Abstract.
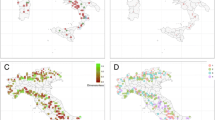
Since 1987 tree crown condition is surveyed annually in large parts of Europe mainly in terms of defoliation. The plot-wise means of defoliation from 1994 to 2000 were evaluated by General Linear Models (GLM) in order to describe country-specific levels of defoliation and age-trends. Additional runs with estimates for influences of insects and fungi were performed. The amount of variance of defoliation explained by country, age and its interaction was between 35% and 59% for the main tree species, except for Quercus ilex. Additionally, up to 10% could be explained by the inclusion of estimates for infestations by insects and fungi. Residuals of the GLMs were taken as a measure of forest condition not biased by country or age effects and interpreted as ‘preliminarily adjusted defoliation’ (PAD). PAD values were analysed using geostatistical methods. The modelled spatial autocorrelations were used for kriging. The resulting maps give an overview on regions with elevated defoliation, which may pinpoint regional causes of defoliation. The elimination of methodologically caused variance is a precondition of any cause–effect oriented analyses. The combination of explorative modelling and geostatistics will promote the choice of further promising predictors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aas, G.: 1998, ‘Morphologische und ökologische Variation mitteleuropäischer Quercus-Arten: Ein Beitrag zum Verständnis der Biodiversität’, IHW-Verlag, Eching, 221 S.
Anonymus: 1987, ‘Council Regulation (EEC) No. 1696/87 laying down certain detailed rules for the implementation of Council Regulation (EEC) No. 3528/86 (inventories, network, reports)’, Official Journal of the European Communities L161/1 of 22 June 1987, 22 p.
Anonymus: 2001, ‘Bericht über den Zustand des Waldes 2000’, BMVEL (Bundesministerium für Verbraucherschutz, Ernährung und Landwirtschaft) Bonn, 79 p.
Atkinson, P. M.: 1997, ‘Scale and Spatial Dependence’, in P. R. van Gardingen, G. M. Foody and P. J. Curran (eds), Scaling-up – from Cell to Landscape, Cambridge University Press Cambridge, 35–60.
Becher, G.: 1999, Waldzustandsanalyse mit multivariaten Verfahren Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 312 p.
Bille-Hansen, J. and Hansen, K.: 2001, ‘Relation between defoliation and litterfall in some Danish Picea abies and Fagus sylvatica stands’, Scand. J. For. Res. 16, 127–137.
Bussotti, F., Gerosa, G., Cenni, E., Cozzi, A., Ferretti, M., Bettini, D. and Nibbi, R.: 2001, ‘Le condizioni delle chiome nei boschi italiani: risultati 1997–2000 (Crown condition in Italian forests. Results 1997–2000)’, Materiali di lavoro della sezione di botanica forestale e ambientale, Dipartimento di Biologia Vegetale dell Universitá di Firenze, Edizioni Tipografia Coppini, 16 p.
Bussotti, F., Gerosa, G., Cenni, E., Cozzi, A., Ferretti, M., Bettini, D. and Nibbi, R.: 2003, ‘Crown condition surveys in Italian forests: Issues in reporting findings’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 85, 221–238.
Cressie, N.: 1991, Statistics for Spatial Data, Wiley New York.
De Vries, W., Reinds, G. J., Deelstra, H. D., Klap, J. M. and Vel, E. M.: 1999, ‘Intensive Monitoring of Forest Ecosystems in Europe. Technical Report 1999’, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, European Commission Geneva, Brussels, 173 p.
De Vries, W., Klap, J. and Erisman, J. W.: 2000, ‘Effects of environmental stress on forest crown condition in Europe. Part I: Hypotheses and approach to the study’, Water, Air, Soil Pollut 119, 317–333.
Dobbertin, M., Landmann, G., Pierrat, J. C. and Müller-Edzards, C.: 1997, ‘Quality of Crown Condition Data’, in C. Müller-Edzards, W. de Vries and J. W. Erisman (eds), Ten Years of Monitoring Forest Condition in Europe, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, European Commission Geneva, Brussels, pp. 7–22.
Dobbertin, M. and Mizoue, N.: 2000, ‘Mit dem Computerprogramm CROCO die Kronenverlichtung erfassen’, Eidgenössische Forschungsanstalt WSL. Informationsblatt Forschungsbereich Wald 2/2000, 5–6.
