Abstract
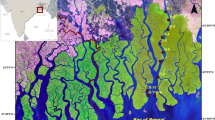
This paper presents a comprehensive account regarding concentration, distribution and possible sources of trace elements (Al, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, Zn) in 20–30 cm sediment cores (<63 μm particle size) collected at the confluence of the Ganges River and Bay of Bengal (Sunderban wetland, India). This work aims to evaluate the fluvio-marine and geochemical processes influencing the metal distribution. The most interesting features are the downward increase of concentrations of majority of the elements reaching overall maximum values at a depth of 10–15 cm observed in station Lot No.8 located along the main stream of the Ganges estuary as well as an overall elevated concentration of all the elements in the lower littoral zone. The interelemental relationship revealed the identical behaviour of elements during its transport in the estuarine environment. The overall variation in concentration can be attributed to differential discharge of effluents originating from industrial and agricultural as well as from domestic sewage. Arsenic exceeded effects range — low (ER — L) concentrations, implying occasional or frequent adverse biological effects. For Cu, Ni and Cr a smaller proportion of samples had exceeded the ER — L values indicating that the dataset would be suitable for future use in evaluating predictive abilities of SQGs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, N., & Subramanian, V. (1984). Erosion and sediment transport in the Ganges river basin (India). Journal of Hydrology, 69, 173–182.
Abu-Hilal, A. H., & Badran, M. M. (1990). Effect of pollution sources on metal concentration in sediment cores from the Gulf of Aqaba (Red Sea). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 21(4), 190–197.
Adams, W. J., Kimerle, R. A., & Barnett, R. A., Jr. (1992). Sediment quality and aquatic life assessment. Environmental Science and Technology, 26, 1865–1875.
Adriano, D. C. (1986). Trace elements in terrestrial environments. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Alagarsamy, R. (2006). Distribution and seasonal variation of trace metals in surface sediments of the Mandovi estuary, west coast of India. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 67, 333–339.
Alongi, D. M. (1996). The dynamics of benthic nutrient pools and fluxes in tropical mangrove forests. Journal of Marine Research, 54, 123–148.
Batley, G. E., & Brockbank, C. I. (1990). Impact of ocean disposal of dredged sediments from the RTA Glebe Island bridge site — A coastal sediment survey. CSIRO report, Center for Advanced Analytical Chemistry, Division of Coal and Energy Technology, Report FT/IR 050.
Bhattacharya, A., & Das, G. K. (2002). Dynamic geomorphic environment of Indian Sunderbans. In S. P. Basu (Ed.) Changing environmental scenario of the Indian subcontinent (pp. 284–298). Kolkata: Acb Publication.
Biksham, G., & Subramanian, V. (1988). Elemental composition of Godavari sediments (Central and Southern Indian Subcontinent). Chemical Geology, 70, 275–286.
Bouillon, S., Mohan, P. C., Sreenivas, N., & Dehairs, F. (2000). Sources of suspended organic matter and selective feeding by ooplankton in an estuarine mangrove ecosystem as traced by stable isotopes. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 208, 70–92.
Bryan, G. W., & Langston, W. J. (1992). Bioavailability, accumulation and effects of heavy metals in sediments with special reference to United Kingdom estuaries: a review. Environmental Pollution, 76, 89–131.
Burton Jr., G. A., & Scott, K. J. (1992). Sediment toxicity evaluation, their niche in ecological assessment. Environmental Science and Technology, 26, 2068–2075.
Caccia, V. G., Millero, F. J., & Palangues, A. (2003). The distribution of trace metals in Florida Bay sediments. Marine Pollution Bulletien, 46, 1420–1433.
Chatterjee, M., Silva Filho, E. V., Sarkar, S. K., Sella, S. M., Bhattacharya, A., Satpathy, K.K., et al. (2007). Distribution and possible source of trace elements in the sediment cores of a tropical macrotidal estuary and their ecotoxicological significance. Environment International, 33, 346–356.
Clark, R. B. (2001). Marine pollution p. 237. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Clark, C. S., Rampla, K. G., Thuppil, V., Chen, C. K., Clark, R., & Roda, S. (2006). The lead content of currently available new residential paint in several Asian countries. Environmental Research, 102(1), 9–12.
Cornwell, J. C., Conley, D. J., Owens, M., & Stevenson, J. C. (1996). Sediment chronology of the eutrophication of Chesapeake Bay. Estuaries, 19, 488–499.
