Abstract
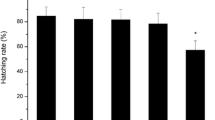
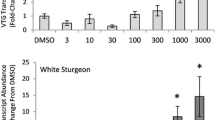
Growing concern over reproductive hormones in the environment demands sensitive and efficient methods by use of molecular biomarkers to detect these contaminants in oviparous vertebrates. In this study, a real-time quantitative RT-PCR was adopted to investigate the expressions of three estrogen-responsive genes, Vtg I, Vtg II and ERα, in hepatic and extrahepatic tissues of male adult zebrafish exposed to varying concentrations of 17β-estradiol (E2) for selected periods. Without exposure to E2, all the genes were expressed in the tissues of male controls with their levels being much lower than those in the respective tissues of female controls. The expressions of hepatic Vtg I and II mRNAs were induced significantly after 1-day exposure to E2 at as low as 0.25 μg L−1. Significant induction in the expression of hepatic ERα mRNA required a higher E2 concentration (≥0.5 μg L−1) and a longer exposure (≥2 days), suggesting that Vtg I and Vtg II are more sensitive to E2 exposure. The induction of Vtg mRNA in the skin of zebrafish was also significant following a short exposure (1 day) to low E2 concentration (0.25 μg L−1), with the levels of Vtg I and Vtg II mRNA being increased by 25 and 5 times, respectively. These results suggest that Vtg I mRNA is a highly sensitive biomarker for determining the estrogenic effects of E2 and that the skin of zebrafish may be an appropriate substitute for liver for such a determination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, L., Goto-Kazeto, R., Trant, J. M., Nash, J. P., Korsgard, B., & Bjerregaard, P. (2005). Short-term exposure to low concentrations of the synthetic androgen methyltestosterone affects vitellogenin and steroid levels in adult male zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquatic Toxicology, 76, 343–352.
Arukwe, A., Kullman, S. W., & Hinton, D. E. (2001). Differential biomarker gene and protein expressions in nonylphenol and estradiol-17 β treated juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology C-Toxicology & Pharmacology, 129, 1–10.
Arukwe, A., Knudsen, F. R., & Goksory, A. (1997). Fish zona radiate (egg shell) protein: A sensitive biomarker for environmental estrogens. Environmental Health Perspectives, 105, 418–422.
Barucca, M., Canapa, A., Olmo, E., & Regoli, F. (2006). Analysis of vitellogenin gene induction as a valuable biomarker of estrogenic exposure in various Mediterranean fish species. Environmental Research, 101, 68–73.
Chen, J. Y., Chen, J. C., & Wu, J. L. (2003). Molecular cloning and functional analysis of high-density lipoprotein-binding protein. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology B-Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 136, 117–130.
Desantis, S., Corriero, A., Cirillo, F., Deflorio, M., Brill, R., Griffiths, M., et al. (2005). Immunohistochemical localization of CYP1A, vitellogenin and Zona radiata proteins in the liver of swordfish (Xiphias gladius L.) taken from the Mediterranean Sea, South Atlantic, South Western Indian and Central North Pacific Oceans. Aquatic Toxicology, 71, 1–12.
Filby, A. L., & Tyler, C. R. (2005). Molecular characterization of estrogen receptors 1, 2a, and 2b and their tissue and ontogenic expression profiles in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Biology of Reproduction, 73, 648–662.
Funkenstein, B., Dyman, A., Levavi-Sivan, B., & Tom, M. (2004). Application of real time PCR for quantitative determination of hepatic vitellogenin transcript levels in the striped sea bream, Lithognathus mormyrus. Marine Environmental Research, 58, 659–663.
Hoyt, P. R., Doktycz, M. J., Beattie, K. L., & Greeley, M. S. (2003). DNA Microarrays detect 4-nonylphenol-induced alterations in gene expression during zebrafish early development. Ecotoxicology, 12, 469–474.
Kime, D. E., Nash, J. P., & Scott, A. P. (1999). Vitellogenesis as a biomarker of reproductive disruption by xenobiotics. Aquaculture, 177, 345–352.
Livak, K. J., & Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the \(2^{{ - {\text{ $ \Delta $ $ \Delta $ Ct}}}} \). method. Methods, 25, 402–408.
Menuet, A., Pellegrini, E., Anglade, I., Blaise, O., Laudet, V., Kah, O., et al. (2002). Molecular Characterization of three estrogen receptor forms in zebrafish: binding characteristics, transactivation properties, and tissue distributions. Biology of Reproduction, 66, 1881–1892.
Moncaut, N., Nostro, F. L., & Maggese, M. C. (2003). Vitellogenin detection in surface mucus of the South American cichlid fish Cichlasoma dimerus induced by estradiol-17 beta effects on liver and gonads. Aquatic Toxicology, 63, 127–137.
Petit, F. G., Metivier, R., Valotaire, Y., & Pakdel, F. (1999). Synergism between a half-site and an imperfect estrogen-responsive element, and cooperation with COUP-TFI are required for estrogen receptor to achieve a maximal estrogen-stimulation of rainbow trout ER gene. European Journal of Biochemistry, 259, 385–395.
Rose, J., Holbech, H., Lindholst, C., Norum, U., Povlsen, A., Korsgaard, B., et al. (2002). Vitellogenin induction by 17β-estradiol and 17a-ethinylestradiol in male zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology C-Toxicology & Pharmacology, 131, 531–539.
Shrader, E. A., Henry, T. R., Greeley, M. S., & Bradley, B. P. (2003). Proteomics in zebrafish exposed to endocrine disrupting chemicals. Ecotoxicology, 12, 485–488.
Tong, Y., Shan, T., Poh, Y. K., Yan, T., Wang, H., Lam, S. H., et al. (2004). Molecular cloning of zebrafish and medaka vitellogenin genes and comparison of their expression in respone to 17β estradiol. Gene, 328, 25–36.
Wang, H., Tan, J. T., Emelyanov, A., Korzh, V., & Gong, Z. Y. (2005). Hepatic and extrahepatic expression of vitellogenin genes in the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Gene, 356, 91–100.
Yamaguchi, A., Ishibashi, H., Kohra, S., Arizono, K., & Tominaga, N. (2005). Short-term effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on the expression of estrogen-responsive genes in male medaka (Oryzias latipes). Aquatic Toxicology, 72, 239–249.
Yamanaka, S., Arizono, K., Matsuda, Y., Soyano, K., Urushitani, H., Iguchi, T., et al. (1998). Development and application of an effective detection method for fish plasma vitellogenin induced by environmental estrogens. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 62, 1196–1200.
Versonnen, B. J., & Janssen, C. R. (2004). Xenoestrogenic effects of ethinylestradiol in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environmental Toxicology, 19, 198–206.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Y., Wang, W., Sheng, G.D. et al. Hepatic and extrahepatic expression of estrogen-responsive genes in male adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) as biomarkers of short-term exposure to 17β-estradiol. Environ Monit Assess 146, 105–111 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0063-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0063-y