Abstract
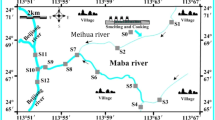
Surface water, suspended particulate matter, pore water, and sediment samples were collected and analyzed for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Yongding New River, South Drainage Canal and North Drainage Canal, which receive most of wastewater from industrial city of Tianjin. PAH concentrations in effluent samples of wastewater treatment plants (WTP) discharging into the South Drainage Canal and North Drainage Canal were quantified for the first time. The results showed that the discharge of the WTPs recently only contributed to the PAH contamination in the canals near the outlets of the WTPs. PAH levels in sediments of the streams were greatly higher than those in soils by riverbank probably due to receiving large amounts of untreated wastewater. Unusually high benz[a] anthracene concentration strongly influenced the seasonal and spatial variation of total PAH concentrations in South Drainage Canal. Paired samples t test of ∑Nap, Fl, Phe, Fluo and ∑Nap, Phe, Fluo, Chry concentrations, which were dominant components in the air samples from non-heating and heating season, respectively, in the suspended particulate matters from the streams showed that PAH source from air deposition was more important for Yongding New River than that for South Drainage Canal and North Drainage Canal. Source apportionment based on PAH profiles indicated that coal combustion was the major PAH contamination source, and coke oven sources and wood combustion also contributed to the PAH contamination of the streams. This was further indicated by organic petrography analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) (1996). Preparing coal samples for microscopical analysis by reflected light. Annual book of ASTM standards, part 26, 2797, gaseous fuels: Coal and coke (p. 270). Philadelphia: ASTM.
Bzdusek, P. A., & Christensen, E. R. (2004). Source apportionment of sediemnt PAHs in lake Calumet, Chicago, application of factor analysis with nonnegative constraints. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 97–103.
Li, A., Jiang, J. K., & Peter, A. S. (2003). Application of EPA CMB8.2 model for source apportionment of sediment PAHs in lake Calumet, Chicago. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 2958–2965.
MacDonald, D. D., Ingersoll, C. G., & Berger, T. A. (2000). Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39, 20–31.
Mai, B. X., Fu, J. M., Sheng, G. Y., Kang, Y. H., Lin, Z., Zhang, G., et al. (2002). Chlorinated and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in riverine and estuarine sediments from Pearl River Delta, China. Environmental Pollution, 117, 457–474.
Mai, B. X., Qi, S. H., Zeng, E. Y., Yang, Q. S., Zhang, G., Fu, J. M., et al. (2003). Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the coastal region off Macao, China, assessment of input sources and transport pathways using compositional analysis. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 4855–4863.
Maskaoui, K., Hong, H. S., Zhang, Z. L., Chen, W. Q., & Zhou, J. L. (2001). Distribution and composition of PAHs in surface waters, porewater and sediments from Xiamen western Bay. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 19, 73–80.
Qiao, M., Wang, C. X., Huang, S. B., Wang, D. H., & Wang, Z. J. (2006). Composition, sources, and potential toxicological significance of PAHs in the surface sediments of the Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake, China. Environment International, 32, 28–33.
Shi, Z., Tao, S., Pan, B., Fan, W., He, X. C., Zuo, Q., et al. (2005). Contamination of rivers in Tianjin, China by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environmental Pollution, 134, 97–111.
Shi, Z., Tao, S., Pan, B., Liu, W. X., & Shen, W. R. (2007). Partitioning and source diagnostics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rivers in Tianjin, China. Environmental Pollution, 146, 492–500.
Spiro, G. T., & Stigliani, M. W. (2003). Air pollution. Chemistry of the environment (2nd ed., p. 222). Beijing: Pearson Education Asia Limited and Tsinghua University Press.
Tao, S., Cui, Y. H., Xu, F. L., Li, B. G., Cao, J., Liu, W. X., et al. (2004). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in agricultural soil and vegetables from Tianjin. Science of the Total Environment, 320, 11–24.
Tianjin Environmental Protection Bureau (2006). Environmental quality report of Tianjin in 2001–2005. Tianjin: Tianjin Environmental Protection Bureau.
Wu, S. P., Tao, S., Xu, F. L., Dawson, R., Lan, T., Li, B. G., et al. (2005). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in dustfall in Tianjin, China. Science of Total Environment, 345, 115–126.
Yang, Y., Ligouis, B., Pies, C., Grathwohl, P., & Hofmann, T. (2008). Occurrence of coal and coal-derived particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a river floodplain soil. Environmental Pollution, 151, 121–129.
Zheng, M. H., Bao, Z. C., Zhang, B., & Xu, X. B. (2001). Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in paper making from a pulp mill in China. Chemosphere, 44, 1335–1337.
Zhou, J. L., Hong, H., Zhang, Z., Maskaoui, K., & Chen, W. (2000). Multi-phase distribution of organic micropollutants in Xiamen Harbour, China. Water Research, 34, 2132–2150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, W., Liu, H., Qu, J. et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in effluents from wastewater treatment plants and receiving streams in Tianjin, China. Environ Monit Assess 177, 467–480 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1648-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1648-4