Abstract
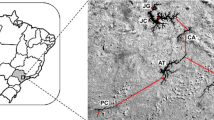
This paper presents an application of water quality mapping through real-time satellite and ground data. The Lake Beysehir which is the largest freshwater lake and drinking water reservoir in Turkey was selected as the study area. Terra ASTER satellite image is used as remote sensing data source for water quality mapping in addition to simultaneously performed in-situ measurements. Ground data is collected simultaneously with the ASTER overpass on June 09, 2005 over the Lake Beysehir. The spatial distribution map is developed by using multiple regression (MR) technique for water quality parameter, which is chlorophyll-a (chl-a). The results indicate that simultaneous ground and satellite remote sensing data are highly correlated (R 2 > 0.86). In the image processing step, geometric correction, image filtering and development of water quality map procedures are performed with the ERDAS Imagine and ArcGIS 9.0 software. The trophic status of Lake Beysehir is considered to be oligotrophic with an average 1.55 µg/l chl-a concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida-Filho, R., & Shimabukuro, Y. E. (2002). Digital processing of a Landsat-TM time series for mapping and monitoring degraded areas caused by independent gold miners, Roraima State, Brazil. Remote Sensing of Environment, 79, 42–50. doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(01)00237-1.
APHA, AWWA, WEF (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (21st edn.). Washington DC, USA: American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation.
Baban, S. M. J. (1993). Detecting water quality parameters in Norfolk Broads, UK, using Landsat imagery. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 14, 1247–1267. doi:10.1080/01431169308953955.
Baban, S. M. J. (1999). Use of remote sensing and geographical information systems in developing lake management strategies. Hydrobiologia, 395–396, 211–226. doi:10.1023/A:1017057820780.
Bilge, F., Yazici, B., Dogeroglu, T., & Ayday, C. (2003). Statistical evaluation of remotely sensed data for water quality monitoring. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 24, 5317–5326. doi:10.1080/0143116031000156828.
Carlson, R. E. (1977). A trophic state index for lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 22(2), 361–369.
Carlson, R. E., & Simpson, J. (1996). A coordinator’s guide to volunteer lake monitoring methods (96 pp.). Madison, Wisconsin: North American Lake Management Society.
Hedger, R. D., Atkinson, P. M., & Malthus, T. J. (2001). Optimizing sampling strategies for estimating mean water quality in lakes using geostatistical techniques with remote sensing. Lakes and Reservoirs: Research and Management, 6, 279–288. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1770.2001.00159.x.
Hellweger, F. L., Schlosser, P., Lall, U., & Weissel, J. K. (2004). Use of satellite imagery for water quality studies in New York Harbor. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 61, 437–448. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2004.06.019.
Jensen, J. R. (2000). Remote sensing of the environment: An earth resource perspective. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Kishino, M., Tanaka, A., & Ishizaka, J. (2005). Retrieval of Chlorophyll a, suspended solids, and colored dissolved organic matter in Tokyo Bay using ASTER data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 99, 66–74. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2005.05.016.
Kloiber, S. M., Brezonik, P. L., & Bauer, M. E. (2002a). Application of Landsat imagery to regional-scale assessments of lake clarity. Water Research, 36, 4330–4340. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00146-X.
Kloiber, S. M., Brezonik, P. L., Olmanson, L. G., & Bauer, M. E. (2002b). A procedure for regional lake water clarity assessment using Landsat multispectral data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 82, 38–47. doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00022-6.
Koponen, S., Pulliainen, J., Kallio, K., & Hallikainen, M. (2002). Lake water quality classification with airborne hyperspectral spectrometer and simulated MERIS data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 79, 51–59. doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(01)00238-3.
Lillesand, T. M., Johnson, W. L., Deuell, R. L., Lindstrom, O. M., & Meisner, D. E. (1983). Use of Landsat data to predict the trophic state of Minnesota lakes. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 49, 219–229.
Metternicht, G. I., & Zinck, J. A. (1998). Evaluating the information content of JERS-1 SAR and Landsat TM data for discrimination of soil erosion features. International Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 53, 143–153. doi:10.1016/S0924-2716(98)00004-5.
Nellis, M. D., Harrington, J. A., & Wu, J. (1998). Remote sensing of temporal and spatial variations in pool size, suspended sediment, turbidity, and Secchi depth in Tuttle Creek Reservoir, Kansas: 1993. Geomorphology, 21, 281–293. doi:10.1016/S0169-555X(97)00067-6.
Östlund, C., Flink, P., Strombeck, N., Pierson, D., & Lindell, T. (2001). Mapping of the water quality of Lake Erken, Sweden, from imaging spectrometry and Landsat Thematic Mapper. The Science of the Total Environment, 268, 139–154. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00683-5.
Reddy, M. A. (1997). A detailed statistical study on selection of optimum IRS LISS pixel configuration for development of water quality models. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 18, 2559–2570. doi:10.1080/014311697217477.
Sabins, F. F. (1996). Remote sensing: Principles and interpretation. New York: Freeman.
Steinman, A. D., Meeker, R. H., Rodusky, A. J., Davis, W. P., & Mcintire, C. D. (1997). Spatial and temporal distribution of algal biomass in a large subtropical lake. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, 139, 29–50.
Thiemann, S., & Kaufmann, H. (2000). Determination of chlorophyll content and trophic state of lakes using field spectrometer and IRS-1C satellite data in the Mecklenburg lake district, Germany. Remote Sensing of Environment, 73, 227–235. doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(00)00097-3.
Toutin, T. (2004). Geometric processing of remote sensing images: Models, algorithms and methods. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 25(10), 1893–1924. doi:10.1080/0143116031000101611.
Wang, F., Luoheng, H., Hsiang-te, K., & Roy, B. V. A. (2006). Applications of landsat-5 TM imagery in assessing and mapping water quality in Reelfoot Lake, Tennessee. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 27(23), 5269–5283. doi:10.1007/s001280202.
Wang, X. J., & Ma, T. (2001). Application of remote sensing techniques in monitoring and assessing the water quality of Taihu Lake. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 67, 863–870. doi:10.1080/01431160500191704.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nas, B., Karabork, H., Ekercin, S. et al. Mapping chlorophyll-a through in-situ measurements and Terra ASTER satellite data. Environ Monit Assess 157, 375–382 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0542-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0542-9