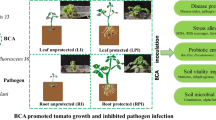
Abstract
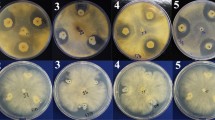
Early blight caused by Alternaria solani is a serious threat to crop production. In this study, the synergistic antagonism mechanism of a biocontrol consortium (including Bacillus subtilis J3 and Pseudomonas fluorescens J8) isolated from the tomato rhizosphere against A.solani was investigated. The consortium (109 CFU/mL, J3:J8(v/v) = 2:3) efficiently inhibited A.solani growth with an inhibition rate of 94.10%, significantly higher than the single culture of J3 or J8 (P < 0.05). The co-cultivation of J3 and J8 significantly enhanced (6.51-146.81%) the expression of the functional genes related to the production of antimicrobial substances, including srfA, fenA, pvds, phlA, and hcnA. Siderophore and 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol (2,4-DAPG) were 55.45-70.18% higher in the consortium than in single strains, significantly contributing to pathogen biocontrol. The interchange of metabolic substances between the bacteria probably improved their performance. This paper presents useful biocontrol bacteria material and provides important information on the synergistic mechanism of the bacteria, which could help to design and implement such biocontrol agents.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abuley, I. K., Hansen, J. G., & Fariñas, L. M. (2023). Evaluation of models based on a generic infection model for controlling early blight in potatoes. Crop Protection, 169, 106229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2023.106229
Ahmed, W., Yang, J., Tan, Y., Munir, S., Liu, Q., Zhang, J., Ji, G., & Zhao, Z. (2022). Ralstonia solanacearum, a deadly pathogen: Revisiting the bacterial wilt biocontrol practices in tobacco and other Solanaceae. Rhizosphere, 21, 100479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2022.100479
Ansari, F. A., & Ahmad, I. (2019). Fluorescent pseudomonas -FAP2 and bacillus licheniformis interact positively in biofilm mode enhancing plant growth and photosynthetic attributes. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 4547 https://europepmc.org/articles/PMC6418123
Attia, M. S., El-Sayyad, G. S., Abd Elkodous, M., & El-Batal, A. I. (2020). The effective antagonistic potential of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria against Alternaria solani-causing early blight disease in tomato plant. Scientia Horticulturae, 266, 109289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109289
Balthazar, C., St-Onge, R., Léger, G., Lamarre, S. G., Joly, D. L., & Filion, M. (2022). Pyoluteorin and 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol are major contributors to pseudomonas protegens Pf-5 biocontrol against Botrytis cinerea in cannabis. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.945498
Bessadat, N., Berruyer, R., Hamon, B., Bataille-Simoneau, N., Benichou, S., Kihal, M., Henni, D. E., & Simoneau, P. (2017). Alternaria species associated with early blight epidemics on tomato and other Solanaceae crops in northwestern Algeria. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 148(1), 181–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-016-1081-9
Biessy, A., & Filion, M. (2021). Phloroglucinol derivatives in plant-beneficial pseudomonas spp.: Biosynthesis. Regulation, and Functions., 11(3), 182 https://www.mdpi.com/2218-1989/11/3/182
Blanco-Vargas, A., Rodríguez-Gacha, L. M., Sánchez-Castro, N., Garzón-Jaramillo, R., Pedroza-Camacho, L. D., Poutou-Piñales, R. A., Rivera-Hoyos, C. M., Díaz-Ariza, L. A., & Pedroza-Rodríguez, A. M. (2020). Phosphate-solubilizing Pseudomonas sp., and Serratia sp., co-culture for Allium cepa L. growth promotion. Heliyon, 6(10). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05218
Carmona-Hernandez, S., Reyes-Pérez, J. J., Chiquito-Contreras, R. G., Rincon-Enriquez, G., Cerdan-Cabrera, C. R., & Hernandez-Montiel, L. G. (2019). Biocontrol of postharvest fruit fungal diseases by bacterial antagonists: A review. Agronomy, 9(3), 121 https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4395/9/3/121
Chen, X., Huang, H., Zhang, S., Zhang, Y., Jiang, J., Qiu, Y., Liu, J., & Wang, A. (2021). Bacillus velezensis WZ-37, a new broad-Spectrum biocontrol strain, promotes the growth of tomato seedlings. Agriculture, 11(7), 581 https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0472/11/7/581
