg) compound found in the sediment. The highest toxic contaminant concentration was Mg at an average of 1,100 mg/kg. The main contamination source of that seems to be Great Meandrous River. More studies are needed to develop a protection and remediation strategy for Dilek National Park.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouyoucous, G. J. (1951). A recalibration of the hydrometer methods for making mechanical analysis of soils. Agronomy Journal, 43, 434–438.
Cakan, H., Yilmaz, K. T., & Duzenli, A. (2005). First comprehensive assessment of the conservation status of the flora of the Cukurova Deltas, southern Turkey. Onyx, 39, 17–21.
Celik, A., Kaska, Y., Bag, H., Aureggi, M., Semiz, G., Kartal, A. A., et al. (2006). Heavy metal monitoring around the nesting environment of green sea turtles in Turkey. Water Air Soil Pollution, 169, 67–79.
Dalman, O., Demirak, A., & Balci, A. (2006). Determination of heavy metals (Cd, Pb) and trace elements (Cu, Zn) in sediments and fish of the southern Aegean sea (Turkey) by atomic adsorption spectrometry. Food Chemistry, 95, 157–162.
Dasdemir, I. (2005). Improving operational planning and managenet of national parks in Turkey: A case study. Environmental Management, 35, 247–257.
Ek, K. H., Morrison, G., Lindberg, P., & Rauch, S. (2004). Comparative tissue distribution of metals in birds in Sweden using ICP-MS and laser ablation ICP-MS. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 47, 259–269.
Franzelitti, S., Locatelli, C., Gerosa, C., Vallini, C., & Fabbri, E. (2004). Heavy metals in tissues of loggerhead turtles (Caretta caretta) from the northwest Adriatic sea. Comprehensve Biochemistry and Physiology, C138, 187–194.
Gardner, S. C., Fitzgerald, S. L., Vargas, B. A., & Rodriguez, L. (2006). Heavy metal accumulation in four species of sea turtles from the Baja California peninsula, Mexico. BioMetals, 19, 91–99.
Godley, B., Thompson, D. R., & Furness, R. (1999). Do heavy metal concentrations pose a threat to marine turtles from the Mediterranean sea? Marine Pollution Bulletin, 38, 497–502.
Guclusoy, H. (2008). Damage to monk seals to gear of the artisanal fishery in the Foca Monk seal pilot conservation area, Turkey. Fisheries Research, 90, 70–77.
Gulcu, K., & Karahan, F. (2004). A review: The history of conservation programs and development of the national parks concept in Turkey. Biodiversity and Conservation, 13, 1373–1390.
Karadede-Akin, H., & Unlu, E. (2007). Heavy metal concentrations in water, sediment, fish, and some benthic organisms from the Tigris River, Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 131, 323–337.
Keskin, Y., Baskaya, R., Ozyaral, O., Yurdun, T., Luleci, N. E., & Hayran, O. (2007). Cadmium, lead, mercury and copper in fish from the Marmara Sea, Turkey. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 78, 258–261.
Kim, J., & Koo, T.-H. (2008). Heavy metal distribution in chicks of two heron species from Korea. Archives Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 54, 740–747.
Kucuksezgin, F., Uluturhan, E., & Batki, H. (2008). Distribution of heavy metals in water, particulate matter and sediments of Gediz River (eastern Aegean). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 141, 213–225.
Lindsay, W. L., & Norvell, W. A. (1978). Development of a DTPA test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 42, 421–428.
Liven-Schulman, I., Leshem, Y., Alon, D., & Yom-Tov, Y. (2004). Causes of population declines in the lesser kestrel Falco naumanni in Israel. Ibis, 146, 145–152.
Maffucci, F., Caurant, F., Bustamante, P., & Bentivegna, F. (2005). Trace element (Cd, Cu, Hg, Se, Zn) accumulation and tissue distribution in loggerhead turtles (Caretta caretta) from the Western Mediterranean sea (southern Italy). Chemosphere, 58, 535–542.
Nam, D. H., Anan, Y., Ikemoto, T., Kim, E. Y., & Tanabe, S. (2005). Distribution of trace elements in subcellular fractions of three aquatic birds. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 51, 750–756.
Olsen, S. R., & Sommers, E. L. (1982). Phosphorous availability indices, Phosphorous soluble in sodium bicarbonate. In A. L. Page, R. H. Miller, & D. R. Keeney (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 2: Chemical and microbiological properties (2nd ed., pp. 19–224). Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
Ozenoglu, H., & Gokler, I. (2002). Liverworts (Marchantiopsida) of the Dilek Peninsula National Park. Turkish Journal of Botany, 26, 297–301.
Powles, H., Bradford, M. J., Bradford, W. R., Doubleday, G. G., Innes, S., & Levings, C. D. (2000). Assessing and protecting endangered marine species. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 57, 669–676.
Rozema, J., Notten, M., Aerts, R., van Gestel, C., Hobbelen, P., & Hamers, T. (2008). Do high levels of diffuse and chronic metal pollution in sediments of Rhine and Meuse floodplains affect structure and functioning of terrestrial ecosystems? Science of the Total Environment, 406, 443–448.
Sakai, H., Saeki, S., Ichihashi, H., Kamezaki, N., Tanabe, S., & Tatsukawa, R. (2000). Growth-related changes in heavy metal accumulation in green turtle (Chelonia mydas) from Yaeyama Islands, Okinawa, Japan. Archives Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39, 378–385.
Schogolev, I., Rudenko, A., & Crivelli, A. J. (2005). Status of pelicans and cormorants on the northern Black Sea. Bird Conservation, International, 15, 63–71.
Shi, H. Q., Cao, L., Barter, M. A., & Liu, N. F. (2008). Status of the East Asian population of the Dalmation pelican Pelecanus crispus: The need for urgent conservation act. Bird Conservation International, 18, 181–193.
Soil Survey Laboratory (2004). Soil survey laboratory methods (SSIR 42).
Talavera-Saenz, A., Gardner, S. C., Rodriquez, R. R., & Vargas, B. A. (2007). Metal profiles used as environmental markers of green turtle (Chelonia mydas) foraging resources. Science of the Total Environment, 373, 94–102.
Thomas, G. W. (1982). Exchangeable cations. In A. L. Page, R. H. Miller, & D. R. Keeney (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 2: Chemical and microbiological properties (2nd ed., pp. 159–166). Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
Walkey, I., & Black, C. A. (1934). An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification for the chromic acid titration method. Soil Science, 37, 29–38.
Yalcin, M. G., Narin, I., & Soylak, M. (2007). Heavy metal contents of the Karasu creek sediments Nigde, Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 128, 352–357.
Zabetoglu, K., Vousta, D., & Samara, C. (2002). Toxicity and heavy metal contamination of surficial sediments from the Bay of Thessaloniki (Northwestern Aegean Sea) Greece. Chemosphere, 29, 17–26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atatanir, L., Turgut, C. & Cutright, T.J. Baseline of the spatial and temporal metal contamination in Dilek National Park, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 179, 201–207 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1729-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1729-4