Abstract
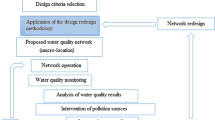
In order to resolve the spatial component of the design of a water quality monitoring network, a methodology has been developed to identify the critical sampling locations within a watershed. This methodology, called Critical Sampling Points (CSP), focuses on the contaminant total phosphorus (TP), and is applicable to small, predominantly agricultural-forested watersheds. The CSP methodology was translated into a model, called Water Quality Monitoring Station Analysis (WQMSA). It incorporates a geographic information system (GIS) for spatial analysis and data manipulation purposes, a hydrologic/water quality simulation model for estimating TP loads, and an artificial intelligence technology for improved input data representation. The model input data include a number of hydrologic, topographic, soils, vegetative, and land use factors. The model also includes an economic and logistics component. The validity of the CSP methodology was tested on a small experimental Pennsylvanian watershed, for which TP data from a number of single storm events were available for various sampling points within the watershed. A comparison of the ratios of observed to predicted TP loads between sampling points revealed that the model's results were promising.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes, P. L.: 1997, Row Crop Pollution Control in Northeast Kansas Kansas State University.
Evans, B. M.: 2002, ‘Development of an Automated GIS-Based Modeling Approach to Support Regional Watershed Assessments’, Ph.D. Thesis, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA.
Gburek, W. J. and Folmar, G. J.: 1999, ‘Flow and chemical contributions to streamflow in an upland watershed: A baseflow survey’, J. Hydrol. 217, 1–18.
Haith, D. A., Mandel, R. and Wu, R. S.: 1992, GWLF – Generalized Watershed Loading Functions, Version 2.0 – User's Manual, Department of Agricultural Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY.
Honisch, M., Hellmeier, C. and Weiss, K.: 2002, ‘Response of surface and subsurface water quality to land use changes’, Geoderma 105, 277–298.
Izurieta, J., G ómez, M. A., Evans, B. E. and Mijangos, M. A.: 2001, ‘Evaluación de la contaminación difusa en la cuenca del Río Apatlaco’, in XI Congreso Nacional de Irrigación. Simposio 5, Manejo Integral de Cuencas, September 19–21, Guanajuato, México.
Lee, K.-Y., Fisher, T. R., Jordan, T., Correll, D. L. and Weller, D.E.: 2000, ‘Modeling the hydrochemistry of the Choptank River basin using GWLF and GIS’, Biogeochemistry 49, 143–173.
McDowell, R. W., Sharpley, A. N., Beegle, D. B. and Weld, J. L.: 2001, ‘Comparing phosphorus management strategies at a watershed scale’, J. Soil Water Conserv. 56, 306–315.
Pionke, H. B., Gburek, W. J. and Sharpley, A. N.: 2000, ‘Critical source area controls on water quality in an agricultural watershed located in the Chesapeake Basin’, Ecol. Eng. 14, 325–335.
Strobl, R. O., Robillard, P. D., Shannon, R. D., Day, R. L. and McDonnell, A.J.: 2006, ‘A water quality monitoring network design methodology for the selection of critical sampling points. Part I, Environ. Monit. Assess. 112(1–3), 137–158.
Vieux, B. E. and Farajalla, N. S.: 1994, ‘Capturing the essential spatial variability in distributed hydrological modelling: Hydraulic roughness’, Hydrol. Process. 8, 221–236.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strobl, R.O., Robillard, P.D., Day, R.L. et al. A water quality monitoring network design methodology for the selection of critical sampling points: Part II. Environ Monit Assess 122, 319–334 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-0358-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-0358-4