Abstract
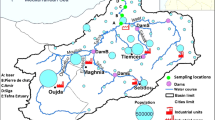
Physical and chemical parameters have been analyzed in water samples from a brackish water lagoon, Küçükçekmece, located on the western outskirts of Istanbul. Samples were collected every two months for a year from nine sampling stations. Of the parameters measured, temperature, pH, salinity, nitrate and phosphate showed changes when compared with the previously published data. The lagoon was found eutrophic as it was reported previously. Sulphate and COD levels were higher when compared with the standards established by the Turkish Water Pollution and Control Regulation. Additionally, concentrations of heavy metals (Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, Zn) in water and bottom sediments were measured and compared with the standards established by the Turkish Water Pollution and Control Regulation and with the previously published data. The results were analysed statistically with respect to location and any relationships between the concentration of the elements in corresponding water and sediment samples were examined. Principal Component Analysis of water samples allowed us to discriminate three areas affected mainly by heavy metal contamination, possibly due to industrial, commercial and/or urban activities. Generally, the concentrations of the heavy metals were higher at stations near the three estuaries, suggesting a direct influence of the three creeks on the pollution of the Küçükçekmece Lagoon. Although elevated levels of Cd were recorded in several water samples, it was not detected in sediment. On the other hand, a particularly high level of Cr pollution was recorded most of the water and sediment samples.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Acara, A., & Gözenalp, F. (1959). The northern lagoons of the Sea of Marmara. Proceedings of the General Fish Council for the Mediterranean, 5, 235–239.
APHA-AWWA-WEF (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington, DC: APHA, AWWA and WEF.
Bağdatlıoğlu, A. Ç. (1996). Egölem Modelinin Lagünlere Uygulanması. Master thesis, Istanbul Technical University, Turkey.
De Miguel, E., Llamas, J. F., Chacón, E., & Mazadiego, L. F. (1999). Sources and pathways of trace elements in urban environment: A multi-elemental qualitative approach. Science of the Total Environment, 235, 355–357.
Girija, T. R., Mahanta, C., & Chandramouli, V. (2007). Water quality assessment of an untreated effluent impacted urban stream: the Bharalu Tributary of the Brahmaputra river, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 130, 221–236.
Guildford, S. J., & Hecky, R. E. (2000). Total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and nutrient limitation in lakes and oceans: Is there a common relationship? Limnology and Oceanography, 45, 1213–1223.
Huang, B., Zhao, Y., Shi, X., Yu, D., Zhao, Y., Sun, W., et al. (2007). Source identification and spatial variability of nitrogen, phosphorus, and selected heavy metals in surface water and sediment in the riverine systems of a peri-urban interface. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part A, 42, 371–380.
Jackson, J. E. (1991). A user’s guide to principal components. New York: Wiley.
Mendoza, J., Botsford, J., Hernandez, J., Montaya, A., Saenz, R., Valles, A., et al. (2004). Microbial contamination and chemical toxicity of the Rio Grande. BMC Microbiology. Retrieved from http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2180/4/17.
Moyle, P. B., & Cech, J. J. (1996). Fishes: An introduction to ichthyology (3rd ed.). New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Müller, A. (2002). Organic carbon burial rates, and carbon and sulfur relationships in coastal sediments of the southern Baltic Sea. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 337–352.
Nixon, S. W. (1995). Coastal marine eutrophication: A definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia, 41, 199–219.
OECD and SWCSMH (2006). Research of the Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD) and the Soil and Water Conservation Society of Metro Halifax (SWCSMH). Retrieved from http://lakes.chebucto.org/TPMODELS/OECD/correlations.html#n-p.
Pehlivan, R., & Yilmaz, O. (2004). Geochemistry and mineralogy of bottom sediments in the Kuçukçekmece Lake, Istanbul, Turkey. ΓΕΟΧИМИЯ (Geochemistry), 9, 1–8.
Persaud, D., Jaagumagi, R., & Hayton, A. (1992). Guidelines for the protection and management of aquatic sediment quality in Ontario. Log 92-2309-067, PIBS, Queen’s Printer for Ontario.
Singh, R. P. (2001). Effect of wastewater disposal and extent of industrial pollution in and around Kanpur, Uttar Paradesh, India. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 60, 31–35.
SKKY (2003). Su Kirliliği Kontrolü Yönetmeliği. Water Pollution and Control Regulation.
Smith, V. H., Tilman, G. D., & Nekola, J. C. (1999). Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environmental Pollution, 100, 179–196.
SPSS Inc. (2006). SPSS release 15.0, USA.
Taner, M. Ü. (2007). Development of water quality index as a sustainability indicator in Küçükçekmece Water Shed, Istanbul. Master thesis, Boğaziçi University.
Topçuoğlu, S., Güngör, N., & Kırbaşoğlu, Ç. (1999). Physical and chemical parameters of Brackish Water Lagoon, Küçükçekmece Lake, in Northwestern Turkey. Toxicology and Environmental Chemistry, 69, 101–108.
Topçuoğlu, S., Kırbasoglu, Ç., Kut, D., Güngör, N., Ölmez, E., & Esen, N. (2001). Vertical particle flux in a brackish water lagoon, Küçükçekmece Lake, in northwestern Turkey. Rapp. Comm. int. Mer Médit., 36, 160.
Topçuoğlu, S., Kut, D., Esen, N., Güngör, N., Seddigh, E., & Küçükcezzar, R. (1998). Trace elements and radionuclides in sediments and biota from the Küçükçekmece Lake. Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer Médit., 35, 294–295.
Ünlü, M. Y., Topçuoğlu, S., & Anıl, Y. D. (1977). Radioecology of the Küçükçekmece Lagoon. ÇNAEM report no. 175, 1–94.
USEPA (1996). United States Environmental Protection Agency. Test methods for evaluating solid waste, SW 846 (3rd ed.). Office of solid waste and emergency response. Washington, DC.
van Duijin, C. (2000). Diseases of fishes. Mountain View, CA: Verisign Inc..
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altun, Ö., Saçan, M.T. & Erdem, A.K. Water quality and heavy metal monitoring in water and sediment samples of the Küçükçekmece Lagoon, Turkey (2002–2003). Environ Monit Assess 151, 345–362 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0276-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0276-8