Abstract
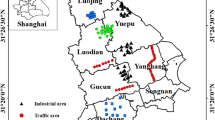
Magnetic parameters and heavy metal concentrations of road dusts collected from two parks with distance about 16 km in Wuhan city, China, were measured. The Guishan Park is circled by main roads with heavy traffic, and the Moshan Park is located on the downwind hills of steelworks and a power plant. Mean values of magnetic susceptibility (χ) and saturation magnetization (M s) of the dusts from the Moshan Park are 1.31 and 1.57 times those from the Guishan Park, respectively. Their magnetic mineralogy is dominated by pseudo-single domain magnetite; however, minor hematite was also identified in those from the Guishan Park. The dominant sources of non-natural magnetic particles and heavy metals were inferred as windblown emissions from the steelworks and the power plant for the Moshan Park, and road/railway traffics for the Guishan Park, respectively. Spatial variation in magnetic properties of road dust in the two parks and their different magnetic behavior propose that the magnetic measurements are sensitive to the different pollutant origins, as well as the urban environment, and that magnetic techniques have a high efficiency in mapping urban environment. Correlation between magnetic parameters and heavy metal concentrations is strongly site-specific: strong correlations were observed in the Moshan Park with correlation coefficients generally higher than 0.800, whereas correlations are poor in the Guishan Park. Therefore, it is strongly recommended that these relationships should be examined thoroughly before magnetic mapping.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angulo, E. (1996). The Tomlinson pollution load index applied to heavy metal “Mussel-Watch” data: A useful index to assess coastal pollution. Science of the Total Environment, 187, 19–56.
Blaha, U., Appel, E., & Stanjek, H. (2008). Determination of anthropogenic boundary depth in soil profiles and semi-quantification of heavy metal loads using magnetic susceptibility. Environmental Pollution, 156, 278–289.
Bućkol, M. S., Magiera, T., Pesonen1, L. J., & Janus, B. (2010). Magnetic, geochemical, and microstructural characteristics of road dust on roadsides with different traffic volumes—Case study from Finland. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 209, 295–306.
Day, R., Fuller, M., & Schmidt, V. (1977). Hysteresis properties of titanomagnetites: Grain-size and compositional dependence. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 13, 260–267.
Dunlop, D. J., & Özdemir, Ö. (1997). Rock magnetism: Fundamentals and frontiers. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Georgeaud, V. M., Rochette, P., Ambrosi, J. P., Vandamme, D., & Williamson, D. (1997). Relationship between heavy metals and magnetic properties in a large polluted catchment: The Etang de Berre (South of France). Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 22, 211–214.
Goddu, S. R., Appel, E., Jordanova, D., & Wehland, F. (2004). Magnetic properties of road dust from Visakhapatnam (India)-—Relationship to industrial pollution and road traffic. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 29, 985–995.
Hanesch, M., Rantitsch, G., Hemetsberger, S., & Scholger, R. (2007). Lithological and pedological influences on the magnetic susceptibility of soil: Their consideration in magnetic pollution mapping. Science of the Total Environment, 382, 351–363.
Harrison, R. M., & Yin, J. (2000). Particulate matter in the atmosphere: Which particle properties are important for its effects on health? Science of the Total Environment, 249, 85–101.
Hoffmann, V., Knab, M., & Appel, E. (1999). Magnetic susceptibility mapping of roadside pollution. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 66, 313–326.
Hunt, A., Jones, J., & Oldfield, F. (1984). Magnetic measurements and heavy metals in atmospheric particulates of anthropogenic origin. Science of the Total Environment, 33, 129–139.
Kapička, A., Jordanova, N., Petrovský, E., & Ustjak, S. (2001). Effect of different soil conditions on magnetic parameters of power-plant fly ashes. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 48, 93–102.
Kapička, A., Jordanova, N., Petrovský, E., & Podrazský, V. (2003). Magnetic study of weakly contaminated forest soils. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 148, 31–44.
Kim, W., Doh, S. J., Park, Y. H., & Yun, S. T. (2007). Two-year magnetic monitoring in conjunction with geochemical and electron microscopic data of roadside dust in Seoul, Korea. Atmospheric Environment, 41, 7627–7641.
Kim, W., Doh, S. J., & Yu, Y. (2009). Anthropogenic contribution of magnetic particulates in urban roadside dust. Atmospheric Environment, 43, 3137–3144.
Lecoanet, H., Lévêque, F., & Ambrosi, J. P. (2001). Magnetic properties of salt-marsh soils contaminated by iron industry emissions (southeast France). Journal of Applied Geophysics, 48, 67–81.
Liu, Q. S., Deng, C. L., Yu, Y. J., Torrent, J., Banerjee, S. K. & Zhu, R. X. (2005). Temperature dependence of magnetic susceptibility in an argon environment: Implications for pedogenesis of Chinese loess/paleosols. Geophysical Journal International, 161, 102–112.
Liu, Q. S., Zeng, Q. L., Yang, T., Qiu, N. & Chan, L. S. (2009). Magnetic properties of street dust from Chibi city, Hubei province, China: Its implications for urban environment. Journal of Earth Science, 20(5), 848–857.
