Abstract
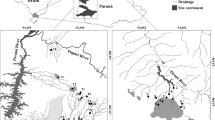
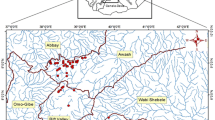
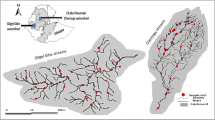
The sensitivity of eleven metrics using macroinvertebrate assemblages were evaluated in an environmental gradient in a tropical river in south-east Brazil. Eight sites were sampled in an altitudinal range of 160−650 m.a.s.l. during 1999 (April and August) and 2000 (February). Four substrates were sampled at each site: riffle litter, pool litter, stony substrates and sediment. Correspondence Analysis indicated that assemblages were primarily more influenced by physical changes (like deforestation and erosion processes) than the water chemistry. The sensitivity of each metric was evaluated through the application of box-and-whisker plot method by its power to assess impairment (metrics should be able to discriminate reference sites from impaired sites) and natural variability (metrics should not discriminate two reference sites). Metrics that failed in at least one of the above premises were not considered as sensitive. In this study, the most sensitive metrics were Shannon index, BMWP-ASPT, %_EPT, and relative abundance of EPT to Chironomidae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alba-Tercedor, J. and Sanchez-Ortega, A.: 1988, ‘Un método rápido y simple para evaluar la calidad biológica de aguas corrientes basado en el de Hellawell (1978)’, Limnética 4, 51–56.
Angrisano, E. B.: 1995, ‘Insecta Trichoptera’, In: E. C. Lopretto and G. Tell (eds.), Ecossistemas de Aguas Continentales: metodologias para su estudio, vol. III, Ediciones Sur La Plata Argentina, pp. 1199–1237.
Armitage, P. D., Moss, D., Wright, J. F. and Furse, M. T.: 1983, ‘The performance of a new biological water quality score system based on macroinvertebrates over a wide range of unpolluted running-water sites’, Water Res. 17(3): 333–347.
Baptista, D. F., Dorvillé, L. F. M., Buss, D. F. and Nessimian, J. L.: 2001, ‘Spatial and temporal organization of aquatic insects assemblages in the longitudinal gradient of a tropical river’, Revista Brasileira de Biologia 61(2), 295–304.
Barbour, M. T., Gerritsen, J., Griffith, G. E., Frydenborg, R., McCarron, E., White, J. S. and Bastian, M. L.: 1996, ‘A framework for biological criteria for Florida streams using macroinvertebrates’, J. N. Amer. Benthol. Soc. 15(2), 185–211.
Barton, D. R.: 1992, ‘A comparison of sampling techniques and summary indices for assessment of water quality in the Yamaska River, Quebec, based on benthic macroinvertebrates’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 21, 225–244.
Cairns, J. Jr., McCormick, P. V. and Niederlehner, B. R.: 1993, ‘A proposed framework for developing indicator of ecosystem health’, Hydrobiologia 263, 1–44.
Cao, Y., Bark, A. W. and Williams, W. P.: 1996, ‘Measuring the responses of macroinvertebrate communities to water pollution: A comparison of multivariate approaches, biotic and diversity indices’, Hydrobiologia 341, 1–19.
Carvalho, A. L. and Calil, E. R.: 2000, ‘Chaves de identificação para as famílias de Odonata (Insecta) ocorrentes no Brasil, adultos e larvas’, Papéis Avulsos Zool. 41(15), 223–241.
Jacobsen, D.: 1998, ‘The effect of organic pollution on the macroinvertebrate fauna of Ecuadorian highland streams’, Arch. Hydrobiol. 143(2), 179–195.
Junqueira, V. M. and Campos, S. C. M.: 1998, ‘Adaptation of the “BMWP” method for water quality evaluation to Rio das Velhas watershed (Minas Gerais, Brazil)’, Acta Limnol. Brasiliensia 10(2), 125–135.
