Abstract
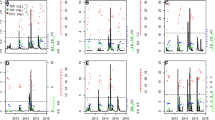
The Bear Brook Watershed in Maine (BBWM) is a long-term, paired watershed experiment that addresses the effects of acid and nitrogen (N) deposition on whole watersheds. To examine stream response at BBWM, we synthesized data on organic matter dynamics, including leaf breakdown rates, organic matter inputs and standing stocks, macroinvertebrate secondary production, and nutrient uptake in treated and reference streams at the BBWM. While N concentrations in stream water and leaves have increased, the input, standing stocks, and breakdown rates of leaves, as well as macroinvertebrate production, were not responsive to acid and N deposition. Both chronic and acute increases of N availability have saturated uptake of nitrate in the streams. Recent experimental increases in phosphorus (P) availability enhanced stream capacity to take up nitrate and altered the character of N saturation. These results show how the interactive effects of multiple factors, including environmental flow regime, acidification, and P availability, may constrain stream response to chronic N deposition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aber, J., McDowell, W., Nadelhoffer, K., Magill, A., Berntson, G., Kamakea, M., et al. (1998). Nitrogen saturation in temperate forest ecosystems—hypotheses revisited. Bioscience, 48, 921–934.
Bernot, M. J., & Dodds, W. K. (2005). Nitrogen retention, removal and saturation in lotic ecosystems. Ecosystems, 8, 442–453.
Chadwick, M. A., & Huryn, A. D. (2003). Effect of a whole-catchment addition on stream detritus processing. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 22, 194–206.
Chadwick, M. A., & Huryn, A. D. (2005a). Effects of atmospheric N deposition on coarse organic matter in a headwater stream. Hydrobiologia, 532, 167–179.
Chadwick, M. A., & Huryn, A. D. (2005b). Response of stream macroinvertebrate production to atmospheric nitrogen deposition and channel drying. Limnology and Oceanography, 50, 228–236.
Cross, W. F., Wallace, J. B., Rosemond, A. D., & Eggert, S. L. (2006). Whole-system nutrient enrichment increases secondary production in a detritus-based ecosystem. Ecology, 87, 1556–1565.
Dangles, O., Gessner, M. O., Guerold, F., & Chauvet, E. (2004). Impacts of stream acidification on litter breakdown: Implications for assessing ecosystem function. Journal of Applied Ecology, 41, 365–378.
Davis, J. C., & Minshall, G. W. (1999). Nitrogen and phosphorus uptake in two Idaho (USA) headwater wilderness streams. Oecologia, 119, 247–255.
Driscoll, C. T., Lawrence, G. B., Bulger, A. J., Butler, T. J., Cronan, C. S., Eagar, C., et al. (2001). Acidic deposition in the northeastern United States: Sources and inputs, ecosystem effects, and management strategies. Bioscience, 51, 180–198.
Earl, S. R., Valett, H. M., & Webster, J. R. (2006). Nitrogen saturation in stream ecosystems. Ecology, 87, 3140–3151.
Ferreira, V., Gulis, V., Graça, M. A. S. (2006). Whole-stream nitrate addition affects litter decomposition and associated fungi but not invertebrates. Oecologia, 149, 718–729.
Galloway, J. N., Aber, J. D., Erisman, J. W., Seitzinger, S. P., Howarth, R. W., Cowling, E. B., et al. (2003). The nitrogen cascade. Bioscience, 53, 341–356.
Greenwood, J. L., Rosemond, A. D., Wallace, J. B., Cross, W. F., & Weyers, H. S. (2007). Nutrients stimulate leaf breakdown rates and detritivore biomass: bottomup effects via heterotrophic pathways. Oecologia, 151, 637–649.
Gress, S. E., Nichols, T. D., Northcraft, C. C., & Peterjohn, W. T. (2007). Nutrient limitation in soils exhibiting differing nitrogen availabilities: What lies beyond nitrogen saturation? Ecology, 88, 119–130.
Griffith, M. B., Perry, S. A., & Perry, W. B. (1993). Growth and secondary production of Paracapnia angulata Hanson (Plecoptera: Capniidae) in Appalachian streams affected by acid precipitation. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 71, 735–743.
Gulis, V., Rosemond, A. D., Suberkropp, K., Weyers, H. S., & Benstead, J. P. (2004). Effects of nutrient enrichment on the decomposition of wood and associated microbial activity in streams. Freshwater Biology, 49, 1437–1447.
Hart, D. D., & Robinson, C. T. (1990). Resource limitation in a stream community: Phosphorus enrichment effects on periphyton and grazers. Ecology, 71, 1494–1502.
Huryn, A. D., & Wallace, J. B. (2000). Life history and production of stream insects. Annual Review of Entomology, 45, 83–110.
Kahl, J. S., Norton, S. A., Fernandez, I. J., Naderhoffer, K. J., Driscoll, C. T., & Aber, J. D. (1993). Experimental inducement of N saturation at the watershed scale. Environmental Science and Technology, 27, 565–568.
Kopáček, J., & Blazka, P. (1994). Ammonium uptake in alpine streams in the high Tatra mountains (Slovakia). Hydrobiologia, 294, 157–165.
