Abstract
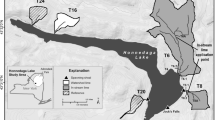
In-situ caged rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) studies reveal significant fish toxicity and fish stress in a river impacted by headwater acid rock drainage (ARD). Stocked trout survival and aqueous water chemistry were monitored for 10 days at 3 study sites in the Snake River watershed, Colorado, U.S.A. Trout mortality was positively correlated with concentrations of metals calculated to be approaching or exceeding conservative toxicity thresholds (Zn, Mn, Cu, Cd). Significant metal accumulation on the gills of fish stocked at ARD impacted study sites support an association between elevated metals and fish mortality. Observations of feeding behavior and significant differences in fish relative weights between study site and feeding treatment indicate feeding and metals-related fish stress. Together, these results demonstrate the utility of in-situ exposure studies for stream stakeholders in quantifying the relative role of aqueous contaminant exposures in limiting stocked fish survival.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R. O., & Neumann, R. M. (1996). Length, weight, and associated structural indices. In B. R. Murphy & D. W. Willis (Eds.), Fisheries techniques—2nd Edition, (pp. 447–482). Bethesda, Maryland, USA: American Fisheries Society.
Avenant-Oldewage, A., & Marx, H. M. (2000). Bioaccumulation of chromium, copper and iron in the organs and tissue of Clarias gariepinus in the Olifants river, Kruger National Park. Water South Africa, 26(4), 569–582.
Belanger, L. (2002). Source and effect of acid rock drainage in the Snake River watershed, Summit County, Colorado, Masters thesis. Boulder, CO, USA: The University of Colorado.
Bell, R. A., Ogden, N., & Kramer, J. R. (2002). The biotic ligand model and a cellular approach to class B metal aquatic toxicity. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology C, 133, 175–188.
Bernier, N. J., & Peter, R. E. (2001). The hypothalamic–pituitary–interrenal axis and the control of food intake in teleost fish. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology B, 129, 639–644.
Boyer, E. W., McKnight, D. M., Bencala, K. E., Brooks, P. D., Anthony, M. W., Zellweger, G. W., et al. (1999). Streamflow and water-quality characteristics for the upper Snake River and deer creek catchments in Summit County, Colorado: Water years 1980 to 1990, occasional paper 53. Boulder, CO, USA: Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research.
Camusso, M., Vigano, L., & Balestrini, R. (1995). Bioconcentration of trace metals in rainbow trout: A field study. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 31, 133–141.
Chadwick & Associates (1985). Fish populations of the Snake River, Tenmile Creek and West Tenmile Creek upstream of Dillon reservoir. Littleton, CO, USA.
Chappie, D. J., & Burton, G. A. (2000). Applications of aquatic and sediment toxicity testing in situ. Soil and Sediment Contamination, 9(3), 219–245.
Dethloff, G. M., Schlenk, D., Hamm, J. T., & Bailey, H. C. (1999). Alterations in physiological parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) with exposure to copper and copper/zinc mixtures. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 42, 253–264.
Farag, A. M., Boese, C. J., Woodward, D. F., & Bergman, H. L. (1994). Physiological changes and tissue metal accumulation in rainbow trout exposed to foodborne and waterborne metals. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 13, 2021–2029.
Farag, A. M., Skaar, D., Nimick, D. A., MacConnell, E., & Hogstrand, C. (2003). Characterizing aquatic health using salmonid mortality, physiology, and biomass estimates in streams with elevated concentrations of arsenic, cadmium, copper, lead, and zinc in the Boulder river watershed, Montana. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 132, 450–467.
Farag, A. M., Stansbury, M. A., Hogstrand, C., MacConnell, E., & Bergman, H. L. (1995). The physiological impairment of free-ranging brown trout exposed to metals in the Clark Fork river, Montana. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science, 52, 2038–2050.
Fey, D. L., Church, S. E., Unruh, D. M., & Bove, D. J. (2001). Water and sediment study of the Snake River watershed, Colorado, Oct. 9–12, 2001, Open-file report 02-0330. Denver, CO, USA: U.S. Geological Survey.
Grosell, M., & Wood, C. M. (2002). Copper uptake across rainbow trout gills: Mechanisms of atypical entry. Journal of Experimental Biology, 206, 1179–1188.
Guy, C. S., Blankenship, H. L., & Nielsen, L. A. (1996). Tagging and marking. In B. R. Murphy & D. W. Willis (Eds.), Fisheries Techniques—2nd Edition (pp. 353–383). Bethesda, Maryland, USA: American Fisheries Society.
Hansen, J. A., Lipton, J., Welsh, P. G., Morris, J., Cacela, D., & Suedkamp, M. J. (2002). Relationship between exposure duration, tissue residues, growth, and mortality in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) juveniles sub-chronically exposed to copper. Aquatic Toxicology, 58, 175–188.
Heath, A. G. (1987). Water pollution and fish physiology. Boca Raton, Florida, USA: CRC.
Horn, B. (2001). Biotoxicity report, Animas River aquatic toxicity profiles with existing water quality conditions: Appendix 6c. In W. Simon, P. Butler, & J. R. Owen, (Eds.), Use attainability analysis for the Animas River watershed, Animas River Stakeholders Group, p. 240, appendices, CD-ROM, http://www.waterinfo.org.arsg/.
HydroGeoLogic Inc., & Allison Geoscience Consultants Inc. (1999). MINTEQA2/PRODEFA2, a geochemical assessment model for Environmental systems: User manual supplement for version 4.0, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Athens, Georgia, USA.