Lu, S. G., & Bai, S. Q. (2006). Study on the correlation of magnetic properties and heavy metals content in urban soils of Hangzhou City, China. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 60, 1–12.
Lu, S. G., Bai, S. Q., Cai, J. B., & Xu, C. (2005). Magnetic properties and heavy metal contents of automobile emission particulates. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition), 6B, 731–735.
Lu, S. G., Wang, H. Y., & Bai, S. Q. (2009). Heavy metal contents and magnetic susceptibility of soils along an urban–rural gradient in rapidly growing city of eastern China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 155, 91–101.
Magiera, T., & Zawadzki, J. (2007). Using of high-resolution topsoil magnetic screening for assessment of dust deposition: Comparison of forest and arable soil datasets. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 125, 19–28.
McIntosh, G., Gómez-Paccard, M., & Osete, M. L. (2007). The magnetic properties of particles deposited on platanus x hispanica leaves in Madrid, Spain, and their temporal and spatial variations. Science of the Total Environment, 382, 135–146.
Moreno, E., Sagnotti, L., Dinarès-Turell, J., Winkler, A., & Cascella, A. (2003). Biomonitoring of traffic air pollution in Rome using magnetic properties of tree leaves. Atmospheric Environment, 37, 2967–2977.
Ng, S. L., Chan, L. S., Lam, K. C., & Chan, W. K. (2003). Heavy metal contents and magnetic properties of playground dust in Hong Kong. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 89, 221–232.
Petrovský, E., & Ellwood, B. B. (1999). Magnetic monitoring of pollution of air, land and waters. In B. A. Maher, & R. Thompson (Eds.), Quaternary climates, environments and magnetism (pp. 279–322). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Petrovský, E., Kapička, A., Jordanova, N., & Borůvka, L. (2001). Magnetic properties of alluvial soils contaminated with lead, zinc and cadmium. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 48, 127–136.
Prajapati, S. K., Pandey, S. K., & Tripathi, B. D. (2006). Monitoring of vehicles derived particulates using magnetic properties of leaves. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 120, 169–175.
Sagnotti, L., Macri, P., Egli, R., & Mondino, M. (2006). Magnetic properties of atmospheric particulate matter from automatic air sampler stations in Latium (Italy): Toward a definition of magnetic fingerprints for natural and anthropogenic PM10 sources. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111, B12S22. doi:10.1029/2006JB004508.
Sharma, A. P., & Tripathi, B. D. (2008). Magnetic mapping of fly-ash pollution and heavy metals from soil samples around a point source in a dry tropical environment. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 138, 31–39.
Spiteri, C., Kalinski, V., Rosler, W., Hoffmann, V., Appel, E., & MAGPROX Team. (2005). Magnetic screening of a pollution hotspot in the Lausitz area, Eastern Germany: Correlation analysis between magnetic proxies and heavy metal contamination in soils. Environmental Geology, 49, 1–9.
Strzyszcz, Z. (1993). Magnetic susceptibility of soils in the areas influenced by industrial emissions. In R. Schulin, A. Sesaules, R. Webster & B. V. Steiger (Eds.), Soil monitoring: Early detection and surveying of soils contamination and degradation (pp. 255–269). Basel: Birkhäuser.
Thompson, R., & Oldfield, F. (1986). Environmental magnetism. London: Allen & Unwin.
Urbat, M., Lehndorff, E., & Schwark, L. (2004). Biomonitoring of air quality in the Cologne conurbation using pine needles as a passive sampler—Part I: Magnetic properties. Atmospheric Environment, 38, 3781–3792.
Xie, S. J., Dearing, J. A., Bloemendal, J., & Boyle, J. F. (1999). Association between the organic matter content and magnetic properties in street dust, Liverpool, UK. Science of the Total Environment, 241, 205–214.
Xie, S. J., Dearing, J. A., Boyle, J. F., Bloemendal, J., & Morse, A. P. (2001). Association between magnetic properties and element concentrations of Liverpool street dust and its implications. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 48, 83–92.
Yang, T., Liu, Q. S., Chan, L. S., & Cao, G. D. (2007a). Magnetic investigation of heavy metals contamination in urban topsoils around the East Lake, Wuhan city, China. Geophysical Journal International, 171, 603–612.
Yang, T., Liu, Q. S., Chan, L. S., & Liu, Z. D. (2007b). Magnetic signature of heavy metals pollution of sediments: Case study from the East Lake in Wuhan, China. Environmental Geology, 52, 1639–1650.
Yang, T., Liu, Q. S., Zeng, Q. L., & Chan, L. S. (2009). Environmental magnetic responses of urbanization processes: Evidence from lake sediments in East Lake, Wuhan, China. Geophysical Journal International, 179, 873–886.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, T., Zeng, Q., Liu, Z. et al. Magnetic properties of the road dusts from two parks in Wuhan city, China: implications for mapping urban environment. Environ Monit Assess 177, 637–648 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1662-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1662-6