Abstract
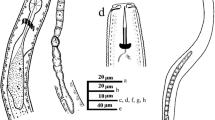
During a nematode survey in Iran a population of Pratylenchus loosi from tea was collected and herein described using morphometrics and several molecular markers and compared with the previous description of this species. Thus, the 18S rRNA gene, D2-D3 expansion regions of the 28S rRNA gene, ITS region, mitochondrial COI and partial nuclear hsp90 gene were amplified. According to morphometrics, the Iranian population was very close to previously described populations except for the stylet which was slightly longer. The phylogenetic reconstruction based on the sequences of all markers are also provided confirming the species differentiation and displaying the position of P. loosi and its relationship with closely related species.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul, S. F., Madden, T. L., Schäffer, A. A., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Miller, W., & Lipman, D. J. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 3389–3402.
Alvani, S., Mahdikhani-Moghdam, E., Rouhani, H., & Mohammadi, A. (2016). A checklist of the family Pratylenchidae Thorne, 1949 from Iran. Zootaxa, 4079, 179–204 https://www.mapress.com/j/zt/.
Azad, A. Y., & Seraji, A. (2016). Shade tree Tonka (Dipteryx odorata) new host for Pratylenchus loos in tea plantation. Iranian Journal of Plant Pathology, 52, Pe295–Pe296. http://www.ijpp.ir/article_22432.html.
Campos, V. P. (2002). Coffee nematode survey in Minas Gerais State, Brazil. Research report of the grant by PNP&D/cafe. EMBRAPA, Brasilia.
Carrasco-Ballesteros, S., Castillo, P., Adams, B. J., & Pérez-Artés, E. (2007). Identification of Pratylenchus thornei, the cereal and legume root-lesion nematode, based on SCAR-PCR and satellite DNA. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 118, 115–125.
Castillo, P., & Vovlas, N. (2007). Pratylenchus (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae): Diagnosis, biology, pathogenicity and management. In Nematology monographs and perspectives (Vol. 6, p. 529). Leiden: Brill. https://doi.org/10.1163/ej.9789004155640.i-523.
Chen, D. Y., Ni, H. F., Yen, J. H., Wu, W. S., & Tsay, T. T. (2009). Identification of root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus penetrans and P. loosi (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae) from strawberry and tea plantations in Taiwan. Plant Pathology Bulletin, 18, 247–262.
de la Pena, E., Karssen, G., & Moens, M. (2007). Distribution and diversity of root-lesion nematodes (Pratylenchus spp.) associated with Ammophila arenaria in coastal dunes of western Europe. Nematology, 9, 881–901. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854107782331289.
De Luca, F., Fanelli, E., Di Vito, M., Reyes, A., & De Giorgi, C. (2004). Comparison of the sequences of the D3 expansion of the 26S ribosomal genes reveals different degrees of heterogeneity in different populations and species of Pratylenchus from the Mediterranean region. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 110, 949–957. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-004-0813-4.
De Luca, F., Di Vito, M., Fanelli, E., Reyes, A., Greco, N., & De Giorgi, C. (2009). Characterization of the heat shock protein 90 gene in the plant parasitic nematode Meloidogyne artiellia and its expression as related to different developmental stages and temperature. Gene, 440, 16–22.
De Luca, F., Troccoli, A., Duncan, L. W., Subbotin, S. A., Waeyenberge, L., Moens, M., & Inserra, R. N. (2010). Characterisation of a population of Pratylenchus hippeastri from bromeliads and description of two related new species, P. floridensis n. sp and P. parafloridensis n. sp., from grasses in Florida. Nematology, 12, 847–868.
De Luca, F., Reyes, A., Troccoli, A., & Castillo, P. (2011). Molecular variability and phylogenetic relationships among different species and populations of Pratylenchus (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae) as inferred from the analysis of the ITS rDNA. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 130, 415–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-011-9763-9.
De Luca, F., Troccoli, A., Duncan, L. W., Subbotin, S. A., Waeyenberge, L., Coyne, D. L., Brentu, F. C., & Inserra, R. N. (2012). Praylenchus speijeri n. sp. (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae), a new root-lesion nematode pest of plantain in West Africa. Nematology, 14, 987–1004. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854112X638424.
Divsalar, N., Jamali, S., Pedramfar, H., & Taheri, H. (2012). Root lesion nematodes (Pratylenchus spp.) on citrus in south-west of Caspian Sea. Journal of Agricultural Technology, 8, 2227–2238.
Dover, G. (1982). Molecular drive: A cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature, 299, 111–117.
