Abstract
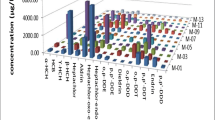
During the recent two decades, a remarkable drop in fertility rates has been noticed almost all over the world. A series of studies have showed that environmental factors had the primary role causing the observed adverse trends in the male reproductive health problems. Especially chlorinated hydrocarbons, for instance polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) and pesticides, could mimic or antagonize the effects of steroid hormones, like estrogens and androgens and possibly interfering with male reproductive capacity. Organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) (i.e. p.p’-DDT, endosulfan...) and PCBs are widespread used chemicals in agriculture and industry for different purposes all over the world. Although direct evidence is lacking, theoretical considerations and epidemiological evidence implicate these compounds as potential hazards to human and wildlife reproductive health. For this purpose, in this study adipose tissue samples have provided from healthy males which were diagnosed as infertile men living in Ankara, Turkey at least for 5 years. Residual levels of OCPs (α-BHC, β-BHC, γ-BHC, HCB, Endosulfan I, II, p,p’-DDE, and p,p’-DDT) and seven major persistent PCB congeners (PCB 28, 52, 101, 118, 138, 153, and 180) were measured in 25 infertile men and 21 healthy men’s adipose tissue samples by GC-ECD. Levels of OCPs and PCBs in adipose tissue of infertile men compared with those provided from controls. When the concentrations of each of the OCP were compared between the fertile and infertile groups, no statistical significance was obtained. Concentrations of each of the PCB congeners were compared between the fertile and infertile groups, no statistical significance was obtained (p > 0.05), except for 2,2’,5,5’-Tetrachlorobiphenyl (PCB 52) (p = 0.032) and 2,2’,3,4,4’,5,5’-heptachlorobiphenyl (PCB 180) (p = 0.017).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, H. R., Andersson, A. M., Arnold, S. F., Autrup, H., Barfoed, M., Beresford, N. A., et al. (1999). Comparison of short term estrogenicity tests for identification of hormone-disrupting chemicals. Environmental Health Perspectives, 107, 89–108. doi:10.2307/3434476.
Ayotte, P., Giroux, S., Dewailly, E., Hernández, A. M., Farias, P., Danis, R., et al. (2001). DDT spraying for malaria control and reproductive function in Mexican men. Epidemiology (Cambridge, Mass.), 12, 366–367. doi:10.1097/00001648-200105000-00022.
Barlas, N. E. (2002). Determination of organochlorine pesticide residues in water and sediment samples in inner Anatolia in Turkey. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 69, 236–242. doi:10.1007/s00128-002-0052-3.
Barlas, N., Cok, I., & Akbulut, N. (2006). The contamination levels of organochlorine pesticides in water and sediment samples in Uluabat Lake, Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 118, 383–391. doi:10.1007/s10661-006-1504-8.
Bhatia, R., Shiau, R., Petreas, M., Weintraub, J. M., Farhang, L., & Eskenazi, B. (2005). Organochlorine pesticides and male genital anomalies in the child health and development studies. Environmental Health Perspectives, 113, 220–224.
Burgaz, S., Atkham, A. E., & Karakaya, A. E. (1994). Organochlorine pesticide contaminants adipose tissue collected in Ankara (Turkey) 1991–1992. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 53, 501–508. doi:10.1007/BF00199018.
Bush, B., Bennett, A. H., & Snow, J. T. (1986). Polychlorobiphenyl congeners, p,p’-DDE, and sperm function in humans. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 15, 333–341. doi:10.1007/BF01066399.
Cok, I., & Satiroglu, H. M. (2004). Polychlorinated biphenyl levels in adipose tissue of primiparous women in Turkey. Environment International, 30, 7–10. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00140-5.
Cok, I., Bilgili, A., Ozdemir, M., Ozbek, H., Bilgili, N., & Burgaz, S. (1997). Organochlorine pesticide residues in human breast milk from agricultural regions of Turkey, 1995–1996. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 59, 577–582. doi:10.1007/s001289900518.
Cok, I., Bilgili, A., Yarsan, E., Bagci, C., & Burgaz, S. (1998). Organochlorine pesticide residue levels in human adipose tissue of residents of Manisa (Turkey), 1995–1996. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 61, 311–316. doi:10.1007/s001289900764.
Cok, I., Görücü, E., Satiroğlu, M. H., & Demircigil, G. C. (2003). Polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) levels in human milk samples from Turkish mothers. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 70, 41–45. doi:10.1007/s00128-002-0153-z.
Cok, I., Donmez, M. K., & Karakaya, A. E. (2004). Levels and trends of chlorinated pesticides in human breast milk from Ankara residents: Comparison of concentrations in 1984 and 2002. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 72, 522–529. doi:10.1007/s00128-004-0275-6.
Cok, I., Toprak, D., Durmaz, T. C., Demirkaya, E., & Kabukçu, C. (2005). Determination of organochlorine contaminants in human milk collected at Afyon, Turkey. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 1, 503–508.
