Abstract
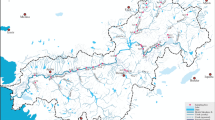
Morphological mentum deformities which represent sublethal effect of exposure to different types of pollutants were evaluated in Chironomus spp. larvae inhabiting three polluted rivers of Juru River Basin in northwestern peninsular Malaysia. Using mentum deformity incidences, the modified toxic score index (MTSI) was developed based on Lenat’s toxic score index (TSI). The suggested MTSI was compared with TSI in terms of its effectiveness to identify different pollutants including heavy metals. The MTSI showed stronger relationship to total deformity incidence expressed as percentage. Additionally, the multivariate RDA model showed higher capability of MTSI to explain the variations in heavy metal contents of the river sediments. The MTSI was recommended in bioassessment of water and sediment quality using the mentum deformities of Chironomus spp. larvae from aquatic ecosystems receiving anthropogenic, agricultural, or industrial discharges.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Shami, S., Rawi, C. S. M., Nor, S. A. M., Ahmad, A. H., & Ali, A. (2010a). Morphological deformities in Chironomus spp. (Diptera: Chironomidae) larvae as a tool for impact assessment of anthropogenic and environmental stresses on three rivers in the Juru River System, Penang, Malaysia. Environmental Entomology, 39, 210–222.
Al-Shami, S. A., Salmah, M. R. C., Abu Hassan, A., & Azizah, M. N. S. (2010b). Temporal distribution of larval Chironomidae (Diptera) in experimental rice fields in Penang, Malaysia. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 13, 17–22.
Aruga, R., Negro, G., & Ostacoli, G. (1993). Multivariate data-analysis applied to the investigation of river pollution. Fresenius Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 346, 968–975.
Azrina, M. Z., Yap, C. K., Ismail, A. R., & Tan, S. G. (2006). Anthropogenic impacts on the distribution and biodiversity of benthic macroinvertebrates and water quality of the Langat River, Peninsular Malaysia. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 64, 337–347.
Bhattacharyay, G., Sadhu, A. K., Mazumdar, A., & Chaudhuri, P. K. (2005). Antennal deformities of chironomid larvae and their use in biomonitoring of heavy metal pollutants in the River Damodar of West Bengal, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 108, 67–84.
Bird, G. A. (1994). Use of chironomid deformities to assess environmental degradation in the Yamaska River, Quebec. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 30, 163–175.
Chester, R., & Voutsinou, F. G. (1981). The initial assessment of trace metal pollution in coastal sediment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 12, 84–91.
Cranston, P. S. (2004). Chironomidae. In C. M. Yule & H. S. Yong (Eds.), The freshwater invertebrates of Malaysia and Singapore. Malaysia: Academy of Science.
De Bisthoven, L. J., & Gerhardt, A. (2003). Chironomidae (Diptera, Nematocera) fauna in three small streams of Skania, Sweden. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 83, 89–102.
De Jonge, M., de Vijuer, B. V., Blust, R., & Bervoets, L. (2008). Responses of aquatic organisms to metal pollution in a lowland river in Flanders: A comparison of diatoms and macroinvertebrates. Science of the Total Environment, 407, 615–629.
Dickman, M., & Rygiel, G. (1996). Chironomid larval deformity frequencies, mortality and diversity in heavy-metal contaminated sediments of a Canadian riverine wetland. Environment International, 22(6), 693–703.
DOE (Department of Environment, Malaysia) (1994). Classification of Malaysian rivers (Vol. 8B), Juru River. Department of Environment, Ministry of Science, Technology and the Environment, Putrajaya, Malaysia.
Epler, J. H. (2001). Identification manual for the larval Chironomidae (Diptera) of North and South Carolina. A guide to the taxonomy of the midges of the southeastern United States, including Florida. Special Publication SJ2001-SP13. North Carolina Department of Environmental and Natural Resources, Raleigh, NC.
Faithful, N. T. (2002). Methods in agricultural chemistry analysis. UK: CABI Publishing.
Fulazzaky, M. A., Teng, W. S., & Mohd Masirin, M. I. (2010). Assessment of water quality status for the Selangor River in Malaysia. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 205, 63–77.
Gonzalez, C. M., Pignata, M. L., & Orellana, L. (2003). Applications of redundancy analysis for the detection of chemical response patterns to air pollution in lichen. Science of the Total Environment, 312, 245–253.
Hamalainen, H. (1999). Critical appraisal of the indexes of chironomid larvae deformities and their use in bioindication. Annales Zoologici Fennici, 36, 179–186.
Hudson, L. A., & Ciborowski, J. J. (1996). Spatial and taxonomic variation in incidence of mouthpart deformities in midge larvae (Diptera: Chironomidae, Chironomini). Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science, 53, 297–304.
