Abstract
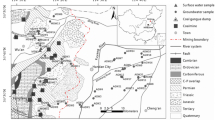
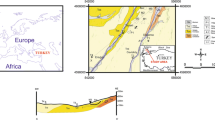
Mining subsidence pool is the special waters formed by coal mining, located near the mine. We understand the impact on these waters of the surrounding coal production activities and the electricity plant through research the content and characteristics of harmful trace elements in coal contained in these waters. Pb, Hg, Se and Cr these four trace elements increase 0.52, 0.78, 0.70 and 0.28% respectively in Datong mining subsidence pool from November 2004 to November 2006; the four elements increase 1.52, 1.23, 1.08 and 1.08% respectively in Xie’er mining subsidence pool; the four elements increase 1.01, 1.06, 1.02 and 0.83% respectively in Pansan mining subsidence pool. The absolute value of Pb, Hg, Se and Cr in mining subsidence pool is related with their background value, while the increase in their concentration and their environment of mine and electricity plant surrounded are closely linked.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng, H. (2001). Existent configuration of sulfur in coal spoils and transitional pathway in natural condition. Shandong Coal Science and Technology, 3, 18–19.
Gui, H. R., & Hu, Y. B. (2001). Study of shallow ground water in giggings city-exploitation and evaluation of shallow ground water in Huainan (pp. 48–80). Beijing: Coal Industry Press.
Meij, R. (1994). Trace element behavior in coal-fired power plants. Fuel Processing Technology, 39(1), 199–217.
Sun, J. X., & Jervis, R. E. (1988). Distributing character in combustion of trace elements in coal. Science in China Series A, 12, 1287–1294.
Wu, D. S. (2004). Leaching behavior of coal spoils and environmental impacts. Earth and Environment, 32, 55–59.
Yin, G. X. (1997). Geological disaster , prevention and cure in colliery environment (p. 109). Beijing: Coal Industry Press.
Zhang, J. Y., Ren, D. Y., Xu, D. W., & Zhao, F. H. (1999). Advances in the studies of selenium in coal. Coal Geology , & Exploration, 27, 16–18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Eq., Gui, Hr. Four trace elements contents of water environment of mining subsidence in the Huainan diggings, China. Environ Monit Assess 146, 203–210 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0072-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0072-x