Cok, I., Donmez, M. K., Satiroglu, H. M., Aydinuraz, B., Henkelmann, B., Kotalik, J., et al. (2007). Concentration of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, polychlorinated dibenzofurans and dioxin-like PCBs in human adipose tissue from Turkish men. Chemosphere, 66, 1955–1961. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.07.071.
Colborn, T., vom Saal, F. S., & Soto, A. M. (1993). Developmental effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals in wildlife and humans. Environmental Health Perspectives, 101, 378–384. doi:10.2307/3431890.
Connor, K., Ramamoorthy, K., Moore, M., Mustain, M., Chen, I., Safe, S., et al. (1997). Hydroxylated polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) as estrogens and antiestrogens: Structure–activity relationships. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 145, 111–123. doi:10.1006/taap.1997.8169.
Cooper, R. L., & Kavlock, R. J. (1997). Endocrine disruptors and reproductive development: A weight-of-evidence overview. The Journal of Endocrinology, 152, 159–166. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1520159.
Dallinga, J. W., Moonen, E. J., Dumoulin, J. C., Evers, J. L., Geraedts, J. P., & Kleinjans, J. C. (2002). Decreased human semen quality and organochlorine compounds in blood. Human Reproduction (Oxford, England), 17, 1973–1979. doi:10.1093/humrep/17.8.1973.
Den Hond, E., Roels, H. A., Hoppenbrouwers, K., Nawrot, T., Thijs, L., Vandermeulen, C., et al. (2002). Sexual maturation in relation to polychlorinated aromatic hydrocarbons: Sharpe and Skakkebaek’s hypothesis revisited. Environmental Health Perspectives, 110, 771–776.
Dwarka, S., Harrison, D. J., Hoodless, R. A., Lawn, R. E., & Merson, G. H. (1995). Organochlorine compound residues in human milk in the United Kingdom 1989–1991. Human and Experimental Toxicology, 14, 451–455. doi:10.1177/096032719501400511.
Faroon, O. M., Keith, S., Jones, D., & De Rosa, C. (2001). Effects of polychlorinated biphenyls on development and reproduction. Toxicology and Industrial Health, 17, 63–93. doi:10.1191/0748233701th097oa.
Flores-Luévano, S., Farías, P., Hernández, M., Romano-Riquer, P., Weber, J. P., Dewailly, E., et al. (2003). DDT/DDE concentrations and risk of hypospadias. Salud p’Ublica de M’Exico, 45, 431–438. doi:10.1590/S0036-36342003000600002.
Golden, R. J., Noller, K. L., Titus, E. L., Kaufman, R. H., Mittendorf, R., Stillman, R., et al. (1998). Environmental endocrine modulators and human health: An assessment of the biological evidence. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 28, 109–227. doi:10.1080/10408449891344191.
Guo, Y. L., Hsu, P. C., Hsu, C. C., & Lambert, G. H. (2000). Semen quality after exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls and dibenzofurans. Lancet, 356, 1240–1241. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02792-6.
Hanf, V., Behnisch, P., Korner, W., Sonntag, C. P., Tinneberg, H. R., & Hagenmaier, H. (1995). Concentrations and congener profiles of PCB in human preovulatory cervical mucus and effects on sperm motility in vitro. Organohalogen Compounds, 26, 155–159.
Hauser, R., Altshul, L., Chen, Z., Ryan, L., Overstreet, J., Schiff, I., et al. (2002). Environmental organochlorines and semen quality: Results of a pilot study. Environmental Health Perspectives, 110, 229–233.
Hauser, R., Chen, Z., Pothier, L., Ryan, L., & Altshul, L. (2003). The relationship between human semen parameters and environmental exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls and p,p’-DDE. Environmental Health Perspectives, 111, 1505–1511.
Hosie, S., Loff, S., Witt, K., Niessen, K., & Waag, K. L. (2000). Is there a correlation between organochlorine compounds and undescended testes? European Journal of Pediatric Surgery, 10, 304–309. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1072381.
Kelce, W. R., Stone, C. R., Laws, S. C., Gray, L. E., Kemppainen, J. A., & Wilson, E. M. (1995). Persistent DDT metabolite p,p ‘-DDE is a potent androgen receptor antagonist. Nature, 375, 581–585. doi:10.1038/375581a0.
Krauthacker, B., Kralj, M., Tkalcevic, B., & Reiner, E. (1986). Levels of β-HCH, HCB p,p’-DDE, p,p’-DDT and PCBs in human milk from a continental town in Croatia, Yugoslavia. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, 58, 69–74. doi:10.1007/BF00378542.
Longnecker, M. P., Klebanoff, M. A., Brock, J. W., Zhou, H., Gray, K. A., Needham, L. L., et al. (2002). Maternal serum level of 1,1-dichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethylene and risk of cryptorchidism, hypospadias, and polythelia among male offspring. American Journal of Epidemiology, 155, 313–322. doi:10.1093/aje/155.4.313.