Macdonald, A., Silk, L., Schwartz, M., & Playle, R. C. (2002). A lead–gill binding model to predict acute lead toxicity to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology C, 133, 227–242.
Marr, J. C. A., Bergman, H. L., Lipton, J., & Hogstrand, C. (1995). Differences in relative sensitivity of naïve and metals-acclimated brown and rainbow trout exposed to metals representative of the Clark Fork river, Montana. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science, 52, 2016–2030.
Mazeaud, M. M., Mazeaud, F., & Donaldson, E. M. (1977). Primary and secondary effects of stress on fish: Some new data with a general review. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 106, 201–212.
McKee, D. A., Ordner, M. T., Houston, D., & Lawrence, A. (1989). Easily constructed, inexpensive cage for aquatic animals, The Progressive Fish-Culturist 51, 166–167.
McKnight, D. M., & Bencala, K. E. (1990). The chemistry of iron, aluminum, and filtered organic material in 3 acidic, metal-enriched, mountain streams, as controlled by watershed and in-stream processes. Water Resources Research, 26(12), 3087–3100.
McKnight, D. M., & Feder, G. L. (1984). The ecological effect of acid conditions and precipitation of hydrous metal-oxides in a rocky-mountain stream. Hydrobiologia, 119(2), 129–138.
Mineral Policy Center (1997). Golden dreams, poisoned streams. Washington, D.C., USA.
Paquin, P. R., Gorsuch, J. W., Apte, S., Batley, G. E., Bowles, K. C., Campbell, P. G. C., et al (2002). The biotic ligand model: A historical overview. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology C, 133, 3–35.
Playle, R. C. (2004). Using multiple metal–gill binding models and the toxic unit concept to help reconcile multiple-metal toxicity results. Aquatic Toxicology, 67, 359–370.
Playle, R. C., Dixon, D. G., & Burnison, K. (1993). Copper and cadmium binding to fish gills: Modification by filtered organic carbon and synthetic ligands. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science, 50, 2667–2677.
Reid, S. D., & McDonald, D. G. (1991). Metal binding activity of the gills of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science, 48, 1061–1068.
Slack, W. T., & O’Connell, M. T. (1998). Design for a portable, modular stream enclosure/exclosure device. Journal of Freshwater Ecology, 13(2), 193–205.
Simpkins, D. G., Hubert, W. A., Del Rio, C. M., & Rule, D. C. (2003). Physiological responses of juvenile rainbow trout to fasting and swimming activity: Effects on body composition and condition indices. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 132(3), 576–589.
Sorensen, E. M. (1991). Metal Poisoning in Fish. Boston, MA, USA: CRC.
Summerfelt, R. C., & Smith, L. S. (1990). Anesthesia, surgery, and related techniques. In C. B. Schreck & P. B. Moyle (Eds.), Methods for Fish Biology (pp. 213–263). Bethesda, Maryland, USA: American Fisheries Society.
Todd, A. S., McKnight, D. M., & Duren, S. (2005). Water quality characteristics for the Snake River, North Fork of the Snake River, Peru creek, and Deer creek in Summit county, Colorado: 2001 to 2002, Occasional paper 57. Boulder, Colorado, USA: Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research.
Todd, A. S., McKnight, D. M., & Wyatt, L. (2003). Abandoned mines, mountain sports, and climate variability: Implications for the Colorado tourism economy. Eos, 84(38), 377–386.
Tytler, P., Tatner, M., & Findlay, C. (1990). The ontogeny of drinking in the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Journal of Fish Biology, 36, 867–875.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (1997). Ecological risk assessment for superfund: Process for designing and conducting ecological risk assessments, EPA-540-R-97-006. Washington, D.C., USA: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (2002). National Recommended Water Quality Criteria: 2002, EPA-822-R-02-047. Washington, D.C., USA: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Van Sickle, J., Baker, J. P., Simonin H. A., Baldigo, B. P., Kretser, W. A., & Sharpe, W. E. (1996). Episodic acidification of small streams in northeastern United States: Fish mortality in field bioassays. Ecological Applications, 6(2), 408–421.
Wedemeyer, G. A., Barton, B. A., & McLeay, D. J. (1990). Stress and acclimation. In C. B. Schreck & P. B. Moyle (Eds.), Methods for Fish Biology (pp. 451–489), Bethesda, Maryland, USA: American Fisheries Society.
Wendelaar Bonga, S. E. (1997). The stress response in fish. Physiological Reviews, 77, 591–625.
Wepener, V., van Vuren, J. H. J., & du Preez, H. H. (2001). Uptake and distribution of a copper, iron and zinc mixture in gill, liver and plasma of a freshwater teleost, Tilapia sparrmanii. Water South Africa, 27(1), 99–108.
Woodling, J. D. (1993). Survival and mortality of brown trout (Salmo trutta) exposed to in situ acutely toxic concentrations of cadmium and zinc, Ph.D. thesis. Boulder, Colorado, USA: University of Colorado.
Zitko, V., & Carson, W. G. (1976). Mechanism of effects of water hardness on lethality of heavy-metals to fish. Chemosphere, 5(5), 299–303.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Todd, A.S., McKnight, D.M., Jaros, C.L. et al. Effects of Acid Rock Drainage on Stocked Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): An In-Situ, Caged Fish Experiment. Environ Monit Assess 130, 111–127 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9382-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9382-7