Abstract
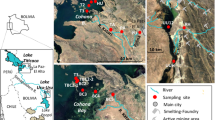
Toxic metal pollution in bodies of water is a source of danger to the health of people living in developing countries. The untreated mine wastes located near some Chinese ore mines may cause water pollution, which ultimately results in various diseases. The aim of the present study is to assess the response of testate amoebae communities to pollution by toxic metals in groundwater, stream water, and aquatic bryophytes in Lanmuchang stream located in the Hg–Tl mineralized area in southwestern Guizhou Province, China. Measurements were made of the levels of Hg, As, Cd, Tl, Cu, Zn, and Pb in three mosses: Hyophila propagulifera, Rhynchostegium riparioides, and Hygroamblystegium tenax. Mean moss concentrations of Hg, As, Cu, Pb, and Zn were significantly higher than stream water values and testate amoebae species richness and abundance were significantly lower in the ‘polluted’ group. We then studied the correlation between toxic metals and testate amoebae. The total species abundance is correlated negatively to Hg and Cu concentrations. Our results indicated that testate amoebae are sensitive to toxic metal pollution and aquatic bryophytes are bioaccumulators of trace metals, and results also showed potential microecosystem health risks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, D. Y., Wang, G. X., Zou, Z. X., & Chen, Y. M. (2003). Lanmuchangite, a new thallium (hydrous) sulphate from Lanmuchang, Guizhou Province, China. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 22, 185–192.
Claveri, B., Guerold, F., & Pihan, J. C. (1995). Use of transplanted mosses and autochthonous liverworts to monitor trace metals in acidic and non-acidic headwater streams Vosges Mountains, France. Science of the Total Environment, 175, 235–244.
Foissner, W. (1988). Taxonomic and nomenclatural revision of Sladecek’slist of ciliates (Protozoa: Ciliophora) as indicators of water quality. Hydrobiologia, 166, 1–64.
Gerdol, R., Bragazza, L., Marchesini, R., Alber, R., Bonetti, L., et al. (2000). Monitoring of heavy metal deposition in Northern Italy by moss analysis. Environmental Pollution, 108, 201–208.
He, L. B., Xiao, T. F., Li, H., & Sun, W. (2007). Hydrogechemical processes of thallium in a rural area of Southwest Guizhou, China. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 26, 52–57.
Helesic, J. (2001). Nonparametric evaluation of environmental parameters determining the occurrence of stonefly larvae (Plecoptera) in streams. Aquatic Sciences, 63, 490–501.
Jiang, J. G., & Shen, Y. F. (2005). Use of the aquatic protozoa to formulate a community biotic index for an urban water system. Science of the Total Environmet, 346, 99–111.
Kauppilal, T., Kihlman, S., & Maekinen, J. (2006). Distribution of Arcellaceans (Testate Amoebae) in the sediments of a mine water impacted bay of Lake Retunen, Finland. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 172, 337–358.
Kishaba, K., & Mitchell, E. A. D. (2005). Changes in testate amoebae (protists) communities in a small raised bog. A 40-year study. Acta Protozoologica, 44, 1–12.
Madoni, P. (1993). Ciliated protozoa and water quality in the Parma River (Northern Italy): Long-term changes in the community structure. Hydrobiologia, 264, 129–135.
Markert, B. A., Breure, A. M., & Zechmeister, H. G. (2003). Bioindicators and biomonitors: Principles, concepts, and applications (pp. 677–736). Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Ltd.
Nguyen-Viet, H., Bernard, N., Mitchel, E. A. D., Cortet, J., Badot, P.-M., et al. (2007a). Relationship between testate amoeba (protist) communities and atmospheric heavy metals accumulated in Barbula indica (bryophyta) in Vietnam. Microbial Ecology, 53, 53–65.
Nguyen-Viet, H., Gilbert, D., Mitchell, E. A. D., Badot, P.-M., & Bernard, N. (2007b). Effects of experimental lead pollution on the microbial communities associated with Sphagnum fallax (bryophyta). Microbial Ecology, 54, 232–241.
Nguyen-Viet, H., Bernard, N., Mitchell, E. A. D., Badot, P.-M., & Gilbert, D. (2008). Effect of lead pollution on testate amoebae communities living in Sphagnum fallax: An experimental study. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 69, 130–138.
Nicolau, A., Martins, M. J., Mota, M., & Lima, N. (2005). Effect of copper in the protistan community of activated sludge. Chemosphere, 58, 605–614.
Nimis, P. L., Fumagalli, F., Bizzotto, A., Codogno, M., & Skert, N. (2002). Bryophytes as indicators of trace metals pollution in the River Brenta (NE Italy). Science of the Total Environment, 286, 233–242.
Patterson, R. T., Barker, T., & Burbidge, S. M. (1996). Arcellaceans (thecamoebians) as proxies of arsenic and mercury contamination in northeastern Ontario lakes. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 26, 172–183.
Reinhardt, E. G., Dalby, A. P., Kumar, A., & Patterson, R. T. (1998). Arcellaceans as pollution indicators in mine tailing contaminated lakes near Cobalt, Ontario, Canada. Micropaleontology, 44, 131–148.
Samecka-Cymerman, A., Kolon, K., & Kempers, A. J. (2002). Heavy metals in aquatic bryophytes from the ore mountains (Germany). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 52, 203–210.
Shen, Y. F. (1999). Protozoology (pp. 1–656). Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
Shen, Y. F., Zhang, Z. S., Gong, X. J., Gu, M. R., Shi, Z. X., et al. (1990). Modern biomonitoring techniques using freshwater microbiota (pp. 41–48). Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press (in Chinese).
Smith, H. G. (1982). The terrestrial protozoan fauna of South Georgia. Polar Biology, 1, 173–179.
Wang, Z. H., Zhang, Z. H., & Li, J. H. (2007). Eco-feature of epiphyte aquatic protozoan community on karst moss in Xiangzhigou, Guizhou. Carsologica Sinica, 26, 249–254 (in Chinese)
Xu, K. D., Choi, J. K., Yang, E. J., Lee, K. C., & Lei, Y. L. (2002). Biomonitoring of coastal pollution status using protozoan communities with a modified PFU method. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 44, 877–886.
Xu, R. L., Sun, X. Y., Yang, C. S., Lan, C. Y. & Wang, M. H. (1999). PFU protozoan communities and their colonization in a treatment system of Pb-Zn mine tailing water. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 5, 357–361 (in Chinese).
Yang, C. S., Shu, W. S., Xu, R. L., & Lan, C. Y. (2000). Applying PFU protozoan community to monitor the effectiveness of constructed wetland in treating waste water from Pb/Zn mine. Environmental Pollution and Control, 20, 20–22 (in Chinese).
Yang, J., Zhang, W. J., Feng, W. S., & Shen, Y. F. (2006). Geographical distribution of testate amoebae in Tibet and northwestern Yunnan and their relationships with climate. Hydrobiologia, 559, 297–304.
Zhang, Z., & Zhang, B. G. (1996). Thallium in low temperature ore deposits, China. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 15, 87–96.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, ZC., Wang, ZH. & Zhang, ZH. Biomonitoring of testate amoebae (protozoa) as toxic metals absorbed in aquatic bryophytes from the Hg-Tl mineralized area (China). Environ Monit Assess 176, 321–329 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1585-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1585-2