Chen, Y.-C., & Huang, C.-H. (2020). Biocontrol of bacterial spot on tomato by foliar spray and growth medium application of bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Trichoderma asperellum. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 156(4), 995–1003. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-020-01947-5
Comeau, D., Balthazar, C., Novinscak, A., Bouhamdani, N., Joly, D. L., & Filion, M. (2021). Interactions between bacillus Spp., Pseudomonas Spp. and Cannabis sativa promote plant growth. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12, 715758. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.715758
Dehner, C. A., Awaya, J. D., Maurice, P. A., & DuBois, J. L. (2010). Roles of siderophores, oxalate, and ascorbate in mobilization of iron from hematite by the aerobic bacterium Pseudomonas mendocina. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 76(7), 2041–2048. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.02349-09
Egamberdieva, D., Jabborova, D., & Hashem, A. (2015). Pseudomonas induces salinity tolerance in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) and resistance to fusarium root rot through the modulation of indole-3-acetic acid. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 22(6), 773–779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.04.019
Fokkema, N. J. (1978). Fungal antagonisms in the phyllosphere. Annals of Applied Biology, 89(1), 115–119. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.1978.tb02582.x
Fu, H., Chung, K.-R., Liu, X., & Li, H. (2020). Aaprb1, a subtilsin-like protease, required for autophagy and virulence of the tangerine pathotype of Alternaria alternata. Microbiological Research, 240, 126537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2020.126537
Ghazy, N., & El-Nahrawy, S. (2021). Siderophore production by Bacillus subtilis MF497446 and Pseudomonas koreensis MG209738 and their efficacy in controlling Cephalosporium maydis in maize plant. Archives of Microbiology, 203(3), 1195–1209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-02113-5
Glickmann, E., Dessaux, Y. (1995). A critical examination of the specificity of the salkowski reagent for indolic compounds produced by phytopathogenic bacteria[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 61(2), 793–796. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.61.2.793-796.1995
Gong, L., Tan, H., Chen, F., Li, T., Zhu, J., Jian, Q., Yuan, D., Xu, L., Hu, W., Jiang, Y., & Duan, X. (2016). Novel synthesized 2, 4-DAPG analogues: Antifungal activity, mechanism and toxicology. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 32266. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32266
González-Jaramillo, L. M., Aranda, F. J., Teruel, J. A., Villegas-Escobar, V., & Ortiz, A. (2017). Antimycotic activity of fengycin C biosurfactant and its interaction with phosphatidylcholine model membranes. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 156, 114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.05.021
Gu, S., Wan, W., Shao, Z., & Zhong, W. (2021). High-throughput method for detecting Siderophore production by rhizosphere bacteria. Bio-protocol, 11(9), e4001. https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.4001
Gurusinghe, S., Brooks, T. L., Barrow, R. A., Zhu, X., Thotagamuwa, A., Dennis, P. G., Gupta, V. V. S. R., Vanniasinkam, T., & Weston, L. A. (2019). Technologies for the Selection, culture and metabolic profiling of unique rhizosphere microorganisms for natural product discovery. Molecules, 24(10), 1955 https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/24/10/1955
Ho, Y.-N., Hoo, S. Y., Wang, B.-W., Hsieh, C.-T., Lin, C.-C., Sun, C.-H., Peng, C.-C., Lin, C., & Yang, Y.-L. (2021). Specific inactivation of an antifungal bacterial siderophore by a fungal plant pathogen. The ISME Journal, 15(6), 1858–1861. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-020-00871-0
Jambhulkar, P. P., Jambhulkar, N., Meghwal, M., & Ameta, G. S. (2016). Altering conidial dispersal of Alternaria solani by modifying microclimate in tomato crop canopy. The Plant Pathology Journal, 32(6), 508–518. https://doi.org/10.5423/PPJ.OA.06.2015.0101
Ji, S. H., Paul, N. C., Deng, J. X., Kim, Y. S., Yun, B. S., & Yu, S. H. (2013). Biocontrol activity of bacillus amyloliquefaciens CNU114001 against fungal plant diseases. Mycobiology, 41(4), 234–242. https://doi.org/10.5941/myco.2013.41.4.234
Jin, J., Yin, Y., Wang, X., & Wen, J. (2022). Metabolic engineering of Bacillus subtilis 168 for the utilization of arabinose to synthesize the antifungal lipopeptide fengycin. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 185, 108528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2022.108528