Daoust, R. J., Moore, T. R., Chmura, G. L., & Magenheimer, J. F. (1996). Chemical evidence and anthropogenic influences in a Bay of Fundy salt-marsh. Journal of Coastal Research, 12, 520–532.
Decov, V. M., Subramanian, V., & Van Grieken, R. (1999). Chemical composition of riverine suspended matter and sediments from the Indian sub-continent. In V. Ittekot, V. Subramanian, & S. Annadurai (Eds.) Biogeochemistry of rivers in tropical South and Southeast Asia. Heft 82. SCOPE Sonderband (pp. 99–109). Hamburg: Mitteilugen aus dem Geologisch-Paläontolgischen Institut der Universität.
Dominik, J., & Stanley, D. J. (1993). Boron, beryllium and sulfur in Holocene sediments and peats of the Nile delta, Egypt: their use as indicators of salinity and climate. Chemical Geology, 104, 203–216.
Dyer, K. R. (1986). Coastal and estuarine sediment dynamics p. 342. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
El-Sayed, M. K. (1982). Effect of sewage effluent on the sediment of Nordasvatnet (a land-locked fjord), Norway. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 13, 85–88.
Folk, R. L., & Ward, W. C. (1957). Brazos River bar, a study of the significance of grain size parameters. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 27, 3–26.
Forstner, U. (1983). Assessment of metal pollution in rivers and estuaries. In I. Thomton (Ed.) Applied environmental geochemistry (pp. 395–423). London: Academic.
Gonneea, M. E., Paytan, A., & Herrera-Silveira, J. A. (2004). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 61, 211–227.
Huntzicker, J. J., Friedlander, S. K., & Davidson, C. I. (1975). Material balance for automobile-emitted lead in Los Angels Basin. Environmental Science & Technology, 9, 448–457.
Janaki-Raman, D., Jonathan, M. P., Srinivasalu, S., Armstron-Altrin, J. S., Mohan, S. P., & Ram-Mohan, V. (2007). Trace metal enrichments in core sediments in Muthupet mangroves, SE coast of India: Application of acid leachable technique. Environmental Pollution, 145(1), 245–257.
Jennerjahn, T. C., & Ittekkot, V. (2002). Relevance of mangroves for the production and deposition of organic matter along tropical continental margins. Naturwissenschaften, 89, 23–30.
Jones, B., & Turki, A. (1997). Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in surficial sediments from Tees Estuary, northeast England. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 34, 768–779.
Jung, H. J., Lee, C. B., Cho, Y. G., & Kong, J.-K. (1996). A mechanism for the enrichment of Cu and depletion of Mn in anoxic marine sediments, Banweol intertidal flat, Korea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 32(11), 782–787.
Kotmire, S. Y., & Bhosale, L. J. (1979). Some aspects of chemical composition of mangrove leaves and sediments. Mahasagar, Bulletin of the National Institute of Oceanography, 12, 149–151.
Krumbein, W. C., & Pettijohn, F. J. (1938). Manual of sedimentary petrology p. 549. New York: Plenum.
Lacerda, L. D., & Abrao, J. J. (1984). Heavy metals accumulation by mangrove and salt marsh intertidal sediments. Revista Brasileira de Botanica, 7, 49–52.
Lakshumanan, C. (2001). Modeling organic carbon deposition, degradation and preservation in sediments of Pichavaram mangrove wetlands, southeast coast of India. PhD thesis, Anna University, Chennai, India, 188 pp.
Lee, S. Y. (1995). Mangrove outwelling: a review. Hydrobiologia, 295, 203–212.
Liao, J. F. (1990). The chemical properties of the mangrove Solonchak in the northeast part of Hainan Island. The Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universities Sunyatseni (Supplement), 9(4), 67–72.
Marín, V., & Olivares, G. (1999). Estacionalidad de la productividad primaria en bahía Mejillones del Sur (Chile): Una aproximación proceso-functional. Revista Chilena de Historia Natural, 72, 629–641.
Monbet, P. (2006). Mass balance of lead through a small macrotidal estuary: the Morlaix River estuary (Brittany, France). Marine Chemistry, 98, 59–80.
Muller, G. (1979). Schermetalle in den sedimenten des Rheins-Veran-derungen seitt, 1971. Umschan, 79, 778–783.
