Abstract
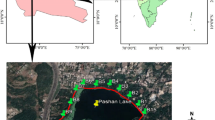
Periphytic diatoms were studied to evaluate the water quality of a newly created lake, formed by the enclosure of the formerly tidal Cardiff Bay (Wales, UK), and the effects of two inflowing rivers which drain densely populated and industrialised catchments. Seven sites in Cardiff Bay and two locations on the inflowing rivers were monitored for diatoms and water chemistry over 2 years. Water quality was assessed using a revised UK trophic diatom index (TDI) and new methods to determine ecological quality ratios and ecological status classes as required by the EU Water Framework Directive. Diatom assemblages reflected spatiotemporal variations in environmental conditions between the rivers and Cardiff Bay and within the bay. In the bay, diatoms reflected differences in river quality and possibly local pollution in certain areas of the lake. High values of the TDI indicated eutrophic to hypertrophic conditions in both rivers and in the bay and diatoms indicated poor ecological status.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ács, É., Reskóné, N. M., Szabó, K., Taba, G., & Kiss, K. T. (2005). Application of benthic diatoms in water quality monitoring of Lake Velence—recommendations and assignments. Acta Botanica Hungarica, 47, 211–223. doi:10.1556/ABot.47.2005.3-4.1.
Anderson, N. J., Rippey, B., & Stevenson, A. C. (1990). Change to a diatom assemblage in a eutrophic lake following point source nutrient re-direction: A paleolimnological approach. Freshwater Biology, 23, 205–217. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.1990.tb00266.x.
Andrews, D., & Gulson, J. (2002). Environmental regulation of the Cardiff Bay barrage. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers—Water and Maritime Engineering, 154, 89–92.
Azous, A. L., & Horner, R. R. (2000). Wetlands and urbanization: Implications for the future. London: Taylor & Francis.
Belton, T. J., Ponader, K. C., & Charles, D. F. (2004). Trophic diatom indices (TDI) and the development of site-specific nutrient criteria. Report New Jersey Center for Environmental Research, The State of New Jersey.
Bennion, H. (1995). Surface-sediment diatom assemblages in shallow, artificial, enriched ponds, and implications for reconstructing trophic status. Diatom Research, 10, 1–19.
Bennion, H., Juggins, S., & Anderson, N. J. (1996). Predicting epilimnetic phosphorus concentrations using an improved diatom-based transfer function and its application to lake management. Environmental Science & Technology, 30, 2004–2007. doi:10.1021/es9508030.
Best, S. (2004). A whim set in concrete. The campaign to stop the Cardiff Bay barrage. Bridgend, Seren.
Biggs, B. J. F., & Smith, R. A. (2002). Taxonomic richness of stream benthic algae: Effects of flood disturbance and nutrients. Limnology and Oceanography, 47, 1175–1186.
Blanco, S., Ector, L., & Bécares, E. (2004). Epiphytic diatoms as water quality indicators in Spanish shallow lakes. Vie et Milieu, 54, 71–79.
Bolton, S. (2006). A report on the distribution of the larvae of Chironomidae in Cardiff Bay 2004–2005. Cardiff: Final Report, Cardiff Harbour Authority.
Bolton, S. (2007). Monitoring of adult Chironomidae in Cardiff Bay 2001–2006. Cardiff: Final Report, Cardiff Harbour Authority.
Bowen, L. (2006). Patterns, causes and consequences of chlorophyll-a dynamics in Cardiff Bay. MSc Thesis, Department of Engineering, Cardiff University, Cardiff.
Bradbury, J. P., & Winter, T. C. (1976). Areal distribution and stratigraphy of diatoms in the sediments of Lake Sallie, Minnesota. Ecology, 57, 1005–1014. doi:10.2307/1941065.
Brönmark, C., & Hansson, L.-A. (2002). Environmental issues in lakes and ponds: Current state and perspectives. Environmental Conservation, 29, 290–307. doi:10.1017/S0376892902000218.
Cardiff Harbour Authority (2004–2007). Water quality monitoring reports. Cardiff: Cardiff Harbour Authority, Cardiff County Council.
Carpenter, S. R., & Cottingham, K. L. (1997). Resilience and restoration of lakes. Conservation Ecology [online], 1. http://www.consecol.org/vol1/iss1/art2/.
