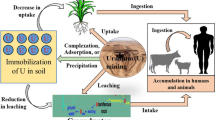
Abstract
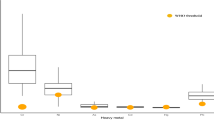
Ingestion of radionuclides and heavy metals through drinking water and food intake represents one of the important pathways for long-term health considerations. Milk and milk products are main constituents of the daily diet. Radionuclides and heavy metals can be apprehended in the ecosystem of the East Singhbhum region which is known for its viable grades of uranium, copper and other minerals. For the risk assessment studies, samples of milk were collected from twelve villages around Bagjata mining area and analysed for U(nat), 226Ra, 230Th, 210Po, Fe, Mn, Zn, Pb, Cu and Ni. Analysis of the results of the study reveals that the geometric mean of U(nat), 226Ra, 230Th and 210Po was 0.021, 0.24, 0.23 and 1.08 Bq l − 1, respectively. The ingestion dose was calculated to be 12.34 μSvY − 1 which is reflecting the natural background dose via the route of ingestion, and much below the 1 mSv limit set in the new ICRP recommendations. The excess lifetime cancer risk was estimated to be 1.72 × 10 − 4 which is within the acceptable excess individual lifetime cancer risk value of 1 × 10 − 4. The geometric mean of Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu and Ni was 4.91, 0.29, 4.77, 0.56 and 0.48 mgl − 1, respectively; whereas the daily intake was computed to be 0.44, 0.03, 0.43, 0.05 and 0.04 mg/day, respectively. Pb was not detected in any of the samples. The hazard quotient revealed that the intake of the heavy metals through the ingestion of milk does not pose any apparent threat to the local people as none of the HQ of the heavy metals exceeds the limit of 1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abollino, O., Aceto, M., Bruzzoniti, M. C., Mentasti, E., & Sarzanini, C. (1998). Speciation of copper and manganese in milk by solid-phase extraction/inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. Annals Chim Acta, 375, 299–306.
Aksu, S. K., Cetinoǧlu, A., & Güçer, Ş. (2004). Determination of trace element contents in cow milk by ICP-MS Adnan Menderes University, 4th AACD Congress, 29 Sept-3 Oct., Kuşadası-Aydin, Turkey Proceedings Book 285.
Amaral, E. C. S., Rochedo, E. R. R., Paretzke, H. G., & Franca, E. P. (1992). The radiological impact of agricultural activities in an area of high natural radioactivity. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 45, 289–292.
Benemariya, H., Robberecht, H., & Deelstra, H. (1993). Zn, Cu and Se in milk and organs of cow and goat from Burundi, Africa. Science of the Total Environment, 128, 83–98.
Bhola, K. L., Dar, K. K., Ramarao, Y. N., Suri Sastry, C., & Mehta, N. R. (1964). A review of Uranium and Thorium deposits in India. In Proceedings of 3rd International Conference of the peaceful uses of Atomic Energy. Multilingual Edition United Nations (Vol. 12, pp. 750–756).
Brzoska, F., Wiewioraw, Michalec, J., & Brzoska, B. (1996). Influence of magnesium oxygen and dolomite on cows productivity, milk composition, electrolyte content in milk and blood serum (in Polish). Rocz Nauk Zoot, 23, 71–74.
Buldini, P. L., Cavalli, S., & Sharma, J. L. (2002). Matrix removal for the ion chromatographic determination of some trace elements in milk. Microchem Journal, 72, 277–284.
Carvalho, F. P. (1995). 210Po and 210Pb intake by the Portuguese population: The contribution of seafood in the dietary intake 210Po and 210Pb. Health Physics, 69, 469–480.
Chhabra, A. S. (1966). Radium 226 in food and man in Bombay and Kerala State (India). British Journal of Radiology, 39, 141–146.
Dang, H. S., Jaiswal, D. D., Parameswaran, M., & Krishnamony, S. (1994). Physical anatomical, physiological and metabolic data for reference man-a proposal. BARC/1994/E/043.
