Abstract
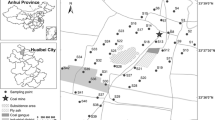
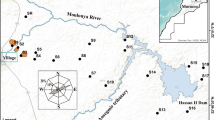
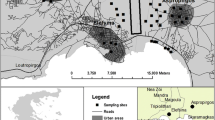
The availability of the five chemical fractions, i.e., exchangeable (F1), carbonate-bound (F2), Fe/Mn oxide-combined (F3), organic matter-complexed (F4), residual (F5), of three heavy metals (Cu, Zn, and Cd), has been investigated by way of a sequential extraction technique based on the characteristics of the coastal soils developed from alluvial deposits, in order to analyze the relationship of the formation and development of coastal soils. The results showed that F1 and F5 of Cu, Zn, and Cd accounted dominantly for 9.11%, 2.74%, and 20.37%, and for 39.49%, 45.18%, and 32.43% of total heavy metal contents, respectively, indicating the order of availability and mobility: Cd > Cu > Zn. F2, F3, and F4 of HMs also featured prominently in the behaviors of heavy metals. Random measurement errors from both sampling and analysis were demonstrated by SAX to be well within the control target of 20% and, therefore, of no impediment to the geochemical interpretation of the data. Significant positive correlation was found between certain fractions of heavy metals and some soil properties. Some negative correlation was also found. The findings were helpful to the soil remediation, fertility adjustment, and plant cultivation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloway, B. J. (1995). Heavy metal in soils (pp. 1–368). London: Blackie.
Alvarez, E. A., Mochon, M. C., Sanchez, J. C. J., & Rodriguez, M. T. (2002). Heavy metal extractable forms in sludge from wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere, 47, 765–775.
Andersson, A. (1975). Relative efficiency of nine different soil extractants. Swedish Journal of Agricultural Research, 5, 125–135.
Ashworth, D. J., & Alloway, B. J. (2004). Soil mobility of sewage sludge derived dissolved organic matter, copper, nickel and zinc. Environmental Pollution, 127, 137–144.
Berti, W. R., & Jacobs, L. W. (1996). Chemistry and phytotoxicity of soil trace elements from repeated sewage sludge applications. Journal of Environmental Quality, 25, 1025–1032.
Calace, N., De Paolis, F., D’Orazio, D., & Petronio, B. M. (1997). Metal speciation in Arno River sediments. Annali di chimica, 87, 743–751.
Chen, Y. X., Wang, K. X., Lin, Q., & Yang, Y. (2001). Effects of heavy metals on ammonification, nitrification and denitrification in maize rhizosphere. Pedosphere, 11, 115–122.
Chlopecka, A., Bacon, J. R., Wilson, M. J., & Kay, J. (1996). Forms of cadmium, lead and zinc in contaminated soils from southwest Poland. Journal of Environmental Quality, 25, 69–79.
Clemente, R., Escolar, A., & Bernal, M. P. (2006). Heavy metals fractionation and organic matter mineralization in contaminated calcareous soil amended with organic materials. Bioresource Technology, 97, 1894–1901.
Feng, G. Q. (2001). Chinese agricultural corporation: Shanghai. Beijing: Chinese Agriculture Press.
Fuentes, A., Llorens, M., Saez, J., Soler, A., Aguilar, M. I., Ortuno, J. F., et al. (2004). Simple and sequential extractions of heavy metals from different sewage sludges. Chemosphere, 54, 1039–1047.
Gu, P. Q., & Wu, Y. P. (2000). Analysis of climatic variation in Fengxian county during 40 years (from 1959 to 1999) and its rational development and utilization in agriculture. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai, 16, 13–18.
Gupta, A. K., & Sarita, S. (2006). Chemical fractionation and heavy metal accumulation in the plant of Sesamum indicum (L.) var. T55 grown on soil amended with tannery sludge: Selection of single extractants. Chemosphere, 64, 161–173.
He, M., Katsutoshi, S., Wang, G. Q., Chen, Z. H., Shu, Y., & Xu, J. J. (2003). Physico-chemical characteristics of the soils developed from alluvial deposits on Chongming Island in Shanghai, China. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 49, 223–229.
Hettiarachchi, G. M., Pierzynski, G. M., & Ransom, M. D. (2001). In situ stabilization of soil lead using phosphorus. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30, 1214–1221.
Hou, C. Q. (1992). Soils in Shanghai (pp. 1–332). Shanghai: Science and Technology Press.
Kaasalainen, M., & Yli-Halla, M. (2003). Use of sequential extraction to assess metal partitioning in soils. Environmental Pollution, 126, 225–233.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2001). Trace elements in soils and plants (pp. 1–335). Boca Raton: CRC.
Li, J. L., He, M., Sun, S. Q., Han, W., Zhang, Y. C., Mao, X. H., et al. (2008). Effect of the behavior and availability of heavy metals on the characteristics of the coastal soils developed from alluvial deposits. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0465-5.
