Abstract
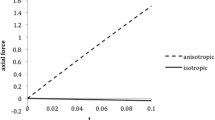
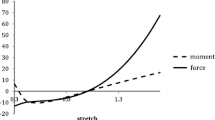
Torsion of solid cylinders in the context of nonlinear elasticity theory has been widely investigated with application to the behavior of rubber-like materials. More recently, this problem has attracted attention in investigations of the biomechanics of soft tissues and has been applied, for example, to examine the mechanical behavior of passive papillary muscles of the heart. A recent study in nonlinear elasticity was concerned specifically with the effects of strain-stiffening on the torsional response of solid circular cylinders. The cylinders are composed of incompressible isotropic nonlinearly elastic materials that undergo severe strain-stiffening in the stress-stretch response. Here we investigate similar issues for fiber-reinforced transversely-isotropic circular cylinders. We consider a class of incompressible anisotropic materials with strain-energy densities that are of logarithmic form in the anisotropic invariant. These models reflect stretch induced strain-stiffening of collagen fibers on loading and have been shown to model the mechanical behavior of many fibrous soft biological tissues. The consideration of anisotropy leads to a more elaborate mechanical response than was found for isotropic strain-stiffening materials. The classic Poynting effect found for rubber-like materials where torsion induces elongation of the cylinder is shown to be significantly different for the transversely-isotropic materials considered here. For sufficiently large anisotropy and under certain conditions on the amount of twist, a reverse-Poynting effect is demonstrated where the cylinder tends to shorten on twisting The results obtained here have important implications for the development of accurate torsion test protocols for determination of material properties of soft tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Criscione, J.C., Lorenzen-Schmidt, I., Humphrey, J.D., Hunter, W.C.: Mechanical contribution of endocardium during finite extension and torsion experiments on papillary muscle. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 27, 123–130 (1999)
Destrade, M., Gilchrist, M.D., Prikazchikov, D.A, Saccomandi, G.: Surface instability of sheared soft tissues. J. Biomech. Eng. 130, 061007 (2008)
Gent, A.N.: A new constitutive relation for rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 69, 59–61 (1996)
Holzapfel, G.A.: Nonlinear Solid Mechanics. Wiley, Chichester (2000)
Holzapfel, G.A.: Similarities between soft biological tissues and rubberlike materials. In: Austrell, P.E., Kari, L. (eds.) Constitutive Models for Rubber IV, Proceedings of the 4th European Conference on “Constitutive Models for Rubber” (ECCMR 2005), Stockholm, Sweden, pp. 607–617. Balkema, Lisse (2005)
Horgan, C.O., Murphy, J.G.: Simple shearing of incompressible and slightly compressible isotropic nonlinearly elastic materials. J. Elast. 98, 205–221 (2010)
Horgan, C.O., Murphy, J.G.: Simple shearing of soft biological tissues. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A (2010). doi:10.1098/rspa.2010.0288
Horgan, C.O., Polignone, D.A.: Cavitation in nonlinearly elastic solids: a review. Appl. Mech. Rev. 48, 471–485 (1995)
Horgan, C.O., Saccomandi, G.: A description of arterial wall mechanics using limiting chain extensibility constitutive models. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 1, 251–266 (2003)
Horgan, C.O., Saccomandi, G.: A new constitutive model for fiber-reinforced incompressible nonlinearly elastic solids. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 53, 1985–2015 (2005)
Horgan, C.O., Saccomandi, G.: Phenomenological hyperelastic strain-stiffening constitutive models for rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 79, 152–169 (2006)
Hoskins, P.R.: Physical properties of tissues relevant to arterial ultrasound imaging and blood velocity measurement. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 33, 1527–1539 (2007)
Humphrey, J.D.: Cardiovascular Solid Mechanics. Springer, New York (2002)
Humphrey, J.D., Barazotto, R.L. Jr., Hunter, W.C.: Finite extension and torsion of papillary muscles: a theoretical framework. J. Biomech. 25, 541–547 (1992)
Kanner, L.M., Horgan, C.O.: On extension and torsion of strain-stiffening rubber-like elastic cylinders. J. Elast. 93, 39–61 (2008)
Lin, H.T., Dorfmann, A.L., Trimmer, B.A.: Soft-cuticle biomechanics: a constitutive model of anisotropy for caterpillar integument. J. Theor. Biol. 256, 447–457 (2009)
Merodio, J., Ogden, R.W.: Mechanical response of fiber-reinforced incompressible nonlinear elastic solids. Int. J. Nonlin. Mech. 40, 213–227 (2005)
Merodio, J., Pence, T.J.: Kink surfaces in a directionally reinforced neo-Hookean material under plane deformation I. J. Elast. 62, 119–144 (2001)
Merodio, J., Saccomandi, G.: Remarks on cavity formation in fiber-reinforced incompressible non-linearly elastic solids. Eur. J. Mech. A, Solids 25, 778–792 (2006)
Merodio, J., Saccomandi, G., Sgura, I.: The rectilinear shear of fiber-reinforced incompressible non-linearly elastic solids. Int. J. Nonlin. Mech. 41, 1103–1115 (2006)
Ogden, R.W.: Elements of the theory of finite elasticity. In: Fu, Y.B., Ogden, R.W. (eds.) Nonlinear Elasticity: Theory and Applications. London Mathematical Society Lecture Notes Series, vol. 283, pp. 1–57. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Ogden, R.W., Saccomandi, G.: Introducing mesoscopic information into constitutive equations for arterial walls. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 6, 333–344 (2007)
Polignone, D.A., Horgan, C.O.: Cavitation for incompressible anisotropic nonlinearly elastic spheres. J. Elast. 33, 27–65 (1993)
Polignone, D.A., Horgan, C.O.: Effects of material anisotropy and inhomogeneity on cavitation for composite incompressible anisotropic nonlinearly elastic spheres. Int. J. Solids Struct. 30, 3381–3416 (1993)
Qiu, G.Y., Pence, T.J.: Remarks on the behavior of simple directionally reinforced incompressible nonlinearly elastic solids. J. Elast. 49, 1–30 (1997)
Rivlin, R.S.: Large elastic deformations of isotropic materials VI. Further results in the theory of torsion, shear and flexure. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 242, 173–195 (1949). Reprinted in: Barenblatt, G.I., Joseph, D.D. (eds.) Collected Papers of R.S. Rivlin, vol. 1, pp. 120–142. Springer, New York (1997)
Sadovsky, A.V., Baldi, P.F., Wan, F.Y.M.: A theoretical study of the in vivo mechanical properties of angiosperm roots: constitutive theories and methods of parameter estimation. J. Eng. Mater. Tech. 129, 483–487 (2007)
Spencer, A.J.M.: Deformations of Fibre-Reinforced Materials. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1972)
Taber, L.A.: Nonlinear Theory of Elasticity: Applications in Biomechanics. World Scientific, Singapore (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horgan, C.O., Murphy, J.G. Torsion of Incompressible Fiber-Reinforced Nonlinearly Elastic Circular Cylinders. J Elast 103, 235–246 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10659-010-9282-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10659-010-9282-5
Keywords
- Incompressible fiber-reinforced transversely-isotropic nonlinearly elastic materials
- Stretch induced strain-stiffening
- Torsion of solid circular cylinders
- Reverse Poynting effect
- Collagen fibers
- Papillary muscles