Nohara, M., & Yokoto, S. (1978). The geochemistry of trace elements in pelagic sediments from the central Pacific basin. Journal of the Geological Society of Japan, 84(4), 165–175.
Nolting, R. F., Ramkema, A., & Everaarts, J. M. (1999). The geochemistry of Cu, Cd, Zn, Ni and Pb in sediment cores from the continental slope of Banc d’ Arquin (Mauritani). Continental Shelf Research, 19, 665–691.
Pantalu, V. R. (1966). Contribution to the study of biology and fishery of some estuarine fishes. Ph. D thesis, Calcutta University.
Pereira, M. E., Duarte, A. C., Millward, G. E., Abrue, S. N., & Vale, C. (1998). An estimation of industrial mercury stored in sediments of a combined area of the lagoon of Aveiro (Portugal). Water Science and Technology, 37(6/7), 125–130.
Periakali, P., Eswaramoorthi, S., Subramanian, S., & Jaisankar, P. (2000). Geochemistry of Pichavaram mangrove sediments, southeast coast of India. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 55, 387–394.
Ramanathan, A. L. (1997). Sediment characteristics of the Pichavaram mangrove environment, southeast coast of India. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 26, 319–322.
Ramanathan, A. L., Subramanian, V., Ramesh, R., Chidambaram, S., & James, A. (1997). Environmental geochemistry of the Pichavaram mangrove ecosystem (tropical), southeast coast of India. Environmental Geology, 37(3), 223–233.
Ramanathan, A. L., Vaithiyanathan, P., Subramanian, V., & Das, B. K. (1993). Geochemistry of the Cauvery estuary, East Coast of India. Estuaries, 16, 459–474.
Ramesh, R., Subramanian, V., & Van Grieken, R. (1990). Heavy metal distribution in sediments of Krishna river basin, India. Environmental Geology and Water Sciences, 15, 207–216.
Ray, A. K., Tripathy, S. C., Patra, S., & Sarma, V. V. (2006). Assessment of Godavari estuarine mangrove ecosystem through trace metal studies. Environment International, 32(2), 219–223.
Rodriguez, L., Marin, V., Farias, M., & Oyarce, E. (1991). Identification of an upwelling zone by remote sensing and in situ measurement. Mejillones del Sur Bay (Antofagasta, Chile). Scientia Marina, 55(3), 467–473.
Ruiz-Fernández, A. C., Páez-Osuna, F., Hillarie-Marcel, C., Soto-Jiménez, M., & Ghaleb, B. (2001). Principal component analysis applied to assessment of metal pollution from urban wastes in the Culiacan River estuary. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 67, 741–748.
Saha, M., Sarkar, S. K., & Bhattacharya, B. (2006). Interspecific variation in heavy metal body concentrations in biota of Sundarban mangrove wetland, northeast India. Environment International, 32, 203–207.
Salomons, W., & Förstner, U. (1984). Metals in the hydrocycle. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Salomons, W., Kerdlik, H., van Pagee, H., Klomp, R., & Schreur, A. (1988). Behaviour and impact assessment of heavy metals in estuary and coastal zone. In U. Seeliger, L. D. de Lacerda, & S. R. Patchineelam (Eds.) Metals in coastal environments of Latin America (pp. 159–198). New York: Springer-Verlag.
Santschi, P. H., Hohener, P., Benoil, G., & Bucholtz-ten Brink, M. (1990). Chemical processes at the sediment–water interface. Marine Chemistry, 30, 269–315.
Sarangi, R. K., Kathiresan, K., & Subramanian, A. N. (2002). Metal concentrations in five mangrove species of the Bhitarkanika, Orissa, east coast of India. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 31(3), 251–253.
Sarkar, S. K., Bhattacharya, B., & Das, R. (2003). Seasonal variations and inherent variability of selenium in marine biota of a tropical wetland ecosystem: Implications for bioindicator species.. Ecological Indicators, 2(4), 367–375.
Sarkar, S. K., Bhattacharya, B., Debnath, S., Bandopadhaya, G., & Giri, S. (2002). Heavy metals in biota from Sunderban wetland ecosystem, India: implications to monitoring the environmental assessment. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 5(2), 207–214.
