Abstract
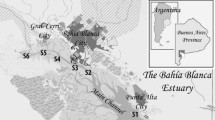
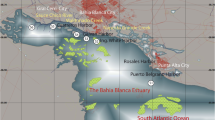
Systematic measurements of both Tributyltin (TBT) and Dibutyltin (DBT) in sediments along different locations in the inner zone of Bahía Blanca estuary were done. Two samples were taken near the main dry dock facility, at Puerto Belgrano naval base, in Argentina. TBT concentrations from non-detected to 170.3 ng Sn g−1 were measured in the inner region of the estuary, and higher one of 3,288 ng Sn g−1 near the dry dock at Puerto Belgrano. DBT values ranging between non-detected and 75.2 ng Sn g−1 were obtained along the principal channel, but extreme concentration of 1,645 ng Sn g−1 was measured at Puerto Belgrano. These values show that this estuary is affected by organotin pollution, mainly in areas of heavy shipyard activities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida, A. C., Wagener, A. L. R., Maia, C. B., & Miekeley, N. (2004). Speciation of organotin compounds in sediment cores from Guanabara Bay, Rio de Janeiro (Brazil) by gas chromatography-pulsed flame photometric detection. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 18, 694–704.
Alzieu, C. (1998). Tributyltin: Case study of a chronic contaminant in the coastal environment. Ocean & Coastal Management, 40, 23–36.
Alzieu, C. (2000). Impact of tributyltin on marine invertebrates. Ecotoxicology, 9, 71–76.
Association of Analytical Communities (AOAC) (1993). Peer verified methods program. Manual on policies and procedures. Arlington, VA: AOAC.
Bhosle, N. B., Garg, A., Jadhav, S., Harjee, R., Sawant, S. S., Venkat, K., et al. (2004). Butyltins in water, biofilm, animals and sediments of the west coast of India. Chemosphere, 57, 897–907.
Botté, S. (2005). El rol de la vegetación en el ciclo biogeoquímico de metales pesados en humedales del estuario de Bahía Blanca. PhD Thesis, Universidad Nacional del Sur, Bahía Blanca, 290 pp.
Brack, K. (2002). Organotin compounds in sediments from the Göta Älv estuary. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 135, 131–140.
Cardellicchio, N., Giandomenico, S., Decataldo, A., & Di Leo, A. (2001). Speciation of butyltin compounds in marine sediments with headspace solid phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Fresenius’ Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 369, 510–515.
Díez, S., Ábalos, M., & Bayona, J. M. (2002). Organotin contamination in sediments from the Western Mediterranean enclosures following 10 years of TBT regulation. Water Research, 36, 905–918.
Ikonomou, M. G., Fernandez, M. P., He, T., & Cullon, D. (2002). Gas chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry based method for the simultaneous determination of nine organotin compounds in water, sediment and tissue. Journal of Chromatography, 975, 319–333.
Maguire, R. J. (1996). The occurrence, fate and toxicity of tributyltin and its degradation products in fresh water environments. NWRI contribution N° 94–106. Canada: National Water Research Institute.
Marcovecchio, J., & Ferrer, L. (2005). Distribution and geochemical partitioning of heavy metals in sediments of the Bahia Blanca Estuary, Argentina. Journal of Coastal Research, 21, 826–834.
McFarland, M., England, S., & Hamilton, M. C. (1995). Assessment of the integrity of chemicals in environmental samples over an extended period of time. DOE FRAP 1996-27. Vancouver BC: Environment Canada, Pacific Region.
Morabito, R., Massanisso, P., & Quevauviller, P. (2000). Derivatization methods for the determination of organotin compounds in environmental samples. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 19, 113–119.
Morabito, R., & Quevauviller, P. (2002). Performances of spectroscopic methods for tributyltin (TBT) determination in the 10 years of the EU-SM&T organotin programme. Spectroscopy Europe, 14, 18–23.
Perillo, G. M. E., Pierini, J. O., Pérez, D. E., & Gómez, E. A. (2001). Suspended sediment circulation in semi-enclosed docks, Puerto Galván, Argentina. Terra et Aqua, 83, 13–20.
Ritsema, R., de Smaele, T., Moens, L., de Jong, A. S., & Donard, O. F. X. (1998). Determination of butyltins in harbor sediment and water by aqueous phase ethylation GC-ICP-MS and hydride generation GC-AAS. Environmental Pollution, 99, 271–277.
Stewart, C., & de Mora, S. J. (1990). A review of the degradation of Tri(n-butyl)tin in the marine environment. Environmental Technology, 11, 565–570.
UNEP/IOC/IAEA (1994). Determination of organotins in environmental samples. Reference Methods for Marine Pollution Studies N° 59, UNEP.
Zar, J. H. (1999). Biostatistical analysis (4th ed., p. 663). New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delucchi, F., Tombesi, N.B., Freije, R.H. et al. Butyltin Compounds in Sediments of the Bahía Blanca Estuary, Argentina. Environ Monit Assess 132, 445–451 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9547-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9547-4