Carpenter, S. R., Caraco, N. F., Correll, D. L., Howarth, R. W., Sharpley, A. N., & Smith, V. H. (1998). Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecological Applications, 8, 559–568. doi:10.1890/1051-0761(1998)008[0559:NPOSWW]2.0.CO;2.
Choe, J. S., Bang, K. W., & Lee, J. H. (2002). Characterization of surface runoff in urban areas. Water Science and Technology, 45, 249–254.
Clarke, K. R., & Gorley, R. N. (2006). Primer v6, user manual/tutorial. Plymouth: PRIMER-E.
Clarke, K. R., & Warwick, R. M. (1994). Changes in marine communities: An approach to statistical analysis and interpretation. Plymouth: Plymouth Marine Laboratory.
Coley, A. R., & Clabburn, P. (2005). GIS visualisation and analysis of mobile hydroacoustic fisheries data: A practical example. Fisheries Management and Ecology, 12, 361–367. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2400.2005.00461.x.
Cook, D., Welch, E. B., Peterson, S., & Nichols, S. A. (2005). Restoration and management of lakes and reservoirs. London: Taylor & Francis.
Council of the European Communities (1991). Directive 1991/91/271/EEC of the European parliament and of the council of 21 May 1991 concerning urban wastewater treatment. Official Journal of the European Communities, L135, 40–52.
Council of the European Communities (2000). Directive 2000/60/EC of the European parliament and of the council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for community action in the field of water policy. Official Journal of the European Communities, L327, 1–72.
Council of the European Union (2006). Directive 2006/7/EC of 15 February 2006 concerning the management of bathing water quality and repealing Directive 76/160/EEC. Official Journal of the European Union, L64, 37–51.
Crompton, D. (2002). Cardiff Bay barrage. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers — Water & Maritime Engineering, 154, 81–88. doi:10.1680/maen.154.2.81.38645.
Davies, G., Butler, D., Mills, M., & Williams, D. (1997). A survey of ferruginous minewater impacts in the Welsh coalfields. Water and Environment Journal, 11, 140–146. doi:10.1111/j.1747-6593.1997.tb00105.x.
Dixit, S. S., Dixit, A. S., & Smol, J. P. (1992). Assessment of changes in lake water chemistry in Sudbury area lakes since preindustrial times. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 49, 8–16.
Douglas, M. S. V., & Smol, J. P. (1995). Periphytic diatom assemblages from high Arctic ponds. Journal of Phycology, 31, 60–69. doi:10.1111/j.0022-3646.1995.00060.x.
Environment Agency Wales (2007). Environmental reports. Cardiff Bay. http://www.environment-agency.gov.uk/regions/wales/.
Firth, J. N. M., Ormerod, S. J., & Prosser, H. J. (1995). The past, present and future of waste management in Wales: A case study of environmental problems in a small European region. Journal of Environmental Management, 44, 163–179.
Foster, I. D. L., Charlesworth, S. M., & Keen, D. H. (1991). A comparative study of heavy metal contamination and pollution in four reservoirs in the English Midlands, UK. Hydrobiologia, 214, 155–162. doi:10.1007/BF00050945.
Gomez, N. (1998). Use of epipelic diatoms for evaluation of water quality in the Matanza-Riachuelo (Argentina), a pampean plain river. Water Research, 3, 2029–2034. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00448-X.
Gomez, N. (1999). Epipelic diatoms from the Matanza-Riachuelo river (Argentina), a highly polluted basin from the pampean plain: Biotic indices and multivariate analysis. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 2, 301–309.
Gulati, R. D., & van Donk, E. (2002). Lakes in The Netherlands, their origin, eutrophication and restoration: State-of-the-art review. Hydrobiologia, 478, 73–106. doi:10.1023/A:1021092427559.
Guzkowska, M. A. J., & Gasse, F. (1990a). The seasonal response of diatom communities to variable water quality in some English urban lakes. Freshwater Biology, 23, 251–264. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.1990.tb00269.x.
Guzkowska, M. A. J., & Gasse, F. (1990b). Diatoms as indicators of water quality in some English urban lakes. Freshwater Biology, 23, 233–250. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.1990.tb00268.x.
