Abstract
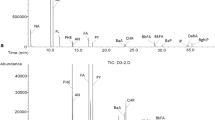
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are a class of environmental pollutants generated from incomplete combustion of organic materials. PAHs in tea have been studied for five locally available brands. Six to seven PAHs from list of 16 priority pollutants (US EPA) were found to be present in samples of various brands of tea. Benzo[a]pyrene (2A: probable human carcinogen) was found in two samples, and naphthalene (2B: possible human carcinogen) was found in all the tea samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bishnoi, N. R., Mehta, U., Sain, U., & Pandit, G. G. (2005). Quantification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in tea and coffee samples of Mumbai City (India) by high performance liquid chromatography. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 107, 399–406.
Cai, L. S., Xing, J., Dong, L., & Wu, C. (2003). Application of polyphenylmethylsiloxane coated fiber for solid-phase microextraction combined with microwave-assisted extraction for the determination of organochlorine pesticides in Chinese teas. Journal of Chromatography A, 1015, 11–21.
Cao, J., Zhao, Y., Liu, J., Xirao, R., Danzeng, S., Daji, D., et al. (2003). Brick tea fluoride as a main source of adult fluorosis. Food and Chemical Toxicolgy, 41, 535–542.
Ciemniak, A. (2005). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in herbs and fruit teas. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig, 56, 317–322.
Dennis, M. J., Massey, R. C., McWeeny, D. J., Knowles, M. E., & Watson, D. (1983). Analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the UK total diets. Food and Chemical Toxicolgy, 21, 569–574.
Fiedler, H., Cheung, C. K., & Wong, M. (2002). H. PCDD/PCDF, chlorinated pesticides and PAH in Chinese teas. Chemosphere, 46, 1429–1433.
Flaten, T. P. (2002). Aluminium in teas concentrations, speciation and bioavailability. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 228, 385–395.
Fung, K. F., Zhang, Z. Q., Wong, J. W. C., & Wong, M. H. (1999). Fluoride contents in tea and soil from tea plantations and the release of fluoride into tea liquor during infusion. Environmental Pollution, 104, 197–205.
Hernandez, J. E., Machado, I. T., Corbella, R., Rodriguez, M. A., & Montelongo, F. G. (1995). n-Alkanes and polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in fresh-frozen and precooked-frozen mussels. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 55, 461–468.
Jarvenpaa, E., Huopalahti, R., & Tapanainen, P. (1996). Use of supercritical fluid extraction/high performance liquid chromatography in the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from smoked and broiled fish. Journal of Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies, 19, 1473–1478.
Lin, D. H., & Zhu, L. Z. (2004). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: pollution and source analysis of a black tea. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 52, 8268–8271.
Lin, D. H., Tu, Y. Y., & Zhu, L. Z. (2005). Concentrations and health risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in tea. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 43, 41–48.
Lodovici, M., Dolaras, P., Casalini, C., Ciappellano, S., & Testolin, G. (1995). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contamination in the italian diet. Food Additives & Contaminants, 12, 703–713.
Mierzwa, J., Sun, Y. C., Chung, Y. T., & Yang, M. H. (1998). Comparative determination of Ba, Cu, Fe, Pb and Zn in tea leaves by slurry sampling electrothermal atomic absorption and liquid sampling inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Talanta, 47, 1263–1270.
Rivera, L., Curto, M. J. C., Pais, P., Galceran, M. T., & Puignou, L. (1996). Solid-phase extraction for the selective isolation of polyaromatic hydrocarbon, azaarenes and heterocyclic aromatic amines in charcoal grilled meat. Journal of Chromatography, 731, 85–94.
Schlemitz, S., & Pfannhauser, W. (1997). Supercritical fluid extraction of mononitrated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from teas correlation with the PAH concentration. Z Lebensm Unters Forsch, 205, 305–310.
Singh, S., & Prakash, V. (2007). The effect of temperature on PAHs emission from incineration of acrylic waste. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 132, 73–77.
US EPA (1997). Code of federal regulation, title 40, part 60, subparts D, Da, Db, Dc (p. 44). Washington, DC: Environmental Protection Agency.
Wang, Z. Y., Cheng, S. J., Zhou, Z. C., Athar, M., Khan, W. A., Bickers, D. R., et al. (1989). Antimutagenic activity of green tea polyphenols. Mutation Research, 223, 273–285.
Wang, Z. Y., Wang, L. D., Lee, M. J., Ho, C. T., Huang, M. T., Conney, A. H., et al. (1995). Inhibition of N-nitrosomethylbenzylamine-induced esophageal tumorigenesis in rats by green and black tea. Carcinogenesis, 16, 2143–2148.
Wong, M. H., Fung, K. F., & Carr, H. P. (2003). Aluminium and fluoride contents of tea, with emphasis on brick tea and their health implications. Toxicology Letters, 137, 111–120.
Ziegenhals, K., Wolfgang, J., & Speer, K. (2008). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in various types of tea. European Food Research and Technology, 228, 83–91.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Vashishth, A. & Vishal PAHs in some brands of tea. Environ Monit Assess 177, 35–38 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1615-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1615-0