Abstract
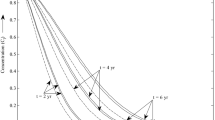
A three-dimensional contaminant transport model has been developed to simulate and monitor the migration of disposal of hydrocarbon exploration produced water in Injection well at 2,100 m depth in the Upper Cretaceous Pab sandstone, Bhit area in Dadu district of Southern Pakistan. The regional stratigraphic and structural geological framework of the area, landform characteristics, meteorological parameters, and hydrogeological milieu have been used in the model to generate the initial simulation of steady-state flow condition in the underlying aquifer’s layers. The geometry of the shallow and deep-seated characteristics of the geological formations was obtained from the drilling data, electrical resistivity sounding surveys, and geophysical well-logging information. The modeling process comprised of steady-state simulation and transient simulation of the prolific groundwater system of contamination transport after 1, 10, 30 years of injection. The contaminant transport was evaluated from the bottom of the injection well, and its short- and long-term effects were determined on aquifer system lying in varying hydrogeological and geological conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, N. (1974). Groundwater resources of Pakistan. Lahore: Ripon.
Ahmad, Z., Kausar, R., & Ahmad, I. (2009). Implications of depletion of groundwater levels in 3 layered aquifers and its management to optimize the supply demand in the urban settlement near Kahota Industrial Triangle area, Islamabad, Pakistan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-0983-9.
Ahmad, Z., & Khawaja, A. A. (1999). Three-dimension flow and solute transport modeling of the Eolian Aquifer in a uniform flow field of a chemical plant. Pakistan Journal of Hydrocarbon Research, 11, 59–74.
Ahmad, Z., & Serrano, S. (2001). Numerical groundwater flow modeling of the Rechna Doab Aquifer, Punjab, Pakistan. In Proceeding of international groundwater modeling conference (IGWMC), MODFLOW 2001 and other modeling odysseys, 12–14 September. Denver, USA: Colorado School of Mines and Geophysics.
Ahmad, Z., Ahmad, I., & Akhtar, G. (1994). A report on groundwater reserve estimation of the Ahmad Khan well field and its safe utilization for the 4000 TPD Luck Cement plant Pezu, D.I.Khan.
Ahmad, Z., Ashraf, M., & Siddiqui, R. F. (1997a). Groundwater computer modeling of the National Park area in the vicinity of Rawal Lake, Islamabad. Journal of Drainage and water Management, 1, 8–21.
Ahmad, Z., Shaista, M., & Gulraiz, A. (1997b). Evaluation of groundwater potential of Islamabad area using logs data of test holes drilled by OGDC. Pakistan Journal of Hydrocarbon Research, 9, 91–101.
Ashraf, A., & Ahmad, Z. (2008). Regional groundwater flow modeling of Upper Chaj Doab of Indus Basin, Pakistan using finite element model (Feflow) and geoinformatics. Geophysical Journal International (GJI), 173, 17–24. doi:10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03708.x.
Brown, J. G., & Glynn, P. D. (2003). Kinetic dissolution of carbonates and Mn oxides in acidic water–measurement of in situ field rates and reactive transport modeling. Applied Geochemistry, 18(8), 1225–1239. doi:10.1016/S0883-2927(03)00010-6.
Conan, C., Bouraoui, F., Turpin, N., de Marsily, G., & Bidoglio, G. (2003). Modeling flow and nitrate fate at catchment scale in Brittany (France). Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 2026–2032.
Harten, A. (1983). High resolution schemes for hyperbolic conservation laws. Journal of Computational Physics, 49, 357–393.
Hedley, R., Warburton, J., & Smewing, J. (2001). Sequence stratigraphy and tectonics in the Kirthar Foldbelt, Pakistan. In Geology and climate of the Arabian Sea region, Geol. Society London.
McDonald, M. G., & Harbaugh, A. W. (1988). A modular three-dimensional finite difference ground-water flow model, US geological survey. Techniques of Water-Resources Investigations, Book 6.
NESPAK (1998). Master feasibility studies for flood management of hill-torrents of Pakistan, supporting vol-IV Sindh Province. Lahore: National Engg. Services Pak.
Pivnik, D. A., & Wells, N. A. (1996). The transition from Tethys to the Himalaya as recorded in northwest Pakistan. GSA Bulletin, 108(10), 1295–1313.
Poeter, E. P., & Hill, M. C. (1999). UCODE, a computer modelling. Computers and Geosciences, 25, 457–462.
Smewing, J. D., Warburton, I., Daley, T., Copestake, P., & Haq, N. U. (2001). Sequence stratigraphy of the Southern Kirthar Foldbelt and Middle Indus Basin Pakistan. In Geology and climate of the Arabian Sea region, Geol. Society London.
WAPDA (1965). Lower Indus report. Physical resources, groundwater, supl.6.1.6. Tubewells and Boreholes, Nara Command.
WAPDA (1989). Rohri hydropower project. Feasibility study. HEPO no.97.
Zheng, C., & Wang, P. P. (1999). A modular three-dimensional multispecies transport model. Washington: US Army Corps of Engineers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, Z., Akhter, G., Ashraf, A. et al. Implications and concerns of deep-seated disposal of hydrocarbon exploration produced water using three-dimensional contaminant transport model in Bhit Area, Dadu District of Southern Pakistan. Environ Monit Assess 170, 395–406 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1241-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1241-x