Khan, F., Tabassum, N., Bamunuarachchi, N. I., & Kim, Y.-M. (2022). Phloroglucinol and its derivatives: Antimicrobial properties toward microbial pathogens. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 70(16), 4817–4838. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.2c00532
Khan, N., Martínez-Hidalgo, P., Ice, T. A., Maymon, M., Humm, E. A., Nejat, N., Sanders, E. R., Kaplan, D., & Hirsch, A. M. (2018). Antifungal activity of bacillus species against fusarium and analysis of the potential mechanisms used in biocontrol. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02363
Khare, E., & Arora, N. K. (2010). Effect of Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in suppression of charcoal rot disease of chickpea. Current Microbiology, 61(1), 64–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-009-9577-6
Knight, C. A., Bowman, M. J., Frederick, L., Day, A., Lee, C., & Dunlap, C. A. (2018). The first report of antifungal lipopeptide production by a Bacillus subtilis subsp. inaquosorum strain. Microbiological Research, 216, 40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2018.08.001
Lin, N., Wang, C., Ding, J., Su, L., Xu, L., Zhang, B., Zhang, Y., & Fan, J. (2020). Efficacy of nanoparticle encapsulation on suppressing oxidation and enhancing antifungal activity of cyclic lipopeptides produced by Bacillus subtilis. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 193, 111143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111143
Lin, Y., Du, D., Si, C., Zhao, Q., Li, Z., & Li, P. (2014). Potential biocontrol bacillus sp. strains isolated by an improved method from vinegar waste compost exhibit antibiosis against fungal pathogens and promote growth of cucumbers. Biological Control, 71, 7–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2013.12.010
Lyu, D., Backer, R., Robinson, W. G., & Smith, D. L. (2019). Plant growth-promoting Rhizobacteria for cannabis production: Yield, cannabinoid profile and disease resistance. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 1761. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01761
Mansour, S. A., Belal, M. H., Abou-Arab, A. A. K., Ashour, H. M., & Gad, M. F. (2009). Evaluation of some pollutant levels in conventionally and organically farmed potato tubers and their risks to human health. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 47(3), 615–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2008.12.019
Mei, L., Liang, Y., Zhang, L., Wang, Y., & Guo, Y. (2014). Induced systemic resistance and growth promotion in tomato by an indole-3-acetic acid-producing strain of Paenibacillus polymyxa. Annals of Applied Biology, 165(2), 270–279. https://doi.org/10.1111/aab.12135
Mejri, S., Siah, A., Coutte, F., Magnin-Robert, M., Randoux, B., Tisserant, B., Krier, F., Jacques, P., Reignault, P., & Halama, P. (2018). Biocontrol of the wheat pathogen Zymoseptoria tritici using cyclic lipopeptides from Bacillus subtilis. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 25(30), 29822–29833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9241-9
Meno, L., Abuley, I. K., Escuredo, O., & Seijo, M. C. (2022). Suitability of early blight forecasting Systems for Detecting First Symptoms in potato crops of NW Spain. Agronomy, 12(7), 1611 https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4395/12/7/1611
Metz, N., & Hausladen, H. (2022). Trichoderma spp. as potential biological control agent against Alternaria solani in potato. Biological Control, 166, 104820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2021.104820
Molina-Santiago, C., Pearson, J. R., Navarro, Y., Berlanga-Clavero, M. V., Caraballo-Rodriguez, A. M., Petras, D., García-Martín, M. L., Lamon, G., Haberstein, B., Cazorla, F. M., de Vicente, A., Loquet, A., Dorrestein, P. C., & Romero, D. (2019). The extracellular matrix protects Bacillus subtilis colonies from pseudomonas invasion and modulates plant co-colonization. Nature Communications, 10(1), 1919. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09944-x
Moussa, M., Ebrahim, W., Kalscheuer, R., Liu, Z., & Proksch, P. (2020). Co-culture of the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa with the fungus fusarium tricinctum induces bacterial antifungal and quorum sensing signaling molecules. Phytochemistry Letters, 36, 37–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2020.01.013