Fanelli, E., Troccoli, A., Capriglia, F., Lucarelli, G., Vovlas, N., Greco, N., & De Luca, F. (2018a). Sequence variation in ribosomal DNA and in the nuclear hsp90 gene of Pratylenchus penetrans (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae) populations and phylogenetic analysis. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 152, 355–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-018-1480-1.
Fanelli, E., Troccoli, A., Capriglia, F., Lucarelli, G., Vovlas, N., Greco, N., & De Luca, F. (2018b). Correction to: Sequence variation in ribosomal DNA and in the nuclear hsp90 gene of Pratylenchus penetrans (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae) populations and phylogenetic analysis. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 152, 573–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-018-1489-5.
Filipjev, I. N. (1936). On the classification of the Tylenchinae. Proc Heminthol Soc Wash, 3, 80–82.
Hajieghrari, B., Mohammadi, M., Kheiri, A., & Maafi, Z. T. (2005). A study about geographical distribution of root lesion nematode (Pratylenchus loosi, Loof 1960) in tea gardens at Gilan Province, Iran. Communications Agricultural Applied Biological Sciences, 70, 889–892.
Hajieghrari, B., Torabi-Giglou, M., & Waeyenberge, L. (2007). Comparative d2/d3 LSU-rDNA sequence study of some Iranian Pratylenchus loosi populations. African Journal of Biotechnology, 6, 2458–2466.
Inserra, R. N., Duncan, L. W., Troccoli, A., Dunn, D., Maia dos Santos, J., Kaplan, D., & Vovlas, N. (2001). Pratylenchus jaehni sp. n. from citrus in Brazil and its relationship with P coffeae and P. loosi (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae). Nematology, 3, 653–665. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854101753536028.
Janssen, T., Karssen, G., Verhaeven, M., Coyne, D., & Bert, W. (2017a). Mitochondrial coding genome analysis of tropical root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne) supports haplotype based diagnostics and reveals evidence of recent reticulate evolution. Scientific Reports, 6.
Janssen, T., Karssen, G., Orlando, V., Subbotin, S. A., & Bert, W. (2017b). Molecular characterization and species delimiting of plant-parasitic nematodes of the genus Pratylenchus from the penetrans group (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 117, 30–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2017.07.027.
Jones, M. G. K., & Fosu-Nyarko, J. (2014). Molecular biology of root lesion nematodes (Pratylenchus spp.) and their interaction with host plants. Annals Applied Biology, 164, 163–181.
Jones, J. T., Haegeman, A., Danchin, E. G. J., Gaur, H. S., Helder, J., Jones, M. G. K., Kikuchi, T., Manzanilla-Lopez, R., Palomares-Rius, J. E., Wesemael, W. M. L., & Perry, R. N. (2013). Top 10 plant-parasitic nematodes in molecular plant pathology. Molecular Plant Pathology, 14, 946–961. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12057.
Kanzaki, N., & Futai, K. (2002). A PCR primer set for determination of phylogenetic relationships of Bursaphelenchus species within xylophilus group. Nematology, 4, 35–41.
Katoh, K., & Standley, D. M. (2013). MAFFT multiple sequence alignment 542 software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 772–780. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst010.
Lazarova, S. S., Malloch, G., Oliveira, C. M., Hübschen, J., & Neilson, R. (2006). Ribosomal and mitochondrial DNA analyses of Xiphinema americanum-group populations. Journal of Nematology, 38, 404–410.
Liu, X., Wang, H., Lin, B., Tao, Y., Zhuo, K., & Liao, J. (2017). Loop-mediated isothermal amplification based on the mitochondrial COI region to detect Pratylenchus zeae. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 148, 435–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-016-1102-8.
Loof, P. A. A. (1960). Taxonomic studies on the genus Pratylenchus (Nematoda). Tijdschrift over Plantenziekten, 66, 29–90.
Majd Taheri, Z., Tanha Maafi, Z., Subbotin, S. A., Pourjam, E., & Eskandari, A. (2013). Molecular and phylogenetic studies on Pratylenchidae from Iran with additional data on Pratylenchus delattrei, Pratylenchoides alkani and two unknown species of Hirschmanniella and Pratylenchus. Nematology, 15, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1163/15685411-00002707.
Mirghasemi, T., & Seraji, A. (2010). Basket grass (Oplismenus compositus) as a new host for tea root lesion nematode, Pratylenchus loosi. Iranian Journal of Plant Pathology, 46, Pe91–Pe92 En27. http://www.irjpp.ir/browse.php?a_id=342&sid=1&slc_lang=en.
Nunn, G. B. (1992). Nematode molecular evolution. Ph.D. In Thesis. UK: University of Nottingham.
