Abstract
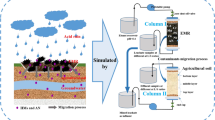
Comparative leaching experiments were carried out using leaching medium with different pH to municipal solid waste in the landfill columns in order to investigate the mobility of heavy metals. The leachate pH and oxidation–reduction potential were measured by oxidation–reduction potential analyzer; the contents of heavy metals were measured by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. It is very different in leaching concentrations of heavy metals; the dynamic leaching of heavy metals decreased with the rise of the leaching amount on the whole. Acid leaching medium had definite influence on the leaching of heavy metals in the early landfill, but it had the obvious inhibition effect on the leaching in the middle and late period of landfill; the neutral and alkaline leaching medium are more beneficial to the leaching of heavy metals. Due to the influence of the environment of landfill, the differences of the results in cumulative leaching amount, leaching rate, and leaching intensity of heavy metals are very big. The calculation results of the release rates of heavy metals prove that the orders of the release rates are not identical under different leaching conditions. Acid rain made heavy metals migrate from municipal solid waste to soil and detain in soil more easily; approached neutral and alkaline leaching mediums are more beneficial to leaching of heavy metals in the municipal solid waste and soil with leachate. The field verification of experimental data showed that the law of heavy metal leaching in municipal solid waste revealed by the experiment has a good consistency with the data obtained by municipal solid waste landfill.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baun, D. L. (2004). Speciation of heavy metals in landfill leachate: A review. Waste Management & Research, 22(1), 3–23. doi:10.1177/0734242X04042146.
Chen, J., & Chen, X. (1999). 3-Dimensional mathematical model for the transportation of Fe and Mn in Arha Reservoir. Advances in Water Science, 10(1), 14–19.
Ding, G., Xu, X., & Fang, X. (1997). Current status and future of acid rain in China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 42(24), 2076–2080. doi:10.1007/BF02882950.
Ding, G., Xu, X., Wang, S., et al. (2004). Database from the acid rain network of China meteorological administration and its preliminary analyses. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 15(supp), 85–94.
Flyhammar, P. (1998). Use of sequential extraction on anaerobic degraded municipal solid waste. The Science of the Total Environment, 212(2), 203–215. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(97)00339-2.
Fu, M., & Zhou, L. (2006). Translocation of lead in contaminated soils facilitated by dissolved organic matter of landfill-leachate. Journal of East China Institute of Technology, 29(2), 171–175.
He, X., & Cao, Y. (2005). Acid rain monitoring of Xiuzhou from 2000 to 2004. Jiangsu Environmental Science and Technology, 18(supp), 92–93.
Hui, L., Wu, Y., Li, X., et al. (2006). Effect of DOM on the mobility of heavy metals in soil. Journal of Liaoning Technical University, 25(supp), 278–280.
Jiang, J.-G., Liang, S.-W., Chen, S., et al. (2002). Prediction for leachate generation at Shenzhen Xiaping MSW landfill. Environmental Protection of Xinjiang, 24(3), 01–04.
Jiang, J., & Wu, Y. (1995). Study on the movement of heavy metals in meadow burozem affected by model acid precipitation. Journal of Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 12(2), 185–190.
Liu, G., Xu, Z., Zhou, G., & Liu, W. (2004). Studies on the character and rule of cadmium release from red soils under the action of acid rain. China Environmental Science, 24(4), 419–423.
Luo, Z., Zhao, J., & Jin, M. (2003). Study on heavy metal to environmental pollution from an old land in WuHan, HuBei Province. Geological Science and Technology Information, 22(3), 97–89.
Shao, L., He, P., & Qu, X. (2007). Release of heavy metals during the initial stage of the bioreactor landfill. China Environmental Science, 27(1), 71–75.
Sheng, D., He, R., & Liu, H. (2003). Biological treatment technology of MSW landfill. Pejing: Chemical Industry Publishing House.
Wan, G.-J., Huang, R.-G., Wang, C.-S., et al. (1992). Distribution and migration characteristics of Fe, Mn in Hongfeng reservoir soil-water interface. Science Bulletin, 35(8), 612–615.
Wang, D., Jiang, X., Bian, Y., et al. (2003). The influence of simulated acid rain on acidity K + leaching regulation of different soil layers. Environmental Sciences (Tokyo), 24(2), 30–33.
Wen, Z., & Wei, B. (2008). Engineering design of Yan-qun municipal solid waste sanitary landfill in Xu-zhou. Municipal Engineering Technology, 26(2), 108–111.
Xiao, Z., He, P., Shao, L., et al. (2005). Effect of the total amount and speciation of heavy metals on its mobility in municipal solid waste landfill. Environmental Chemistry, 24(3), 265–269.
Yang, Q., & Cha, K. (2005). Analysis of transfer and conversion characteristics of trace metal pollutants in MSW landfill. Sichuan Environment, 24(6), 96–98.
Zhang, H., & Ma, D. (2001). The release of heavy metals from wastes associated with urban human life in the dump soil. Environmental Chemistry, 20(1), 43–46.
Zhang, H., Ma, D., Xie, Q., et al. (1999). An approach to study heavy metal pollution caused by modern city development in Nanjing, China. Environmental Geology, 38(3), 223–228. doi:10.1007/s002540050418.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, HH., Sang, SX. Study on the law of heavy metal leaching in municipal solid waste landfill. Environ Monit Assess 165, 349–363 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0951-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0951-4