Mukherjee, P. K., Hurley, J. F., Taylor, J. T., Puckhaber, L., Lehner, S., Druzhinina, I., Schumacher, R., & Kenerley, C. M. (2018). Ferricrocin, the intracellular siderophore of Trichoderma virens, is involved in growth, conidiation, gliotoxin biosynthesis and induction of systemic resistance in maize. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 505(2), 606–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.170
Ongena, M., & Jacques, P. (2008). Bacillus lipopeptides: Versatile weapons for plant disease biocontrol. Trends in Microbiology, 16(3), 115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2007.12.009
Pal, K. K., Tilak, K. V. B. R., Saxena, A. K., Dey, R., & Singh, C. S. (2000). Antifungal characteristics of a fluorescent pseudomonas strain involved in the biological control of Rhizoctonia solani. Microbiological Research, 155(3), 233–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0944-5013(00)80038-5
Paulin, M. M., Novinscak, A., Lanteigne, C., Gadkar, V. J., & Filion, M. (2017). Interaction between 2,4-Diacetylphloroglucinol- and hydrogen cyanide-producing pseudomonas brassicacearum LBUM300 and Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganensis in the tomato rhizosphere. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 83(13), e00073–e00017. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00073-17
Prieto, P., Navarro-Raya, C., Valverde-Corredor, A., Amyotte, S. G., Dobinson, K. F., & Mercado-Blanco, J. (2009). Colonization process of olive tissues by Verticillium dahliae and its in planta interaction with the biocontrol root endophyte Pseudomonas fluorescens PICF7. Microbial Biotechnology, 2(4), 499–511. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-7915.2009.00105.x
Rajapitamahuni, S., Bachani, P., Sardar, R. K., & Mishra, S. (2019). Co-cultivation of siderophore-producing bacteria Idiomarina loihiensis RS14 with Chlorella variabilis ATCC 12198, evaluation of micro-algal growth, lipid, and protein content under iron starvation. Journal of Applied Phycology, 31(1), 29–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1591-2
Rezzonico, F., Zala, M., Keel, C., Duffy, B., Moënne-Loccoz, Y., & Défago, G. (2007). Is the ability of biocontrol fluorescent pseudomonads to produce the antifungal metabolite 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol really synonymous with higher plant protection? New Phytologist, 173(4), 861–872. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01955.x
Ricci, E., Schwinghamer, T., Fan, D., Smith, D. L., & Gravel, V. (2019). Growth promotion of greenhouse tomatoes with pseudomonas sp. and bacillus sp. biofilms and planktonic cells. Applied Soil Ecology, 138, 61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.02.009
Santhanam, R., Menezes, R. C., Grabe, V., Li, D., Baldwin, I. T., & Groten, K. (2019). A suite of complementary biocontrol traits allows a native consortium of root-associated bacteria to protect their host plant from a fungal sudden-wilt disease. Molecular Ecology, 28(5), 1154–1169. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.15012
Sasirekha, B., & Shivakumar, S. (2012). Statistical optimization for improved indole-3-acetic acid (iaa) production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and demonstration of enhanced plant growth promotion. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 12, 863–873. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162012005000038
Sun, X., Xu, Z., Xie, J., Hesselberg-Thomsen, V., Tan, T., Zheng, D., Strube, M. L., Dragoš, A., Shen, Q., Zhang, R., & Kovács, Á. T. (2022). Bacillus velezensis stimulates resident rhizosphere pseudomonas stutzeri for plant health through metabolic interactions. The ISME Journal, 16(3), 774–787. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-021-01125-3
Sur, S. G., & Alan. (2015). Understanding the function of the cyclic antifungal Lipopeptide Fengycin using all-atom md simulation. Biophysical Journal, 108(2), 84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2014.11.490
Suresh, P., Rekha, M., Gomathinayagam, S., Ramamoorthy, V., Sharma, M. P., Sakthivel, P., Sekar, K., Valan Arasu, M., & Shanmugaiah, V. (2022). Characterization and assessment of 2, 4-Diacetylphloroglucinol (DAPG)-producing Pseudomonas fluorescens VSMKU3054 for the Management of Tomato Bacterial Wilt Caused by Ralstonia solanacearum. Microorganisms, 10(8), 1508 https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/10/8/1508