Harris, E., Falconer, R. A., Kay, D., & Stapleton, C. (2002). Development of a modelling tool to quantify faecal indicator levels in Cardiff Bay. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers—Water and Maritime Engineering, 154, 129–135.
Hawes, I. H., & Smith, R. (1993). Effect of localised nutrient enrichment on the shallow epilithic periphyton of oligotrophic Lake Taupo. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 27, 365–372.
Hofmann, G. (1994). Aufwuchs-Diatomeen in Seen und ihre Eignung als Indikatoren der Trophie. In H. Lange-Bertalot (Ed.), Bibliotheca Diatomologica, (Vol. 30). Berlin: J. Cramer.
Hunter, P. D., & Gander, H. C. W. (2002). Cardiff Bay barrage: Planning and design. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers—Water and Maritime Engineering, 154, 117–128.
Hürlimann, J., & Schanz, F. (1988). Periphyton diatom communities and trophic states of three shallow lakes in the Pfynwald region of canton Valais, Schwitzerland. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, 78(Supplement), 351–371.
Johnes, P. J., Foy, R., Butterfield, D., & Haygarth, P. M. (2007). Land use scenarios for England and Wales: Evaluation of management options to support “good ecological status” in surface freshwaters. Soil Use and Management, 23(Suppl.1), 176–194. doi:10.1111/j.1475-2743.2007.00120.x.
Jongman, R. H. G., Ter Braak, C. J. F., & Van Tongeren, O. F. R. (1995). Data analysis in community and landscape ecology. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Jørgensen, S. E., Löffler, H., Rast, W., & Straškraba, M. (2005). Lake and reservoir management. Developments in water science (Vol. 54). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Jüttner, I., Rothfritz, H., & Ormerod, S. J. (1996). Diatoms as indicators of river quality in the Nepalese Middle Hills with consideration of the effects of habitat-specific sampling. Freshwater Biology, 36, 475–486. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2427.1996.00101.x.
Jüttner, I., Sharma, S., Dahal, B. M., Ormerod, S. J., Chimonides, P. J., & Cox, E. J. (2003). Diatoms as indicators of stream quality in the Kathmandu Valley and Middle Hills of Nepal and India. Freshwater Biology, 48, 2065–2084. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2427.2003.01138.x.
Kelly, M., Juggins, S., Guthrie, R., Pritchard, S., Jamieson, J., Rippey, B., et al. (2008). Assessment of ecological status in UK rivers using diatoms. Freshwater Biology, 53, 403–422.
Kelly, M. G. (1998). Use of the trophic diatom index to monitor eutrophication in rivers. Water Research, 32, 236–242. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00157-7.
Kelly, M. G., Adams, C., Graves, A. C., Jamieson, J., Krokowski, J., Lycett, E. B., et al. (2001). The trophic diatom index: A user’s manual. Revised edition. Bristol: Environment Agency R & D Technical Report E2/TR2.
Kelly, M. G., Juggins, S., Bennion, H., Burgess, A., Yallop, M., Hirst, H., et al. (2006). Use of diatoms for evaluating ecological status in UK freshwaters. Bristol: Science Report to the UK Environment Agency.
Kelly, M. G., Penny, C. J., & Whitton, B. A. (1995). Comparative performance of benthic diatom indices used to assess river water quality. Hydrobiologia, 302, 179–188.
Kelly, M. G., & Whitton, B. A. (1995). The trophic diatom index: A new index for monitoring eutrophication in rivers. Journal of Applied Phycology, 7, 433–444. doi:10.1007/BF00003802.
King, L., Barker, P., & Jones, R. I. (2000). Epilithic algal communities and their relationship to environmental variables in lakes of the English Lake District. Freshwater Biology, 45, 425–442. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2427.2000.00633.x.
Kitner, M., & Poulíčková, A. (2003). Littoral diatoms as indicators for the eutrophication of shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia, 506–509, 519–524. doi:10.1023/B:HYDR.0000008567.99066.92.
Krammer, K. (1997). Die cymbelloiden Diatomeen. Eine Monographie der weltweit bekannten Taxa. Bibliotheca Diatomologica, 36, 37. doi:10.1159/000119358.
Krammer, K. (2002). Cymbella. In H. Lange-Bertalot (Ed.), Diatoms of Europe (Vol. 3). Rugell: A.R.G. Gantner.