Kopáček, J., Hejzlar, J., Borovec, J., Porcal, P., & Kotorova, I. (2000). Phosphorus inactivation by aluminum in the water column and sediments: Lowering of in-lake phosphorus availability in an acidified watershed-lake ecosystem. Limnology and Oceanography, 45, 212–225.
Kopáček, J., Brzakova, M., Hejzlar, J., Nedoma, J., Porcal, P., & Vrba, J. (2004). Nutrient cycling in a strongly acidified mesotrophic lake. Limnology and Oceanography, 49, 1202–1213.
Mulholland, P. J., Elwood, J. W., Palumbo, A. V., & Stevenson, R. J. (1986). Effect of stream acidification on periphyton composition, chlorophyll, and productivity. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 43, 1846–1858.
Mulholland, P. J., Palumbo, A. V., & Elwood, J. W. (1987). Effects of acidification on leaf decomposition in streams. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 6, 147–158.
Mulholland, P. J., Driscoll, C. T., Elwood, J. W., Osgood, M. P., Palumbo, A. V., Rosemond, A. D., et al. (1992). Relationships between stream acidity and bacteria, macroinvertebrates, and fish—a comparison of north temperate and south temperate mountain streams, USA. Hydrobiologia, 239, 7–24.
Mulholland, P. J., Tank, J. L., Webster, J. R., Bowden, W. B., Dodds, W. K., Gregory, S. V., et al. (2002). Can uptake length in streams be determined by nutrient addition experiments? Results from an interbiome comparison study. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 21, 544–560.
Niyogi, D. K., Lewis, W. M., & McKnight, D. M. (2002). Effects of stress from mine drainage on diversity, biomass, and function of primary producers in mountain streams. Ecosystems, 5, 554–567.
Norton, S. A., Kahl, J. S., Fernandez, I. J., Rustad, L. E., Scofield, J. P., & Hanes, T. A. (1994). Response of the Bear Brook Watershed in eastern Maine to the addition of (NH4)2SO4: Three year results. Forest Ecology and Management, 68, 61–73.
Norton, S., Fernandez, I., Amirbahman, A., Coolidge, K., & Navratil, T. (2006). Aluminum, phosphorus, and oligotrophy—assembling the pieces of the puzzle. Proceedings of the International Association of Theoretical and Applied Limnology, 29, 1877–1886.
O’Brien, J. M., Dodds, W. K., Wilson, K. C., Murdock, J. N., & Eichmiller, J. (2007). The saturation of N cycling in Central Plains streams: 15-N experiments across a broad gradient of nitrate concentrations. Biogeochemistry, 84, 31–49.
Paine, R. T., Tegner, M. J., & Johnson, E. A. (1998). Compounded perturbations yield ecological surprises. Ecosystems, 1, 535–545.
Pretty, J. L., Giberson, D. J., & Dobson, M. (2005). Resource dynamics and detritivore production in an acid stream. Freshwater Biology, 50, 578–591.
Reinhardt, R. L., Norton, S. A., Handlery, M., & Amirbahman, A. (2004). Dynamics of P, Al, and Fe during high discharge episodic acidification at the Bear Brook Watershed in Maine, USA. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 4, 311–323.
Roy, S., Norton, S., Fernandez, I. J., & Kahl, J. (1999). Linkages of P and Al export at high discharge at the Bear Brook Watershed in Maine. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 55, 133–147.
Sherman, J., Fernandez, I. J., Norton, S. A., Ohno, T., & Rustad, L. E. (2006). Soil aluminum, iron, and phosphorus dynamics in response to long-term experimental nitrogen and sulfur additions at the Bear Brook watershed in Maine, USA. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 121, 421–429.
Simon, K. S., Niyogi, D. K., Frew, R. D., & Townsend, C. R. (2007). Nitrogen dynamics in grassland streams along a gradient of agricultural development. Limnology and Oceanography, 52, 1246–1257.
Strauss, E. A., & Lamberti, G. L. (2000). Regulation of nitrification in aquatic sediments by organic carbon. Limnology and Oceanography, 45, 1854–1859.
Uddameri, V., Norton, S. A., Kahl, J. S., & Scofield, J. P. (1995). Randomized intervention analysis of the response of the West Bear Brook Watershed to chemical manipulation. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 79, 131–146.
Vitousek, P. M., Aber, J. D., Howarth, R. W., Likens, G. E., Matson, P. A., Schindler, D. W., et al. (1997). Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: Sources and consequences. Ecological Applications, 7, 737–750.
Wallace, J. B., Webster, J. R., & Cuffney, T. F. (1982). Stream detritus dynamics: Regulation by invertebrate consumers. Oecologia, 53, 197–200.
Webster, J. R., & Valett, H. M. (2006). Solute dynamics. In: F. R. Hauer, & G. A. Lamberti (Eds.), Methods in stream ecology (pp. 169–186). New York: Academic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simon, K.S., Chadwick, M.A., Huryn, A.D. et al. Stream ecosystem response to chronic deposition of N and acid at the Bear Brook Watershed, Maine. Environ Monit Assess 171, 83–92 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1532-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1532-2