Abstract
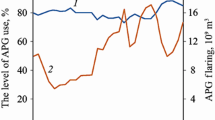
In a petroleum refinery the hydrocarbon emissions which are mostly fugitive in nature are emitted from process, offsites and periodic accidental releases such as: materials storage & handling, process, equipment leaks, solvent evaporation, combustion sources, waste treatment etc. In India, the monitoring of such emissions in a refinery are limited as also the standards are not set for its limit in ambient air. Hence there is an urgent need for generating a database for such emissions. Recently in India, MoEF/CPCB has set some guidelines under CREP rules for monitoring such emissions in a refinery. A detailed monitoring of the hydrocarbon emissions from different sources in a typical 10.5 MMTPA Indian refinery is undertaken during 1999–2001 and the results are presented. It is observed that the storage tank emissions alongwith process leaks form the major contributor towards fugitive hydrocarbon emissions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Central Pollution Control Board: 1995, Emission Regulation 54, 770.
CONCAWE Report: 1997, ‘Regulatory guidelines of environmental concern to the oil industry in Western Europe’, Vol. 161, p. 30.
Crawford: 1976, Air Pollution Control Theory, Mc-Graw Hill, New York, 248p.
Comprehensive Industry Document: 1981, Oil Refineries, 1980–81, CPCB, New Delhi.
Code of Practice for Air Pollution Control in Petroleum Refineries: 1981, Indian Standards Institution, New Delhi.
CONCAWE: 1995, ‘Assessing air quality for european auto/oil refinery: Initial findings’, CONCAWE Review 4(2), 6–11.
CONCAWE Report 1(95): 1993, ‘Survey on oil refineries waste disposal methods quantities and cost’, 1995, Vol. 1, pp. 38.
Hasan, M. Z. and Rao, P.: 2001, ‘Environmental Control in a Refinery: A Case Study’, in Proceeding of RAWN Conference on Waste Minimization held at Banaras, India, Vol. 24, pp. 123–129.
NEERI Report, Rapid Environmental Impact Assessment Studies Of Gujarat Refinery, India (1998–99 and 2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, P., Ankam, S., Ansari, M. et al. Monitoring of Hydrocarbon Emissions in a Petroleum Refinery. Environ Monit Assess 108, 123–132 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-3961-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-3961-x