Krammer, K., & Lange-Bertalot, H. (1986–1991). Bacillariophyceae. In H. Ettl, G. Gärtner, J. Gerloff, H. Heynig, & D. Mollenhauer (Eds.), Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa (Vol. 2/1–2/4). Stuttgart: Gustav Fischer.
Lange-Bertalot, H. (2001). Navicula sensu stricto. 10 Genera Separated from Navicula sensu lato. Frustulia. In H. Lange-Bertalot (Ed.), Diatoms of Europe (Vol. 2), Rugell: A.R.G. Gantner.
Lim, D. S. S., Kwan, C., & Douglas, M. S. V. (2001). Periphytic diatom assemblages from Bathurst Island, Nunavut, Canadian High Arctic: An examination of community relationships and habitat preferences. Journal of Phycology, 37, 379–392. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8817.2001.037003379.x.
Lobo, E. A., Bes, D., Tudesque, L., & Ector, L. (2004). Water quality assessment of the Pardinho River, RS, Brazil, using epilithic diatom assemblages and faecal coliforms as biological indicators. Vie et Milieu, 54, 115–125.
Lobo, E. A., Katoh, K., & Aruga, Y. (1995). Response of epilithic diatom assemblages to water pollution in rivers in the Tokyo Metropolitan area, Japan. Freshwater Biology, 34, 191–204. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.1995.tb00435.x.
Mance, G. (1981). The quality of urban storm discharges—a review. Water Research Centre Environmental Protection Report 192-M, Stevenage.
Meriläinen, J. J., Hynynen, J., Palomäki, A., Mäntykoski, K., & Witick, A. (2003). Environmental history of an urban lake: A palaeolimnological study of Lake Jyväsjärvi, Finland. Journal of Paleolimnology, 30, 387–406. doi:10.1023/B:JOPL.0000007229.46166.59.
Mortberg, U. M., Balfors, B., & Knol, W. C. (2007). Landscape ecological assessment: A tool for integrating biodiversity issues in strategic environmental assessment and planning. Journal of Environmental Management, 82, 457–470. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.01.005.
Muscutt, A. D., & Withers, P. J. A. (1996). The phosphorus content of rivers in England and Wales. Water Research, 30, 1258–1268. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(95)00290-1.
Ormerod, S. J., & Jüttner, I. (2009). Water quality effects on Welsh rivers: A polluted past, an uncertain future? In D. D. Williams, & C. Duigan (Eds), The rivers of Wales. Leiden: Backhys Publishers (in press).
Passy, S. I. (2001). Spatial paradigms of lotic diatom distribution: A landscape ecology perspective. Journal of Phycology, 37, 370–378. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8817.2001.037003370.x.
Perry, J., & Vanderklein, E. (1996). Water quality. Management of a natural resource. Oxford: Blackwell Science.
Platt, N. J. (2002). Cardiff Bay barrage: Construction. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers – Water & Maritime Engineering, 154, 137–148. doi:10.1680/maen.154.2.137.38644.
Platt, R. H., Rowntree, R. A., & Muick, P. C. (1994). The ecological city: Preserving and restoring urban biodiversity. Amherst: University of Massachusetts Press.
Potapova, M. G., & Charles, D. F. (2003). Distribution of benthic diatoms in U.S. rivers in relation to conductivity and ionic composition. Freshwater Biology, 48, 1311–1328. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2427.2003.01080.x.
Potapova, M. G., Charles, D. F., Ponader, K. C., & Winter, D. M. (2004). Quantifying species indicator values for trophic diatom indices: A comparison of approaches. Hydrobiologia, 517, 25–41. doi:10.1023/B:HYDR.0000027335.73651.ea.
Poulíčková, A., Duchoslav, M., & Dokulil, M. (2004). Littoral diatom assemblages as bioindicators of lake trophic status: A case study from perialpine lakes in Austria. European Journal of Phycology, 39, 143–152. doi:10.1080/0967026042000201876.
Reichardt, E. (1999). Zur Revision der Gattung Gomphonema. Die Arten um G. affine/insigne, G. angustatum/micropus, G. acuminatum sowie gomphonemoide Diatomeen aus dem Oberoligozän in Böhmen. Rugell: A.R.G. Gantner.