Ingersoll, C. G., & Nelson, M. K. (1990). Testing sediment toxicity with Hyalella azteca (Amphipoda) and Chironomus riparius (Diptera). In W. G. Landis & W. H. V. D. Schalie (Eds.), Aquatic toxicology and risk assessment. Philadelphia: American Society for Testing and Materials.
Lenat, D. R. (1993). Mentum deformities of Chironomus larvae to evaluate the effects of toxicity and organic loading in streams. Journal of North American Benthological Society, 12(3), 265–269.
Lim, P. E., & Kiu, M. Y. (1995). Determination and speciation of heavy metals in sediment of the Juru River, Penang, Malaysia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 35, 85–95.
MacDonald, E. E., & Taylor, B. R. (2006). Incidence of mentum deformities in midge larvae (Diptera: Chironomidae) from North Nova Scotia, Canada. Hydrobiologia, 563, 277–287.
Madden, C. P., Suter, P. J., Nicholas, B. C., & Austin, A. D. (1992). Deformities in chironomid larvae as indicator of pollution (pesticide) stress. Netherlands Journal of Aquatic Ecology, 26, 551–557.
Martinez, E. A., Moore, B. C., Schaumloffel, J., & Dasgupta, N. (2004). Teratogenic versus mutagenic abnormalities in chironomid larvae exposed to Zinc and Lead. Archive of Environmental contamination and Toxicology, 47, 193–198.
Mat, L., & Maah, M. J. (1994). Sediment trace metal concentrations from the mudflats of Kuala Juru and Kuala Muda of Malaysia. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 53, 740–746.
Morse, J. C., Bae, Y. J., Munkhjargal, G., Sangpradub, N., Tanida, K., Vshivkova, T. S., et al. (2007). Freshwater biomonitoring with macroinvertebrates in East Asia. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 5, 33–42.
Reynolds, S. K., & Ferrington, L. C. (2001). Temporal and taxonomic patterns of mouthpart deformities in larval midges (Diptera: Chironomidae) in relation to sediment chemistry. Journal of Freshwater Ecology, 16(1), 15–27.
Reynolds, S. K., & Ferrington, L. C. (2002). Differential morphological responses of Chironomid larvae to severe heavy metal exposure (Diptera: Chironomidae). Journal of the Kansas Entomological Society, 75(3), 172–184.
Servia, M. J., Cobo, F., & Gonzales, M. A. (1998). Deformities in larval Prodiamesa olivacea (Meigen, 1818) (Diptera: Chironomidae) and their use as bioindicators of toxic sediment stress. Hydrobiologia, 385, 153–162.
Shriadah, M. A. (1998). Metals pollution in marine sediments of the United Arab Emirates creeks along the Arabian Gulf shoreline. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 60, 417–424.
Tan, S. G., & Yap, C. K. (2006). Biochemical and molecular indicators in aquatic ecosystems: current status and further applications in Malaysia. Aquatic Ecosystem Health and Management, 9(2), 227–236.
ter Braak, C. J. F. (1989). CANOCO—an extension of decorana to analyze species–environment relationships. Hydrobiologia, 184, 169–170.
ter Braak, C. J. F., & Prentice, I. C. (1988). A theory of gradient analysis. Advances in Ecological Research, 18, 271–317.
Tomar, M. (1999). Quality assessment of water and waste water. New York: Lewis Publishers.
Vermeulen, V. C. (1995). Elaborating chironomid deformities as bioindication of toxic sediment stress: The potential application of mixture toxicity concepts. Annales Zoologici Fennici, 32, 265–285.
Veroli, A. D., Selvaggi, R., Pellegrino, R. M., & Goretti, E. (2010). Sediment toxicity and deformities of chironomid larvae in Lake Piediluco. Chemosphere, 79, 33–39.
Warwick, W. F. (1985). Morphological abnormalities in Chironomidae (Diptera) larvae as measures of toxic stress in fresh-water ecosystems—Indexing antennal deformities in Chironomus Meigen. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 42, 1881–1914.
Warwick, W. F., & Tisdale, N. A. (1988). Morphological deformities in Chironomus, Cryptochironomus, and Procladius (Diptera: Chironomidae) from two differentially stressed sites in Tobin lakes, Saskatchewan. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science, 45, 1123–1144.
Watanabe, N. C., Harada, S., & Komai, Y. (2000). Long-term recovery from mine drainage disturbance of a macroinvertebrate community in the Ichi-kawa river, Japan. Hydrobiologia, 429, 171–180.
Wiederholm, T. (1984). Incidence of deformed chironomid larvae (Diptera: Chironomidae) in Swedish lakes. Hydrobiologia, 109, 243–249.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Shami, S.A., Salmah, M.R.C., Hassan, A.A. et al. Evaluation of mentum deformities of Chironomus spp. (Chironomidae: Diptera) larvae using modified toxic score index (MTSI) to assess the environmental stress in Juru River Basin, Penang, Malaysia. Environ Monit Assess 177, 233–244 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1630-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1630-1