Karr, J. R.: 1981, ‘Assessment of biotic integrity using fish communities’, Fisheries 6(6), 21–27.
Kerans, B. L., Karr, J. R. and Ahlstedt, S. A.: 1992, ‘Aquatic invertebrate assemblages: Spatial and temporal differences among sampling protocols’, J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 11, 377–390.
Kurtz, J. C., Jackson, L. E. and Fisher, W. S.: 2001, ‘Strategies for evaluating indicators based on guidelines from the Environmental Protection Agency’s Office of Research and Development’, Ecol. Indicators 1, 49–60.
Lemly, A. D.: 1982, ‘Modification of benthic insect communities in polluted streams: Combined effects of sedimentation and nutrient enrichment’, Hydrobiologia 87, 229–245.
Magurran, A. E. (ed.): 1991, Ecological Diversity and Its Measurement. Chapman & Hall London UK.
Merritt, R. W. and Cummins, K. W. (eds.): 1996, An Introduction to the Aquatic Insects of North America, 3rd ed., Kendall/Hunt Publishing Dubuque IA, EUA.
Nieser, N. and de Melo, A. L.: 1997, Os heterópteros aquáticos de Minas Gerais. Editora UFMG, Belo Horizonte Brasil.
Pinder, L. C. V., Ladle, M., Gledhill, T., Bass, J. A. B. and Matthews, A. M.: 1987, ‘Biological surveillance of water quality. 1. A comparison of macroinvertebrate surveillance methods in relation to assessment of water quality, in a chalk stream’, Arch. Hydrobiol. 109, 207–226.
Parsons, T. R., Maita, Y. and Lalli, C. M.: 1984, A Manual of Chemical and Biological Methods for Seawater Analysis. Pergamon Press Oxford UK.
Plafkin, J. L., Barbour, M. T., Porter, K. D., Gross, S. K. and Hughes, R. M.: 1989, ‘Rapid Bioassessment Protocols for use in Streams and Rivers: Benthic Macroinvertebrates and Fish’, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Washington DC, EPA-444/4-89-001.
Rabeni, C. F.: 2000, ‘Evaluating physical habitat integrity in relation to the biological potential of streams’, Hydrobiologia 422/423, 245–256.
Relyea, C. D., Minshall, G. W. and Danehy, R. J.: 2000, ‘Stream Insects as Bioindicators of Fine Sediment’, Proceedings of the ASCE Watershed Management 2000 Conference, June 2000 Ft. Collins Colorado.
Resh, V. H. and Jackson, J. K.: 1993, ‘Rapid Assessment Approaches to Biomonitoring using Benthic Macroinvertebrates’, in D. M. Rosenberg and V. H. Resh (eds.), Freshwater Biomonitoring and Benthic Macroinvertebrates, Chapman & Hall New York, pp. 195–233.
Resh, V. H.: 1995, Freshwater Benthic Macroinvertebrates and Rapid Assessment Procedures for Water Quality Monitoring in Developing and Newly Industrialized Countries, Biological Assessment and Criteria: Tools for Water Resource Planning and Decision Making, Lewis Publishers Boca Raton Florida, pp. 195–233.
Sokal, R. R. and Rohlf, F. J.: 1995, Biometry. Freeman, New York.
Thorne, R. St. J. and Williams, W. P.: 1997, ‘The response of benthic macroinvertebrates to pollution in developing countries: A multimetric system of bioassessment’, Freshw. Biol. 37, 671–686.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA), 1994, ‘Environmental Monitoring and Assessment Program Indicator Development Strategy’, in M. C. Barber (ed.), US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development Washington DC, EPA/620/R-94/022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SILVEIRA, M.P., BAPTISTA, D.F., BUSS, D.F. et al. APPLICATION OF BIOLOGICAL MEASURES FOR STREAM INTEGRITY ASSESSMENT IN SOUTH-EAST BRAZIL. Environ Monit Assess 101, 117–128 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-9141-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-9141-1