Abstract
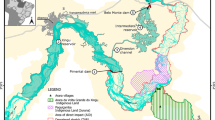
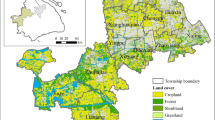
Currently, river landscape evaluations cannot be conducted by the general public, due to their lack of professional training. However, consulting professionals is time consuming and costly. The research conducted addresses both problems by (1) developing suitable criteria for assessing river environments, and (2) formulating a strategy for using the proposed criteria, thereby creating an effective method for river management by non-professionals. This research was carried out, in accordance with Visual Resource Management theory, at 12 survey sites along the ChungKang River. The landscape quality sequences acquired were then evaluated using a revised and simplified assessment model. The same process was repeated on the Touchien River to verify its feasibility. This research developed both specific criteria as well a method for evaluating river landscapes, which can be employed by non-professional river project managers. Ultimately, the aim of this research is to develop and promote sustainable river resource management.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baschak, L.A., & Brown R.D. (1995). An ecological framework for the planning, design and management of urban river greenways. Landscape and Urban Planning, 33, 211–225.
Brown, T., Keans, T., & Kaplan, S. (1986). Aesthetics and management: bridging the gap. Landscape and Urban Planning, 13, 1–10.
Buhyoff, G.J., Leuschner, W.A., & Arndt L.K. (1980). Replication of a scenic preference function. Forest Science, 26, 227–230.
Chen, K.T. (2001). A landscape ecology approach to establishing the evaluation method of river corridor. National Chung-Hsing University pp. 5–26.
Chen, S.Y., & Tang, S.B. (2002). A study of classification criteria for river landscapes – A case study of ChungKang River. In Proceedings of the 13th hydraulic engineering conference. July 30–31, 2002, Yunlin, Taiwan, Vol. 1, pp. 91–99.
Farina, A. (2000). Landscape ecology in action. Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers pp. 36–60.
Forman, R.T.T., & Godron, M. (1986). Landscape ecology. USA: Wiley pp. 33–190.
Gregory, K.J., & Davis R.J. (1993). The perception of riverscape aesthetics: an example from two Hampshire Rivers. Journal of Environment Management, 39, 171–185.
Hao, D.M. (1988). Introduction to ecology, 9th edition. Taipei, Taiwan: Foundation of Hsus, Inc pp. 311–336.
Huang, S.L. (2000). Ecological land use planning. Taipei, Taiwan: Chansbook pp. 69–122.
Kaltenborn, B.P., & Bjerke, T. (2002). Associations between environmental value orientations and landscape preferences. Landscape and Urban Planning, 59, 1–11.
Kuo, M. (2003). Green and blue network: the theory and practice of sustainable landscape planning. Taipei, Taiwan: Chansbook, Inc pp. 353–360
Leopold, L.B., & Marchand, M. (1968). On the quantitative inventory of the riverscape. Water Resources Research, 4, 709–717.
Meitner, M.J. (2004). Scenic beauty of river views in the Grand Canyon: relating perceptual judgments to locations. Landscape and Urban Planning, 68, 3–13.
National River Authority. (1993). River landscape assessment conservation – Methods and procedures, conservation. Bristol, UK: Technica1 Handbook 2.
Ou, S.J., & Lee, S.H. (1996). An application and review of landscape evaluation theory used in Taiwan. In The sustaining landscape of the 21st century, Topic III: Landscape Road Greenway and Greenway System, pp. 1–12.
Park, R.E. (1982). Human ecology. In: G. A. Theodorson (ed.), Urban patterns. USA: The Pennsylvania State University pp. 20–27.
Shannon, S., Smardon, R., & Knudson, M. (1995). Using visual assessment as a foundation for greenway planning in the St. Lawrence river valley. Landscape and Urban Planning, 33, 357–371.
Shlisky, A.J. (1993). Application of a landscape analysis approach at the river basin scale. The North Fork John Day Basin Restoration Project pp. 1–3.
Smardon, R.C. (1986). Review of agency methodology for visual project analysis. In R. C. Smardon, J. F. Palmer & J. P. Felleman (eds.), Foundations for visual project analysis. USA: Wiley pp. 141–166.
Smith, R.L., & Smith T.M. (2003). Elements of ecology, 5th edition. Menlo Park, Canada: The Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company, Inc pp. 177–191.
Taylor, J.G., Zube, E.H., & Sell, J.L. (1987). Landscape assessment and perception research methods. In R. B. Bechtel, & R. W. Marans (eds.), Methods in environmental and behavioral research. New York: Nostrand Reinhold pp. 361–393.
van den Berg, A.E., Vlek, C.A.J., & Coeterier, J.F. (1998). Group differences in the aesthetic evaluation of nature development plans: a multilevel approach. Journal of Environment and Psychology, 18, 141–157.
Wang, C.M. (1992). River ecology reservation, pp. 37–94. Taichung, Taiwan: National Museum of Natural Science.
Wang, H.L. (2004). The establishment of urban eco-network system with Taichung city as a case study. In The 41st IFLA world Congress, International Federation of Landscape Architecture pp. 28–58.
Water Resources Agency (WRA). (2005). Ministry of economic affairs. Report for Taiwan Rivers, http://www.wra.-gov.tw/ct.asp.
Water Resources Management and Policy Research Center (WRMPRC). (2005). Tankang university, college of engineering. River Resource in Taiwan, http://www.water.tku.edu.-tw/water_river.asp.
Wright, D.F. (1977). A site evaluation scheme for use in the assessment of potential nature reserves. Biology Conservation, 11, 293–305.
Yu, K.J. (1998). Landscape, culture, ecology and perception. Taipei, Taiwan: Garden Culture, Inc pp. 67–83.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, SY., Lin, JY. Developing a simplified river landscape assessment model: Examples from the Chungkang and Touchien rivers, Taiwan. Environ Monit Assess 127, 489–502 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9297-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9297-3