Dang, H. S., Jaiswal, D. D., Parameswaran, M., Deodhar, K. P., & Krishnamony, S. (1996). Age dependent physical and anatomical Indian data for application in internal dosimetry. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 63, 217–222.
Davies, J. E., Freed, V. H., & Whittemore, F. W. (1986). An agro medical approach to pesticide management. Coral Gables, FL: University of Miami School of Medicine.
Dobrzañski, Z., Koacz, R., Górecka, H., Chojnacka, K., & Bartkowiak, A. (2005). The content of microelements and trace elements in raw milk from cows in the Silesian Region. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 14(5), 685–689.
Douglas, S. (1967). Radiatioassay procedures for Environmental samples. National Center for Radiological Health, Rockville, Maryland, Geneva section 3–3.
Enb, A., Abou Donia, M. A., Abd-Rabou, N. S., Abou-Arab, A. A. K., & El-Senaity, M. H. (2009). Chemical composition of raw milk and heavy metals behavior during processing of milk products. Global Veterinaria, 3(3), 268–275.
Fernandez, G., Rodriguez, I. M., Castro, G. V., Carrazana, G., & Martinez, R. N. (2004). Radiological surveillance of foods and drinking water in the Cuban Republic. In Proceedings of the 11th Conference of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA), Madrid, Spain, May 23–28.
Figgins, P. E. (1961). Radiochemistry of polonium. National Academy of Science, NS Series, 3037.
Hernandez, F., Hernandez-Armas, J., Catalan, A., Fernandez-Aldecoa, J. C., & Landeras, M. I. (2004). Activity concentrations and mean effective dose of foodstuffs on the Island of Tenerife, Spain. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 111, 205–210.
Hyde, E. K. (1960). Radiochemistry of thorium. National Academy of Science, NS series, 3004.
ICRP (2007). Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection ICRP Publication 103. Annals ICRP, 37, 2–4.
ICRP-68 (1994). International Commission on Radiological Protection Report. Dose Coefficients for Intakes of Radionuclides by Workers. ICRP 68, Annals of ICRP, Pergamon Press.
IDF (1979). International Dairy Federation Bulletin, Chemical Residues in milk and milk products. I.D.F. Document, 133.
Jain, S. C., Mehta, S. C., Kumar, B., Reddy, A. R., & Nagaratnam, A. (1995). Formulation of the reference Indian adult: Anatomical and physiological data. Health Physics, 68, 509–522.
Jochum, R., Fuchs, A., Cser, A., Menzel, H., & Lombeck, I. (1995). Trace mineral status of full term infants fed human milk, milk based formula or partially hydrolysed whey protein formula. Analyst, 120, 905–909.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2001). Trace elements in soils and plants (3rd Ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC.
Kannan, V., Iyengar, M. A. R., & Ramesh, R. (2001). Dose estimates to the public from 210Po ingestion via dietary sources at Kalpakkam (India). Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 54, 663–674.
Khan, K., Ahmad, N., Matiullah, Khan, H. M. (1997). Gamma spectrometric studies of different brands of phosphatic fertilizers. Science International, 9, 125–126.
Khandekar, R. N. (1977). Polonium-210 in Bombay diet. Health Physics, 33, 148–150.
Kolthoff, I. M., & Elving, P. J. (1962). Treatise on analytical chemistry (Part 2, Vol. 9).
Lante, A., Lomolino, G., Cagnin, M., & Spettoli, P. (2004). Content and characterization of minerals in milk and in crescenza and squacquerone Italian fresh cheese by ICP-OES. Food Control, 17, 229–233.
Licata, P., Trombetta, D., Cristani, M., Giofre, F., Martino, D., Calo, M., et al. (2004). Levels of “toxic” and “essential” metals in samples of bovine milk from various dairy farms in Calabria, Italy. Environmental Research, 30, 1–6.
Lokeshwari, H., & Chandrappa, G. T. (2006). Impact of heavy metal contamination of Bellandur Lake on soil and cultivated vegetation. Current Science, 91(5), 10.
Martin, M. H., & Coughtrey, P. J. (1982). Biological monitoring of heavy metal pollution. London: Applied Science.