Dufrêne, E. and Bréda, N.: 1995, ‘Estimation of deciduous forests leaf area index using direct and indirect methods’, Oecologia 104, 156–162.
Ellenberg, H.: 1996, ‘Botanical aspects of landscape ecology with outlooks on forest dieback’, Progr. Botany 57, 1–16.
Ewald, J., Reuther, M., Nechwatal, J. and Lang, K.: 2000, ‘Monitoring von Schäden in Waldökosystemen des bayerischen Alpenraumes’, Bayerisches Staatsministerium für Landesentwicklung und Umweltfragen, Materialien 155, 235 p.
Ferretti, M.: 1998, ‘Potential and limitations of visual indices of tree condition’, Chemosphere 36, 1031–1036.
Ghosh, S., Landmann, G., Pierrat, J. C. and Müller-Edzards, C.: 1997, ‘Spatio-temporal Variation in Defoliation’, in C. Müller-Edzards, W. de Vries and J. W. Erisman (eds), Ten Years of Monitoring Forest Condition in Europe, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, European Commission Brussels, Geneva, pp. 35–50.
Göttlein, A. and Pruscha, H.: 1996, ‘Der Einfluß von Bestandeskenngrößen, Topographie, Standort und Witterung auf die Entwicklung des Kronenzustandes im Bereich des Forstamtes Rothenbuch’, Forstw. Cbl. 115, 146–162.
Gower, S. T. and Norman, J. M.: 1991, ‘Rapid estimation of leaf area index in conifer and broad-leafed plantations’, Ecology 72, 1896–1900.
Hendriks, C. M. A., de Vries, W. and van den Burg, J.: 1994, ‘Effects of acid deposition on 150 forest stands in the Netherlands’, DLO Winand Staring Centre for Integrated Land, Soil and Water Research, Wageningen, Report 69(2), 55 p.
Hornvedt, R.: 1997, ‘Relationship between visually assessed crown density and measured foliage density, and between visually assessed crown colour and measured chlorophyll content in mature Norway spruce’, Aktuelt fra Skogforsk (Ås) 10/97, 23–25.
Innes, J. L.: 1988, ‘Forest health surveys: Problems in assessing observer objectivity’, Can. J. For. Res. 18, 560–565.
Innes, J. L. and Boswell, R. C.: 1988, ‘Forest health surveys 1987. Part 2: analysis and interpretation’, For. Comm. Bull. London 79, 52.
Innes, J. L. and Boswell, R. C.: 1989, ‘Monitoring of forest condition in the United Kingdom 1988’, For. Comm. Bull. London 88, 70.
Innes, J. L. and Boswell, R. C.: 1990, ‘Reliability, presentation and relationships amongst data from inventories of forest condition’, Can. J. For. Res. 20, 790–799.
Innes, J. L., Landmann, G. and Mettendorf, B.: 1993, ‘‘Consistency of observations of forest tree defoliation in three European countries’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 25, 29–40.
Innes, J. L.: 1994, ‘The occurrence of flowering and fruiting on individual trees over 3 years and their effects on subsequent crown condition’, Trees 8, 139–150.
Jalkanen, R. E., Aalto, T. O., Innes, L. J., Kurkela, T. T. and Townsend, I. K. 1994, ‘Needle retention and needle loss of Scots pine in recent decades at Thetford and Alice Holt, England’, Can. J. For. Res. 24, 863–867.
Kallweit, R. E.: 1999, ‘Monitoring des Waldzustandes in Brandenburg. Das Level 2-Programm als Bestandteil der forstlichen Umweltkontrolle’, Beitr. Forstwirtsch. u. Landsch.ökol. 33, 97–102.
Kandler, O. and Innes, J. L.: 1995, ‘Air pollution and forest decline in central Europe’, Environ. Pollut. 90, 171–180.
Klap, J., Voshaar, J. O., de Vries, W. and Erisman, J. W.: 1997, ‘Relationships between Crown Condition and Stress Factors’, in C. Müller-Edzards, W. de Vries, J. W. Erisman (eds), Ten Years of Monitoring Forest Conditions in Europe, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, European Commission Brussels, Geneva, pp. 277–307.
Klap, J. M., Voshaar, J. O. H., de Vries, W. and Erisman, J. W.: 2000, ‘Effects of environmental stress on forest crown condition in Europe. Part IV: Statistical analysis of relationships’, Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 119, 387–420.
