Abstract
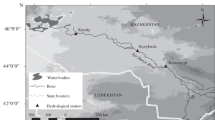
Sixteen water quality parameters have been monitored at four stations located along the Maroon River during 1989–2008. The trend analysis was performed on seasonal and annual time-scales using the Mann–Kendall test, the Sen’s slope estimator and the linear regression. The relationships of the water quality parameters to river discharge were also investigated. The statistical methods showed both positive and negative trends in annual water quality data. However, significant trends were detected by the statistical methods only in calcium, magnesium, sodium absorption ratio, pH, and turbidity series. The results indicated that the concentrations of the water quality parameters increased in spring and winter seasons, while the concentrations were diluted in summer and autumn seasons in the last two decades. Moreover, the highest numbers of significant trends were found in the spring and summer series, respectively. According to the regression analysis, most of the water quality parameters were negatively correlated with river discharge.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonopoulos, V., Papamichail, D., & Mitsiou, K. (2001). Statistical and trend analysis of water quality and quantity data for the Strymon river in Greece. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 5(4), 679–691.
Bouza-Deano, R., Ternero-Rodriguez, M., & Fernandez-Espinosa, A. J. (2008). Trend study and assessment of surface water quality in the Ebro River (Spain). Journal of Hydrology, 361, 227–239.
Chang, H. (2008). Spatial analysis of water quality trends in the Han River basin, South Korea. Water Research, 42, 3285–3304.
Charles, D. F., Whitehead, D. R., Engstrom, D. R., Fry, B. D., Hites, R. A., Norton, S. A., et al. (1987). Paleolimnological evidence for recent acidification of Big Moose Lake, Adirondack Mountains, N.Y. (USA). Biogeochemistry, 3, 267–296.
Evans, C. D., & Jenkins, A. (2000). Surface water acidification in the South Pennines II. Temporal trends. Environmental Pollution, 109, 21–34.
Gilbert, R. O. (1987). Statistical methods for environmental pollution monitoring. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Harriman, R., Morrison, B. R. S., Birks, H. J. B., Christie, A. E. G., Collen, P., & Watt, A. W. (1995). Long-term chemical and biological trends in Scottish streams and lochs. Water Air Soil Pollution, 85, 701–706.
Hirsch, R. M., Alexander, R. B., & Smith, R. A. (1991). Selection of methods for the detection and estimation of trends in water quality. Water Resources Research, 27, 803–814.
Huth, R., & Pokorna, L. (2004). Parametric versus non-parametric estimates of climatic trends. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 77, 107–112.
Jaagus, J. (2006). Climatic changes in Estonia during the second half of the 20th century in relationship with changes in large-scale atmospheric circulation. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 83, 77–88.
Kannel, P. R., Lee, S., Kanel, S. R., Khan, S. P., & Lee, Y. S. (2007). Spatial –temporal variation and comparative assessment of water qualities of urban river system: A case study of the river Bagmati (Nepal). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 129, 433–459.
Matsubara, H., Morimoto, S., Sase, H., Ohizumi, T., Sumida, H., Nakata, M., et al. (2009). Long-term declining trends in river water pH in central Japan. Water Air Soil Pollution, 200, 253–265.
Modarres, R., & Silva, V. P. R. (2007). Rainfall trends in arid and semi-arid regions of Iran. Journal of Arid Environments, 70, 344–355.
Mohlenberg, F., Petersen, S., Petersen, A. H., & Gameiro, C. (2007). Long-term trends and short-term variability of water quality in Skive Fjord, Denmark—Nutrient load and mussels are the primary pressures and drivers that influence water quality. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 127, 503–521.
Naddafi, K., Honari, H., & Ahmadi, M. (2007). Water quality trend analysis for the Karoon River in Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 134, 305–312.
Partal, T., & Kahya, E. (2006). Trend analysis in Turkish precipitation data. Hydrological Processes, 20, 2011–2026.
Ravichandran, S. (2003). Hydrological influences on the water quality trends in Tamiraparani Basin, South India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 87, 293–309.
Salmi, T., Maatta, A., Anttila, P., Ruoho-Airola, T., & Amnell, T. (2002). Detecting trends of annual values of atmospheric pollutants by the Mann–Kendall test and Sen’s slope estimates, vol. 31. Helsinki: Publications on Air Quality.
Sen, P. K. (1968). Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. Journal of American Statistical Association, 63(324), 1379–1389.
Soulsby, C., Turnbull, D., Hirst, D., Langan, S. J., & Owen, R. (1997). Reversibility of stream acidi®cation in the Cairngorm region of Scotland. Journal of Hydrology, 195, 291–311.
Tabari, H., & Marofi, S. (2010). Changes of pan evaporation in the west of Iran. Water Resources Management, doi:10.1007/s11269-010-9689-6.
Tabari, H., Marofi, S., Kashkuli, H. A., Hasounizadeh, H., & Amirian, A. (2010). Evaluation of climate change effects on surface water resources in Maroon basin. 8th International River Engineering Conference, Shahid Chamran University, 26–28 January, Ahwaz, Iran (in Persian with English abstract).
Tsanis, I. K., & El-Shaarawi, A. H. (1992). Trend evaluation of water quality parameters in the Niagara and St. St. Lawrence Rivers. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 23, 205–218.
Watt, W. D., Scott, C. D., & White, W. J. (1983). Evidence of acidification of some Nova Scotia Rivers and its impact on Atlantic Salmon. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 40, 462–473.
Wright, R. F., Dale, T., Gjessing, E. R., Hendrey, G., Henriksen, A., Johannessen, M., et al. (1976). Impact of acid precipitation on freshwater ecosystems in Norway. Water Air Soil Pollution, 6, 483–499.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabari, H., Marofi, S. & Ahmadi, M. Long-term variations of water quality parameters in the Maroon River, Iran. Environ Monit Assess 177, 273–287 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1633-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1633-y