McDonald, P., Jackson, D., Leonard, D. R. P., & McKay, K. (1999). An assessment of 210Pb and 210Po terrestrial foodstuffs from regions of potential technological enhancement in England and Wales. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 43, 15–29.
Miller, J. C., & Miller, J. N. (1989). Statistics for analytical chemistry (2nd Ed.). New York: Horwood.
Moore, H. E., Martell, E. A., & Poet, S. E. (1976). Sources of Polonium-210 in atmosphere. Environmental Science and Technology, 10, 586–589.
Oskarsson, A., Jorhim, L., Sundberg, J., Nilsson, N. G., & Albanus, L. (1992). Lead poisoning in cattle, transfer of lead to milk. Science of the Total Environment, 111, 83–94.
Ostapczuk, P., Valenta, R., Rutzel, H., & Nurnberg, H. W. (1987). Application of differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry to the determination of heavy metals in environmental samples. Science of the Total Environment, 60, 1–16.
Othman, I., & Yassine, T. (1995). Natural radioactivity in the Syrian environment. Science of the Total Environment, 170, 119–124.
Ragjavayya, M., Iyengar, M. A. R., & Markose, P. M. (1980). Estimation of Radium-226 by emanometry. Bulletin of India Association for Radiation protection, 3(4), 11–15.
Richards, L. A. (1968). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkaline soils (1st Ed.). New Delhi Agri: IBH Publications Company. Handbook No. 60.
Saracevic, L., Samek, D., Mihalj, A., & Gradascevic, N. (2009). The natural radioactivity in vicinity of the brown coal mine Tusnica–Livno, BiH. Radioprotection, 44(5), 315–320.
Sarangi, A. K., & Singh, A. S. (2006). Vein type uranium mineralisation in Jaduguda, Uranium deposits, Singhbhum, India. In Intern.Symp.on understanding the genesis of ore deposits to meet the demands of 21th century: Association on the genesis of ore deposits (Vol. 12, pp. 54–61), Moscow.
Schroeder, G. (2003). Chemical aspects of environmental studies (in Polish). Ed. by UAM Poznan, Medicine.
Shacklette, H. T., Erdman, J. A., & Harms, T. F. (1978). In F. W. Oehme (Ed.), Trace elements in plant foodstuffs, in toxicity of heavy metals in the environment, Part 1 (p. 25). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Tripathi, R. M., Raghunath, R., Sastry, V. N., & Krishnamoorthy, T. M. (1999). Daily intake of heavy metals by infants through milk and milk products. Science of the Total Environment, 227, 229–235.
UNEP, FAO, WHO (1992). Assessment of dietary intake of chemical contaminants. WHO/HPP/FOS/92.6, UNEP/GEMS/92.F2, United Nations Environmental Program, Nairobi.
UNSCEAR (2000). United nations scientific committee on the effects of atomic radiation (Sources, Effects and Risks of Ionizing Radiation, Report to the General Assembly with Scientific Annexes, United Nations, New York. 1, 126–127.
US-EPA (1989). Health effect assessments summary tables (HEAST) and user’s guide, Office of Emergency and Remedial Response. Washington DC, USA: US Environmental Protection Agency.
US-EPA (1991). Role of the Baseline Risk Assessment in Superfund Remedy Selection Decisions (Memorandum from D. R. Clay, OSWER 9355.0–30, April 1991) US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington DC, USA. Internet: www.epa.gov/oswer/riskassessment/baseline.htm.
US-EPA (1993). Carcinogenicity assessment. IRIS (Integrated Risk Information System), 2003; US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington DC, USA. Internet: www.epa.gov/iris.
Wayne, R. O. (1990). A physical explanation of the lognormality of pollutant concentrations. Journal of the Air and Management Association, 40, 1378–1383.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is not included in your organization’s subscription. However, you may be able to access this article under your organization’s agreement with Elsevier.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giri, S., Singh, G., Jha, V.N. et al. Risk assessment due to ingestion of natural radionuclides and heavy metals in the milk samples: a case study from a proposed uranium mining area, Jharkhand. Environ Monit Assess 175, 157–166 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1502-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1502-8