Sarkar, S. K., Franciscovic-Bilinski, S., Bhattacharya, A., Saha, M., & Bilinski, H. (2004). Levels of elements in the surficial estuarine sediments of the Hugli river, northeast India and their environmental implications. Environment International, 30, 1089–1098.
Sarkar, S. K., Saha, M., Takada, H., Bhattacharya, A., Mishra, P., & Bhattacharya, B. (2007). Water quality management in the lower stretch of the river Ganges, east coast of India: An approach through environmental education. Journal for Cleaner Production, 15(16), 1459–1467.
Shaw, T. J., Gieskes, J. M., & Jahnke, R. A. (1990). Early digenesis in differing depositionsl environments. The response of transition metals in pore water. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 54, 1233–1246.
Silva-Filho, E. V., Wasserman, J. C., & Lacerda, L. D. (1998). History of metal inputs recorded on sediment cores from a remote environment. Ciencia y Cultura, 50(5), 374–376.
Stull, J. K., Baird, R. B., & Heesen, T. C. (1986). Marine sediment core profiles of trace constituents offshore of a deep waste-water outfall. Journal of the Water Pollution Control Federation, 58, 985–991.
Subramanian, V., Jha, P. K., & Van Grieken, R. (1988). Heavy metals in the Ganges estuary. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 19, 290–293.
Szefer, P., Kusak, A., Szefer, K., Glasby, G. P., Jankowska, H., Wolowicz, M., et al. (1998). Evaluation of anthropogenic influx of metallic pollutants into Puck Bay, Southern Baltic. Applied Geochemistry, 13, 293–304.
Szefer, P., & Skwarzec, B. (1988). Distribution and possible sources of some elements in the sediment cores of the southern Baltic. Marine Chemistry, 23, 109–129.
Tam, N. F. Y., & Wong, Y. S. (1993). Retention of nutrients and heavy metals in mangrove sediments receiving wastewater of different strengths. Environmental Technology, 14, 719–729.
Tam, N. F. Y., & Wong, Y. S. (1995). Retention and distribution of heavy metals in mangrove soils receiving wastewater. Environmental Pollution, 94, 283–291.
Tam, N. F. Y., & Wong, Y. S. (2000). Spatial variation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Hong Kong mangrove swamps. Environmental Pollution, 110, 195–205.
Tomlinson, D. C., Wilson, J. G., Harris, C. R., & Jeffrey, D. W. (1980). Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen, 33, 566.
Turkian, K. K., & Wedephol, K. H. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth crust. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America, 72, 175–192.
UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme). (1985). GESAMP: Cadmium, lead and tin in marine environment. United Nations Environment Programme: Regional Seas Reports and Studies No. 56, 90 pp.
Valette-Silver, H. J. (1993). The use of sediment cores to reconstruct historical trends in contamination of estuarine and coastal sediments. Estuaries, 16(3B), 577–588.
Valiela, I., & Cole, M. L. (2002). Comparative evidence that salt marshes and mangroves may protect seagrass meadows from land-derived nitrogen loads. Ecosystems, 5, 92–102.
Volkman, J. K., Rohjans, J., Rullkotter, J., Scholz-Bottcher, B. M., & Liebezeit, G. (2000). Sources and diagenesis of organic matter in tidal flat sediments from the German Wadden Sea. Continental Shelf Research1139–1158.
Waldichuk, M. (1985). Biological availability of metals to marine organisms. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 16, 7–11.
Walkey, A., & Black, T. A. (1934). An examination of the Dugtijaraff method for determining soil organic matter and proposed modification of the chronic and titration method. Soil Science, 37, 23–38.
Wang, C. K., Chu, K. H., Chen, Q. C., & Ma, X. I. (1995). Environmental research in pearl river and coastal areas. Guangzhou, China: Guangdang Higher Education Press.
Winkles, H. J., Vink, J. P. M., & Beurskens, J. E. M. (1993). Distribution and geochronology of priority pollutants in a large sedimentation area, River Rhine, the Netherlands. Applied Geochemistry, 52, 95–101.
Yim, M. W., & Tam, N. F. Y. (1999). Effects of waste-water borne heavy metals on mangrove plants and soil microbial activities. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 39, 176–186.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chatterjee, M., Massolo, S., Sarkar, S.K. et al. An assessment of trace element contamination in intertidal sediment cores of Sunderban mangrove wetland, India for evaluating sediment quality guidelines. Environ Monit Assess 150, 307–322 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0232-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0232-7