Revitt, M., Shutes, B., & Scholes, L. (1999). The use of constructed wetlands for reducing the impacts of urban surface runoff on receiving water quality. In E. B. Ellis (Ed.), Impacts of urban growth on surface water and groundwater quality (IAHS Publication, 259). Wallingford: IAHS.
Ruggiu, D., Luglié, A., Cattaneo, A., & Panzani, P. (1998). Paleoecological evidence for diatom response to metal pollution in Lake Orta (N. Italy). Journal of Paleolimnology, 20, 333–345. doi:10.1023/A:1007929926526.
Sayer, C. D., & Roberts, N. (2001). Establishing realistic restoration targets for nutrient-enriched shallow lakes: Linking diatom ecology and paleoecology at the Attenborough Ponds, U.K. Hydrobiologia, 448, 117–142. doi:10.1023/A:1017597221052.
Schönfelder, I., Gelbrecht, J., Schönfelder, J., & Steinberg, C. E. W. (2002). Relationships between littoral diatoms and their chemical environment in northeastern German lakes and rivers. Journal of Phycology, 38, 66–82. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8817.2002.01056.x.
Simkhada, B., Jüttner, I., & Chimonides, P. J. (2006). Diatoms in lowland ponds of Koshi Tappu, Eastern Nepal—relationships with chemical and habitat characteristics. International Revue of Hydrobiology, 91, 574–593. doi:10.1002/iroh.200610852.
Smol, J. P. (2002). Pollution of lakes and rivers. A paleoenvironmental perspective. London: Arnold.
Spirn, A. W. (1984). The granite garden. New York: Basic Books.
Steinberg, C., & Schiefele, S. (1988). Biological indication of trophy and pollution of running waters. Z. Wasser-Abwasser-Forschung, 21, 227–234.
Stenger-Kovács, C., Buczkó, K., Hajnal, É., & Padisák, J. (2007). Epiphytic, littoral diatoms as bioindicators of shallow lake trophic status: Trophic diatom index for lakes (TDIL) developed for Hungary. Hydrobiologia, 589, 141–154. doi:10.1007/s10750-007-0729-z.
Stevenson, R. J. (1984). Epilithic and epipelic diatoms in the Sandusky River, with emphasis on species diversity and water pollution. Hydrobiologia, 114, 161–175.
Stoermer, E. F., & Smol, J. P. (1999). The diatoms: Applications for the environmental and earth sciences. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Ter Braak, C. J. F., & Šmilauer, P. (2002). Canoco reference manual and CanoDraw for Windows user’s guide. Software for canonical community ordination (version 4.5). Wageningen, České Budějovice: Biometris.
The Countryside Agency (2005). The countryside in and around towns. Wetherby: Countryside Agency Publications.
Van Dam, H., Mertens, A., & Sinkeldam, J. (1994). A coded checklist and ecological indicator values of freshwater diatoms from The Netherlands. Netherlands Journal of Aquatic Ecology, 28, 117–133. doi:10.1007/BF02334251.
Van Metre, P. C., Mahler, B. J., & Furlong, E. T. (2000). Urban sprawl leaves its PAH signature. Environmental Science & Technology, 34, 4064–4070. doi:10.1021/es991007n.
Vaughan, I. P., Newberry, C., Hall, D. J., Liggett, J. S., & Ormerod, S. J. (2008). Evaluating large-scale effects of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis on non-biting midges (Chironomidae) in a eutrophic urban lake. Freshwater Biology, 53, 2117–2128.doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2008.02043.x.
Vincent, W. F., Gibbs, M. M., & Spigel, R. H. (1991). Eutrophication process regulated by a plunging river inflow. Hydrobiologia, 226, 51–63. doi:10.1007/BF00007779.
Williams, A. T., & Simmons, S. L. (1999). Sources of riverine litter. The River Taff, South Wales, UK. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 112, 197–216. doi:10.1023/A:1005000724803.
Winter, J. G., & Duthie, H. C. (2000). Epilithic diatoms as indicators of stream total N and total P concentrations. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 19, 32–49. doi:10.2307/1468280.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jüttner, I., Chimonides, P.J. & Ormerod, S.J. Using diatoms as quality indicators for a newly-formed urban lake and its catchment. Environ Monit Assess 162, 47–65 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0775-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0775-2