Abstract
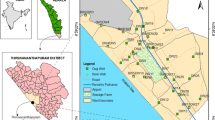
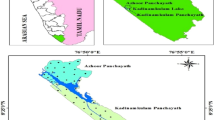
Groundwater from 33 monitoring of peripheral wells of Karachi, Pakistan were evaluated in terms of pre- and post-monsoon seasons to find out the impact of storm water infiltration, as storm water infiltration by retention basin receives urban runoff water from the nearby areas. This may increase the risk of groundwater contamination for heavy metals, where the soil is sandy and water table is shallow. Concentration of dissolved oxygen is significantly low in groundwater beneath detention basin during pre-monsoon season, which effected the concentration of zinc and iron. The models of trace metals shown in basin groundwater reflect the land use served by the basins, while it differed from background concentration as storm water releases high concentration of certain trace metals such as copper and cadmium. Recharge by storm water infiltration decreases the concentration and detection frequency of iron, lead, and zinc in background groundwater; however, the study does not point a considerable risk for groundwater contamination due to storm water infiltration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baehr, A. L., Stakackelberg, P. E., & Baker, R. J. (1999). Evaluation of the atmosphere as source of volatile organic compound in shallow groundwater. Water Resources Research, 35(1), 127–136. doi:10.1029/1998WR900030.
Balaram, B. (1992). Application of ICP-MS for the determination of trace elements in environmental samples. In Proceedings of the 9th international symposium of analytical techniques for fossil fuels and lubricants (pp. 333–335). University of Delhi and IOL, Faridabad.
Bowen, H. J. M. (1979). Environmental chemistry of the element (p. 333). London: Academic.
Burton, G. A. (1992). Sediment toxic city assessment(pp. 201–205). Miami, USA: Lewis.
Cox, J. H., Allick, S., & Be, E. (1998). Characterization of storm water contaminated sediment and debris for determining proper disposal methods. In Department of environmental protection, division of water facilities, 2600Blairstone Road. Tallahassee, Florida.
Dorsis, P., & Warren, L. J. (1980). Distribution of heavy metals between the minerals and organic debris in a contaminated marine sediment. In R. A. Baker (Ed.), Contaminants and sediments (vol. 1, pp. 119–139). Michigan, USA: Ann Arbor Science.
Fisher, D., Charles, E. G., & Baehr, A. L. (2003). Effects of storm water infiltration on quality of groundwater beneath retention and detention basins. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 129(5), 464–471. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2003)129:5(464).
Gazdar, M. N. (1989). Sustainable water resources management options in Indus basin. In Energy and resources center seminar (unpublished). University of California, Berkeley, USA.
Hathhorm, W. E., & Yonge, D. R. (1995). The assessment of groundwater pollution potential resulting from stormwater infiltration BMPs. Washington State Transportation Center (TRAC), Pullman Wash.
James, L. R., & Celeste, A. J. (2004). Geo chemical characterization of shallow groundwater in the Eutaw Aquifer, Montgomery, Alabama. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 40(4), 851–861. doi:10.1111/j.1752-1688.2004.tb01050.x.
Jones, P. H., & Jeffery, B. A. (1992). Environmental impact of road salting. In F. M. D’Itri (Ed.), Chemical deicers and the environment (pp. 1–116). Chelsea, Mich: Lewis.
Joseph, N. K., Anthony, G., Catherin, N., Johenson, M. K., & Joel, G. (2007). The seasonal and spatial variation of labile copper, iron, manganese, lead and zinc sediment fractions in lake Naivasha, Kenya. Lake and Reservoir. Research Management, 12(4), 303–313.
Khanif, Y. M., Van Clemput, O., & Baert, L. (1984). Interaction between nitrogen fertilization, rain fall, and groundwater pollution in sandy soil. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 22, 447–452. doi:10.1007/BF00282615.
Mark, S. L. (2003). Evaluation of selected heavy metal concentrations in soils of an urban storm water retention basin. A thesis presented to the graduate school of the University of Florida in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science University of Florida.
Mikkelsen, P. S., Hafliger, M., Ochs, M., Jacobsen, P., Tjell, J. C., & Boller, M. (1997). Pollution of soil and groundwater from infiltration of highly contaminated storm water—A case study. Journal of Water Science Technology, 36, 325–330. doi:10.1016/S0273-1223(97)00578-7.
Pankow, J. F., Thompson, N. R., Johnson, R. L., Bacher, A. L., & Zogorski, J. S. (1997). The urban atmosphere as a non point source for the transport of MTBE and other volatile organic compound to shallow groundwater. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(1), 2821–2828. doi:10.1021/es970040b.
Rahman, A., Lee, H. K., & Khan, M. A. (1997). Domestic water contamination in rapidly growing megaacities of Asia: case of Karachi, Pakistan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 44, 339–360. doi:10.1023/A:1005747732104.
Squillace, P. J., Zogorski, J. S., Wilber, W. G., & Price, C. V. (1996). Preliminary assessment of the occurance and possible sources of MTBE in groundwater in the united state, 1993–1994. Environmental Science & Technology, 30(5), 1721–1730. doi:10.1021/es9507170.
US EPA (n.d.) Injection wells: an introduction to their use, operation, and regulation. Ground water Protection Council, Oklahoma City, OK.
World Health Organization (WHO) (1993). Guidelines for drinking-water quality. Geneva.
Zubair, A. (1998). Doctoral thesis on groundwater pollution and its environmental impact on health in Karachi region–Pakistan. University of Ulster, Northern Ireland, UK.
Zubair, A., & Farooq, M. A. (2008). Assessments of infiltration rate and effects on water quality of selected infiltration media for use in storm water run off in Karachi–Pakistan. In Accepted for oral presentation in ninth international conference on modeling, monitoring and management of water pollution held on June 9–11, 2008. Alicant, Spain.
Zubair, A., Amanatullah, K., Gulraiz, H., & Mujeeb, A. (2000). The mechanism controlling the groundwater chemistry in the Karachi region, Sindh, Pakistan. Karachi University Journal of Science, 28(2), 49–56.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zubair, A., Hussain, A., Farooq, M.A. et al. Impact of storm water on groundwater quality below retention/detention basins. Environ Monit Assess 162, 427–437 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0807-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0807-y