Palomares-Rius, J. E., Guesmi, I., Horrigue-Raouani, N., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Liébanas, G., & Castillo, P. (2014). Morphological and molecular characterisation of Pratylenchus oleae n. sp. (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae) parasitizing wild and cultivated olives in Spain and Tunisia. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 140, 53–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0443-4.
Park, B. Y., Choi, D., Lee, J., Choi, Y., & Shin, G. (2002). An unrecorded species of Pratylenchus loosi Loof (Tylenchida: Pratylenchidae) from tea in Korea. Korean Journal of Applied Entomology, 41, 299–303.
Seraji, A., Porjam, E., Tanha Maafi, Z., & Safaie, N. (2006). Biology and population dynamics of tea root lesion nematode (Pratylenchus loosi) in Iran. Iranian Journal of Plant Pathology, 43, 42–43.
Siddiqi, M. R. (2000). Tylenchida parasites of plants and insects (2nd ed.p. 833). Wallingford: CABI Publishing.
Singh, P. R., Nyragatare, A., Janssen, T., Couvreur, M., Decraemer, W., & Bert, W. (2018). Morphological and molecular characterisation of Pratylenchus rwandae n. sp. (Tylenchida: Pratylenchidae) associated with maize in Rwanda. Nematology, 20, 781–794. https://doi.org/10.1163/15685411-00003175.
Skantar, A. M., & Carta, L. K. (2004). Molecular characterization and phylogenetic evaluation of the hsp90 gene from selected nematodes. Journal Nematology, 36, 466–480.
Subbotin, S. A., Ragsdale, E. J., Mullens, T., Roberts, P. A., Mundo-Ocampo, M., & Baldwin, J. G. (2008). A phylogenetic framework for root-lesion nematodes of the genus Pratylenchus (Nematoda): Evidence from 18S and D2–D3 expansion segments of 28S ribosomal RNA genes and morphological characters. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 48, 491–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2008.04.028.
Sultana, T., Han, H., & Park, J. K. (2013). Comparison of complete mitochondrial genomes of pine wilt nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and Bursaphelenchus mucronatus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoidea) and development of a molecular tool for species identification. Gene, 520, 39–46.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A., & Kumar, S. (2013). MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 2725–2729.
Troccoli, A., Subbotin, S. A., Chitambar, J. J., Janssen, T., Waeyenberge, L., Stanley, J. D., Duncan, L. W., Agudelo, P., Uribe, G. E. M., Franco, J., & Inserra, R. N. (2016). Characterisation of amphimictic and parthenogenetic populations of Pratylenchus bolivianus Corbett, 1983 (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae) and their phylogenetic relationships with closely related species. Nematology, 18, 651–678.
van den Berg, E., Tiedt, L. R., Stanley, J. D., Inserra, R. N., & Subbotin, S. A. (2017). Characterisation of some Scutellonema species (Tylenchida: Hoplolaimidae) occurring in Botswana, South Africa, Costa Rica and the USA, with description of S. clavicaudatum sp. n. and a molecular phylogeny of the genus. Nematology, 19, 131–173. https://doi.org/10.1163/15685411-00003037.
Vrain, T. C., Wakarchuk, D. A., Lèvesque, A. C., & Hamilton, R. I. (1992). Intraspecific rDNA restriction fragment length polymorphism in the Xiphinema americanum group. Fundamental and Applied Nematology, 15, 563–573.
Waeyenberge, L., Ryss, A., Moens, M., Pinochet, J., & Vrain, T. C. (2000). Molecular characterisation of 18 Pratylenchus species using rDNA restriction fragment length polymorphism. Nematology, 2, 135–142.
Zhou, K., Zou, M., Duan, M., He, S., & Wang, G. (2015). Identification and analysis of retrogenes in the east Asian nematode Caenorhabditis sp. 5 genome. Genome, 58, 349–355. https://doi.org/10.1139/gen-2014-0147.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors certify that 1) do not have any actual or potential conflict of interest, 2) the study described is original and has not been published previously, and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere, 3) all prevailing local, national and international regulations and conventions, and normal scientific ethical practices, have been respected. We also certify that all authors have reviewed the manuscript and approved the final version of manuscript before submission.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
No specific permits were required for the described studies. Permission for sampling the crop orchards was granted by the landowner. The samples from wild plants were obtained in public areas, forests, and other natural areas studied. The sites are not protected in any way.
Informed consent
All the authors certify that the work carried out in this research followed the principles of ethical and professional conduct. The study was designed by all authors for scientific research only, as well as data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The author’s institutions were informed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirghasemi, S.N., Fanelli, E., Troccoli, A. et al. Molecular variability of the root-lesion nematode, Pratylenchus loosi (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae), from tea in Iran. Eur J Plant Pathol 155, 557–569 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-019-01792-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-019-01792-1