Abstract
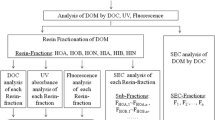
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) and its potential to form disinfection by-products (DBPs) during drinking water treatment raise challenges to water quality control. Understanding both chemical and physical characteristics of DOM in source waters is key to better water treatment. In this study, the DOM from four typical source waters in China was fractionated by XAD resin adsorption (RA) and ultrafiltration (UF) techniques. The trihalomethane formation potential (THMFP) of all fractions in the DOM were investigated to reveal the major THM precursors. The fraction distributions of DOM could be related to their geographical origins in a certain extent. The dominant chemical fraction as THM precursors in the DOM from south waters (East-Lake reservoir in Shenzhen and Peal rivers in Guangzhou) was hydrophobic acid (HoA). The size fraction with molecular weight (MW) <1 kDa in both south waters had the highest THMFP. The results of cluster analysis showed that the parameters of fractions including DOC percentage (DOC%), UV254%, SUVA254 (specific UV254 absorbance) and THMFP were better for representing the differences of DOM from the studied waters than specific THMFP (STHMFP). The weak correlation between SUVA254 and STHMFP for either size or XAD fractions suggests that whether SUVA254 can be used as an indicator for the reactivity of THM formation is highly dependent on the nature of organic matter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiken, G. R. (1984). Evaluation of ultrafiltration for determining molecular weight of fulvic acid. Environmental Science & Technology, 18(12), 978–981.
Aiken, G. R., Thurman, E. M., & Malcolm, R. L. (1979). Comparison of XAD macroporous resins for the concentration of fulvic acid from aqueous solution. Analytical Chemistry, 51(11), 1799–1803.
Amy, G. L., Collins, M. R., Kuo, C. J., & King, P. H. (1987). Comparing gel permeation chromatography and ultrafiltration for the molecular weight characterization of aquatic organic matter. Journal – American Water Works Association, 79(1), 43–49.
Bolto, B. A., Dixon, D. R., Eldridge, R. J., & King, S. J. (1998). The use of cationic polymers as primary coagulants in water treatment. In H. H. Hahn, E. Hoffmann, & H. Ødeguard (Eds.), Chemical water and wastewater treatment V (pp. 173–185). Berlin: Springer.
Chang, E. E., Chiang, P. C., Chao, S. H., & Lin, Y. L. (2006). Relationship between chlorine consumption and chlorination by-products formation for model compounds. Chemosphere, 64(7), 1196–1203.
Chang, E. E., Chiang, P. C., Ko, Y. W., & Lan, W. H. (2001). Characteristics of organic precursors and their relationship with disinfection by-products. Chemosphere, 44(5), 1231–1236.
Chiang, P. C., Chang, E. E., & Liang, C. H. (2002). NOM characteristics and treatabilities of ozonation processes. Chemosphere, 46(6), 929–936.
Chin, Y. P., Aiken, G. R., & Danielsen, K. M. (1997). Binding of pyrene to aquatic and commercial humic substances: The role of molecular weight and aromaticity. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(6), 1630–1635.
Chow, A. T., Gao, S., & Dahlgren, R. A. (2005). Physical and chemical fractionation of dissolved organic matter and trihalomethane precursors: A review. Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology, 54(8), 475–507.
Croue, J. P. (2004). Isolation of humic and non-humic NOM fractions: Structural characterization. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 92(1–3), 193–207.
Edzwald, J. K. (1993). Coagulation in drinking water treatment: Particles, organics and coagulants. Water Science and Technology, 27(11), 21–35.
Edzwald, J. K., Becker, W. C., & Wattier, K. L. (1985). Surrogate parameters for monitoring organic-matter and THM precursors. Journal – American Water Works Association, 77(4), 122–132.
Guo, L., & Santschi, P. H. (1996). A critical evaluation of cross-flow ultrafiltration technique for sampling colloidal organic carbon in seawater. Marine Chemistry, 55(1–2), 113–127.
Imai, A., Fukushima, T., Matsushige, K., & Kim, Y. H. (2001). Fractionation and characterization of dissolved organic matter in a shallow eutrophic lake, its inflowing rivers, and other organic matter sources. Water Research, 35(17), 4019–4028.
Imai, A., Matsushige, K., & Nagai, T. (2003). Trihalomethane formation potential of dissolved organic matter in a shallow eutrophic lake. Water Research, 37(17), 4284–4294.
Kitis, M., Karanfil, T., Wigton, A., & Kilduff, J. E. (2002). Probing reactivity of dissolved organic matter for disinfection by-product formation using XAD-8 resin adsorption and ultrafiltration fractionation. Water Research, 36(15), 3834–3848.
Leenheer, J. A. (1981). Comprehensive approach to preparative isolation and fractionation of dissolved organic carbon from natural waters and wastewaters. Environmental Science & Technology, 15(5), 578–587.
Leenheer, J. A., & Croue, J. P. (2003). Characterizing dissolved aquatic organic matter. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(1), 18A–26A.
Li, C. W., Benjamin, M. M., & Korshin, G. V. (2000). Use of UV spectroscopy to characterize the reaction between NOM and free chlorine. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(12), 2570–2575.
Martin-Mousset, B., Croue, J. P., Lefebvre, E., & Legube, B. (1997) Distribution and characterization of dissolved organic matter of surface waters. Water Research, 31(3), 541–553.
Panyapinyopol, B., Marhaba, T. F., Kanokkantapong, V., & Pavasant, P. (2005). Characterization of precursors to trihalomethanes formation in Bangkok source water. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 120(1–3), 229–236.
Rook, J. J. (1976). Haloforms in drinking water. Journal – American Water Works Association, 68(3), 168–172.
Sharp, E. L., Parsons, S. A., & Jefferson, B. (2006). Seasonal variations in natural organic matter and its impact on coagulation in water treatment. Science of the Total Environment, 363(1–3), 183–194.
APHA, AWWA, & WEF (1995). Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water (19th ed.). Washington, DC: APHA, AWWA, & WEF.
Weishaar, J. L., Aiken, G. R., Bergamaschi, B. A., Fram, M. S., Fujii, R., & Mopper, K. (2003). Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as and indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(20), 4702–4708.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Q., Wang, D., Wei, Q. et al. Size and resin fractionations of dissolved organic matter and trihalomethane precursors from four typical source waters in China. Environ Monit Assess 141, 347–357 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9901-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9901-1