Abstract
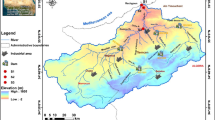
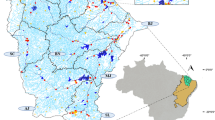
The Euphrates and Tigris watersheds originating from Turkey and passing through Syria and Iraq are one of the most important transboundary watersheds in the Middle East. Long-term data (1971 to 2002) from 14 stations over the Euphrates river and seven stations over the Tigris river were analyzed and compared using the nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis and Mann–Kendall trend tests, and box-and-whisker plots. The upper Euphrates river had significantly lower values of flow rate (FR), water temperature (WT), electrical conductivity (EC), Cl, and SO4 than did the lower Euphrates river. The middle Euphrates river had significantly higher Na, K, HCO3, Cl, sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), and boron (B) and lower EC and SO4 than the lower Euphrates river. The upper west Tigris river had higher EC, Ca + Mg, and SO4 and lower FR, Na, and SAR than the lower Tigris river. The upper east Tigris river had higher HCO3 and B and lower FR and WT than the lower Tigris river.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcamo, J., & Henrichs, T. (2002). Critical regions: A model-based estimation of world water resources sensitive to global changes. Aquatic Sciences, 64, 352–362.
Babkin, V. I. (2004). Water resources of the Russian Federation in the 20th century. Water Resources, 31, 357–362.
Charles, J. V., Gren, P., Salisbury, J., & Richard, B. L. (2000). Global water resources: Vulnerability from climate change and population growth. Science, 289, 284–288.
EIE (2002). Observations of water qualities in Turkey’s rivers. Ankara: EIE.
Hooper, R. P., Aulenbach, B. T., & Kelly, V. J. (2001). The national stream quality accounting network: A flux-based approach to monitoring the water quality of large rivers. Hydrological Processes, 15, 1089–1106.
Kendall, M. G. (1970). Rank correlation methods (4th ed.). London: Griffin.
Odemis, B., & Evrendilek, F. (2007). Monitoring water quality and quantity of national watersheds in Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 133, 215–229.
Odemis, B., & Evrendilek, F. (2008). Multivariate analysis of watershed health and sustainability in Turkey. The International Journal of Sustainable Development and World Ecology, 15, 265–272.
Postel, S. (2000). Entering an area of water scarcity: The challenges ahead. Ecological Applications, 10, 941–948.
Smith, R. A., Alexander, R. B., & Wolman, M. G. (1987). Water quality trends in the nation’s rivers. Science, 174, 1607–1615.
Tekinel, O., Çevik, B., Kanber, R., & Baytorun, N. (1989). South East Anatolia project. Adana: Cukurova University, Faculty of Agriculture, 15.
TRSHW (2002). Actual and projected water use and distribution. Ankara: TRSHW (in Turkish).
UNEP (1992). Saving our planet: Challenges and hopes. Nairobi: UNEP, 200.
USSL (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Washington, D.C.: US Department of Agriculture, Handbook No. 60.
World Resources Institute WRI (1990). World resources 1990–91. New York: Oxford University Press, 385. A report by the World Resources Institute in collaboration with the United Nations Environment Programme and the United Nations Development Programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Odemis, B., Sangun, M.K. & Evrendilek, F. Quantifying long-term changes in water quality and quantity of Euphrates and Tigris rivers, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 170, 475–490 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1248-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1248-3