Landmann, G. and Bouhot-Delduc, L.: 1995, ‘Ground Monitoring of Crown Condition of Forest Trees in the French Mountains’, in: G. Landmann and M. Bonneau (eds), Forest Decline and Atmospheric Deposition Effects in the French Mountains Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 3–40.
Lorenz, M.: 1993, ‘Die Europäische Waldzustandserfassung’, Z. ökologie u. Naturschutz 2, 245–251.
Lorenz, M., Seidling, W., Mues, V., Becher, G. and Fischer, R.: 2001, Forest Condition in Europe: Results of the 2000 Large-Scale Survey, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, European Commission Geneva, Brussels, 103 p. + Annexes.
Mather, R., Freer-Smith, P. and Savill, P.: 1995, ‘Analysis of the changes in forest condition in Britain 1989 to 1992’, For. Comm. Bull. 116 HMSO, London.
Mizoue, N.: 1999, ‘Development of Image Analysis Systems for Crown Condition Assessment in Forest Health Monitoring’, Dissertation, CROCO, Kyushu University, 89 p.
Mues, V. and Seidling, W.: 2003, Evaluations of the International Cross-Calibration Courses 2001 and 2002, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, Geneva, 78 p.
Pannatier, Y.: 1996, VARIOWIN, Software for Spatial Data Analysis in 2D Springer, New York, 91 p.
Poikolainen, J. and Kubin, E.: 1997, ‘On the correlation between needle litterfall and defoliation in a Scots pine stand and in a Norway spruce stand’, Aktuelt fra Skogforsk (Ås) 10/97, 30–33.
Pouttu, A. and Dobbertin, M.: 2000, ‘Needle-retention and density patterns in Pinus sylvestris in the Rhone Valley of Switzerland: Comparing results of the needle-trace method with visual defoliation assessments’, Can. J. For. Res. 30, 1973–1982.
Ripley, B. D.: 1981, Spatial Statistics, Wiley and Sons New York.
Roloff, A.: 1989, ‘Kronenentwicklung und Vitalitätsbeurteilung ausgewählter Baumarten der gemäßigten Breiten’, Schriften aus der Forstlichen Fakultät der Univ. Göttingen und der Niedersächsischen Forstlichen Versuchsanstalt 89, 258 p.
Sander, C. and Eckstein, D.: 1994, ‘Reconstruction of the foliation of Picea abies by means of needle traces’, Scand. J. For. Res. 9, 311–315.
SAS Institute Inc.: 1990, SAS/STAT User’s Guide, 4th ed., SAS Institute Inc. Cary (USA) 1668 p.
Schöpfer, W. and Hradetzky, J.: 1984, ‘Der Indizienbeweis: Luftverschmutzung maßgebliche Ursache der Walderkrankung’, Forstw. Cbl. 103, 231–248.
Schütt, P. and Cowling, E. B.: 1985, ‘Waldsterben, a general decline of forests in central Europe: symptoms, development, and possible causes’, Plant Dis. 69, 548–558.
Seidling, W.: 2000, Multivariate Statistics within Integrated Studies in Tree Crown Condition in Europe – An Overview, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, European Commission Geneva, Brussels, 56 p. + Annexes.
Seidling, W.: 2001, Integrative Studies on Forest Ecosystem Conditions: Multivariate Evaluations on Tree Crown condition for Two Areas with Distinct Deposition Gradients, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, European Commission, Flemish Community Geneva, Brussels, Ghent, 88 p.
Solberg, S.: 1999, ‘Crown density changes of Norway spruce and the influence form increased age on permanent plots in Norway during 1988–97’, Eur. J. For. Path 29, 219–230.
Strand, G. H.: 1996, ‘Detection of observer bias in ongoing forest health monitoring programmes’, Can. J. For. Res. 26, 1692–1696.
Ulrich, B., Mayer, R. and Khanna, P. K.: 1980, ‘Chemical changes due to acid precipitation in a loess-derived soil in central Europe’, Soil Sci. 130, 193–199.
UNECE (United Nations Economic Commission for Europe) 1998, Manual on Methodologies and Criteria for Harmonized Sampling, Assessment, Monitoring and Analysis of the Effects of Air Pollution on Forests, UNECE Hamburg, Geneva.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SEIDLING, W., MUES, V. STATISTICAL AND GEOSTATISTICAL MODELLING OF PRELIMINARILY ADJUSTED DEFOLIATION ON AN EUROPEAN SCALE. Environ Monit Assess 101, 233–247 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-9304-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-9304-0