Magnusdottir, E. V., Thorsteinsson, T., Thorsteinsdottir, S., Heimisdottir, M., & Olafsdottir, M. (2005). Persistent organochlorines, sedentary occupation, obesity and human male subfertility. Human Reproduction (Oxford, England), 20, 208–215. doi:10.1093/humrep/deh569.
Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry (1982) Registered pesticides in Turkey. Ankara: Zirai Mucadele ve Zirai Karantina Genel Mudurlugu.
Navas, J. M., & Segner, H. (1998). Antiestrogenic activity of anthropogenic and natural chemicals. Environental Science and Pollution Research, 5, 75–82. doi:10.1007/BF02986390.
Pauwels, A., Covaci, A., Weyler, J., Delbeke, L., Dhont, M., De Sutter, P., et al. (2000). Comparison of persistent organic pollutant residues in serum and adipose tissue in a female population in Belgium, 1996–1998. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39, 265–270. doi:10.1007/s002440010104.
Pines, A., Cucos, S., Ever-Handani, P., & Ron, M. (1987). Some organochlorine insecticide and polychlorinated biphenyl blood residues in infertile males in the general Israeli population of the middle 1980s. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 16, 587–597. doi:10.1007/BF01055815.
Roy, D., Palangat, M., Chen, C. W., Thomas, R. D., Colerangle, J., Atkinson, A., et al. (1997). Biochemical and molecular changes at the cellular level in response to exposure to environmental estrogen-like chemicals. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, 50, 1–29. doi:10.1080/009841097160573.
Rozati, R., Reddy, P. P., Reddanna, P., & Mujtaba, R. (2002). Role of environmental estrogens in the deterioration of male factor fertility. Fertility and Sterility, 78, 1187–1194. doi:10.1016/S0015-0282(02)04389-3.
Schlebusch, H., Wagner, U., van der Ven, H., Al-Hasani, S., Dietrich, K., & Krebs, D. (1989). Polychlorinated biphenyls: The occurrence of the main congeners in follicular and sperm fluids. Journal of Clinical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry. Zeitschrift fur Klinische Chemie und Klinische Biochemie, 27, 663–667.
Schoula, R., Hajslova’, J., Bencko, V., Poustka, J., Haladova’, K., & Vizek, V. (1996). Occurrence of persistent organochlorine contaminants in human milk collected in several regions of Czech Republic. Chemosphere, 33, 1485–1494. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(96)00287-1.
Sharpe, R. M. (1995). Another DDT connection. Nature, 375, 538–539. doi:10.1038/375538a0.
Silvestroni, L., & Palleschi, S. (1999). Effects of organochlorine xenobiotics on human spermatozoa. Chemosphere, 39, 1249–1252. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00192-7.
Skakkebaek, N. E., Rajpert-De Meyts, E., & Main, K. M. (2001). Testicular dysgenesis syndrome: An increasingly common developmental disorder with environmental aspects. Human Reproduction (Oxford, England), 16, 972–978. doi:10.1093/humrep/16.5.972.
Skakkebaek, N. E., Jorgensen, N., Main, K. M., Rajpert-De Meyts, E., Leffers, H., Andersson, A. M., et al. (2006). Is human fecundity declining? International Journal of Andrology, 29, 2–11. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2605.2005.00573.x.
Soto, A. M., Chung, K. L., & Sonnenschein, C. (1994). The pesticides endosulfan, toxaphene, and dieldrin have estrogenic effects on human estrogen-sensitive cells. Environmental Health Perspectives, 102, 380–383. doi:10.2307/3431626.
Toft, G., Hydbom, A. R., Tyrkiel, E., Shvets, M., Giwercman, A., Lindh, C. H., et al. (2006). Semen quality and exposure to persistent organochlorine pollutants. Epidemiology (Cambridge, Mass.), 17, 450–458. doi:10.1097/01.ede.0000221769.41028.d2.
Toppari, J., Larsen, J. C., Christiansen, P., Giwercman, A., Grandjean, P., Guillette, L. J. Jr, et al. (1996). Male reproductive health and environmental xenoestrogens. Environmental Health Perspectives, 104, 741–803. doi:10.2307/3432709.
Turgut, C. (2003). The contamination with organochlorine pesticides and heavy metals in surface water in Küçük Menderes River in Turkey, 2000–2002. Environment International, 29, 29–32. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00127-7.
Wagner, U., Schlebusch, H., van der Ven, H., van der Ven, K., Diedrich, K., & Krebs, D. (1990). Accumulation of pollutants in the genital tract of sterility patients. Journal of Clinical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry. Zeitschrift fur Klinische Chemie und Klinische Biochemie, 28, 683–688.
Weiss, J. M., Bauer, O., Blüthgen, A., Ludwig, A. K., Vollersen, E., Kaisi, M., et al. (2006). Distribution of persistent organochlorine contaminants in infertile patients from Tanzania and Germany. Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics, 23, 393–399. doi:10.1007/s10815-006-9069-6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çok, I., Durmaz, T.C., Durmaz, E. et al. Determination of organochlorine pesticide and polychlorinated biphenyl levels in adipose tissue of infertile men. Environ Monit Assess 162, 301–309 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0797-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0797-9