Li, R. Y., Yang, H., Zhou, Z. G., Lu, J. J., Shao, X. H., & Jin, F. (2007). Fractionation of heavy metals in sediments from Dianchi Lake, China. Pedosphere, 17, 265–272.
Liu, G. S. (1996). Soil physico-chemical analysis and description of soil profiles (pp. 1–26). Beijing: Chinese Standard Press.
Lottermoser, B. G. (1997). Natural enrichment of top soils with chromium and other heavy metals in Port Macquire, New South Wales, Australia. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 35, 1165–1176.
Ma, L. Q., & Rao, G. N. (1997). Chemical fractionation of cadmium, copper, nickel, and zinc in contaminated soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 26, 259–264.
Ma, X. R., & Su, D. M. (2000). Manual of drugs and microbes (pp. 70–74). Beijing: Science Press.
Markus, J. A., & Mcbrathey, A. B. (1996). An urban soil study: Heavy metals in Globe. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 34, 453–465.
McGrath, S. P., Zhao, F. J., & Lombi, E. (2001). Plant and rhizosphere processes involved in phytoremediation of metal-contaminated soils. Plant Soil, 232, 207–214.
McLaren, R. G., Kanjanapa, K., Navasumrit, P., Gooneratne, S. R., & Ruchirawat, M. (2004). Cadmium in the water and sediments of the Chao Phraya River and associated waterways, Bangkok, Thailand. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 154, 385–398.
Mckeague, J. A., & Day, J. H. (1966). Dithionite and oxalate-extractable Fe and Al as aids in differentiating various classes. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 46, 13–22.
Norrström, A. C., & Jacks, G. (1998). Concentration and fractionation of heavy metals in roadside soils receiving de-icing salts. Science of the Total Environment, 218, 161–174.
Obrador, A., Mingot, J. I., Alvarez, J. M., & Rico, M. I. (1997). Metal mobility and potential bioavailability in organic matter-rich soil sludge mixtures: Effect of soil type and contact time. Science of the Total Environment, 206, 117–126.
Ramsey, M. H. (1993). Sampling and analytical quality control (SAX) for improved error estimation in the measurement of Pb in the environment using robust analysis of variance. Applied Geochemistry, 2, 149–153.
Richard, J. B., & Gregory, C. A. (1985). Applied regression analysis and experimental design. New York: Marcel Dekker.
Samuel, B. G., Neil, J. S., & Theresa, M. (2000). Using SPSS for Windows: Analyzing and understanding data. Upper Saddle River: Prentice.
Sanchez, G., Moyano, A., & Munez, C. (1999). Forms of cadmium, lead and zinc in polluted mining soils and uptake by plants (Soria Province, Spain). Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 30, 1385–1402.
Shi, W., Bischoff, M., Turco, R., & Konopka, A. (2002). Long-term effects of chromium and lead upon the activity of soil microbial communities. Applied Soil Ecology, 21, 169–177.
Shrivastava, S. K., & Banerjee, D. K. (2004). Speciation of metals in sewage sludge and sludge-amended soils. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 152, 219–232.
Sims, J. T., & Kline, J. S. (1991). Chemical fractionation and plant uptake of heavy metals in soil amended with co-compost sewage sludge. Journal of Environmental Quality, 20, 387–395.
Su, D. C., & Wong, J. W. C. (2004). Chemical speciation and phytoavailability of Zn, Cu, Ni and Cd in soil amended with fly-ash stabilized sewage sludge. Environment International, 29, 895–900.
Sun, B., Sun, H., & Zhang, T. L. (2004). Bio-environmental effects and index of remediation of multi-heavy metals polluted red soils. Environmental Science, 25, 104–110.
Tack, F. M. G., & Verloo, M. G. (1995). Chemical speciation and fractionation in soil and sediment heavy metal analysis: A review. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 59, 225–238.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C., & Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51, 844–851.
Tu, C., Zheng, C. R., & Chen, H. M. (2000). Effects of heavy metal pollution on potassium behavior in Typic Udic Ferrisol. Pedosphere, 10, 21–30.
Udom, B. E., Mbagwu, J. S. C., Adesodun, J. K., & Agbim, N. N. (2004). Distributions of zinc, copper, cadmium and lead in a tropical ultisol after long-term disposal of sewage sludge. Environment International, 30, 467–470.
Wu, Q. L., Yang, Y. A., & Xie, Z. M. (2000). Microelement & biological health (pp. 208–281). Guizhou: Science and Technology Press.
Xi, C. P. (1998). The Soils of China (pp. 1–1246). Beijing: Chinese Agriculture Press.
Zhang, Q. L., Shi, X. Z., Huang, B., Yu, D. S., Wang, H. J., Blombaeck, K., et al. (2005). Characteristics of spatial variability of soil available lead, zinc, copper and cadmium in a vegetable base in the suburbs of Nanjing. Soils, 37, 41–47.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., He, M., Han, W. et al. Availability and mobility of heavy metal fractions related to the characteristics of the coastal soils developed from alluvial deposits. Environ Monit Assess 158, 459–469 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0596-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0596-8