Thokchom, E., Thakuria, D., Kalita, M. C., Sharma, C. K., & Talukdar, N. C. (2017). Root colonization by host-specific rhizobacteria alters indigenous root endophyte and rhizosphere soil bacterial communities and promotes the growth of mandarin orange. European Journal of Soil Biology, 79, 48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2017.02.003
Tian, T., Sun, B., Shi, H., Gao, T., He, Y., Li, Y., Liu, Y., Li, X., Zhang, L., Li, S., Wang, Q., & Chai, Y. (2021). Sucrose triggers a novel signaling cascade promoting Bacillus subtilis rhizosphere colonization. The ISME Journal, 15(9), 2723–2737. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-021-00966-2
Verma, S. K., Kingsley, K. L., Bergen, M. S., Kowalski, K. P., & White, J. F. (2018). Fungal disease prevention in seedlings of Rice (Oryza sativa) and other grasses by growth-promoting seed-associated endophytic bacteria from invasive Phragmites australis. Microorganisms, 6(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6010021
Wu, J.-Y., Ng, J., Shi, M., & Wu, S.-J. (2007). Enhanced secondary metabolite (tanshinone) production of salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots in a novel root–bacteria coculture process. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 77(3), 543–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1192-5
Wu, Q., Ni, M., Dou, K., Tang, J., Ren, J., Yu, C., & Chen, J. (2018). Co-culture of bacillus amyloliquefaciens ACCC11060 and Trichoderma asperellum GDFS1009 enhanced pathogen-inhibition and amino acid yield. Microbial Cell Factories, 17(1), 155. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-1004-x
Wu, R.-T., Chen, J.-Y., Liu, S., Niu, S.-H., Liao, X.-D., & Xing, S.-C. (2022). Cyclic AMP and biofilms reveal the synergistic proliferation strategy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli under the costimulation of high concentrations of microplastics and enrofloxacin. Science of the Total Environment, 838, 156470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156470
Yu, C., Liu, X., Zhang, X., Zhang, M., Gu, Y., Ali, Q., Mohamed, M. S. R., Xu, J., Shi, J., Gao, X., Wu, H., & Gu, Q. (2021). Mycosubtilin produced by Bacillus subtilis ATCC6633 inhibits growth and mycotoxin biosynthesis of fusarium graminearum and fusarium verticillioides. Toxins, 13(11), 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13110791
Zhou, H., Wei, H., Liu, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, L., & Tang, W. (2005). Improving biocontrol activity of Pseudomonas fluorescens through chromosomal integration of 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol biosynthesis genes. Chinese Science Bulletin, 50(8), 775–781. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183678
Zhuo, T., Chen, S., Wang, D., Fan, X., Zhang, X., & Zou, H. (2022). Expression of the ripAA gene in the Soilborne pseudomonas mosselii can promote the control efficacy against tobacco bacterial wilt. Biology (Basel), 11(8), 1170 https://www.mdpi.com/2079-7737/11/8/1170
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Dr. Yong Wang, School of Plant Protection, Northwest A&F University for providing the Alternaria solani strain for this study. We are grateful to Dr. Weizhen Fang of the Analysis & Testing center, Southwest Jiaotong University for the technical support. We are also grateful to Mr. Yu Wang and Mr. Hang Qiu for their help in the initial writing.
Contributions
JYX conceived and designed the study. LJP, NH, MHT, HQ and LB revised the manuscript. QZP and WC provide fund support and supervision. LB, QZP and WC share the corresponding authorship. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51978576), the Key Research and Development Plan of Sichuan Province (23SYSX0128, 23ZHSF0040), the Science and Technology Project of Chengdu (2022-YF05-00909-SN, 2022-YF05-00269-SN), Science and Technology Project of Sichuan Tobacco Company of China National Tobacco Corporation (SCYC202109).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Highlight
• Pseudomonas-Bacillus co-cultivation synergistically antagonized Alternaria solani;
• Overexpression of genes related to antibiotic production in the consortium;
• Antibiotic production increased in the consortium;
• Growth promoting and disease control were obtained with the consortium.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 904 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Y., Li, J., Niu, H. et al. Synergistic antagonism mechanism of Bacillus-Pseudomonas consortium against Alternaria solani. Eur J Plant Pathol 167, 715–726 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-023-02747-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-023-02747-3