Abstract
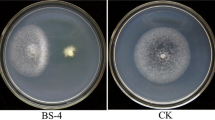
Seedling blight caused by Rhizoctonia solani is a serious soil-borne disease on flax. In this study, we isolated a bacterial strain HZ-72 from the rhizosphere soil of flax with obvious inhibitory effect on R. solani and other six plant fungal pathogens. Strain HZ-72 was identified as Bacillus subtilis based on morphological, physiological, biochemical characteristics and 16S rDNA sequence analysis. In greenhouse experiments, the control efficiency of strain HZ-72 reached 83.34%. Additionally, in vitro assays indicated that cell wall-degrading enzymes such as protease and cellulase, volatile compounds, proteins and lipopeptides produced by strain HZ-72 all contributed to its antagonistic activity against R. solani. To our knowledge, this is the first report on the use of a rhizosphere B. subtilis strain as a biocontrol agent for the biocontrol of flax seedling blight caused by R. solani.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashour, A. Z. A., & Aida, H. (2000). Biocontrol of flax seedling blight with mixtures of Pseudomonas spp. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 3(3), 368–371.
Bach, E., Seger, G. D. S., Fernandes, G. C., Lisboa, B. B., & Passaglia, L. M. P. (2016). Evaluation of biological control and rhizosphere competence of plant growth promoting bacteria. Applied Soil Ecology, 99, 141–149.
Buchanan, R. E., & Gibbons, N. E. (1984). Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology (8th Chinese ed.). Beijing: Science Press.
Calvo, H., Marco, P., Blanco, D., Oria, R., & Venturini, M. E. (2017). Potential of a new strain of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BUZ-14 as a biocontrol agent of postharvest fruit diseases. Food Microbiology, 63, 101–110.
Chauhan, A. K., Maheshwari, D. K., Kim, K., & Bajpai, V. K. (2016). Termitarium-inhabiting Bacillus endophyticus TSH42 and Bacillus cereus TSH77 colonizing Curcuma longa L.: Isolation, characterization, and evaluation of their biocontrol and plant-growth-promoting activities. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 62(10), 880–892.
Chen, S. F., Zhang, M. S., Wang, J. Y., Lv, D., Ma, Y. F., Zhou, B., & Wang, B. (2017). Biocontrol effects of Brevibacillus laterosporus AMCC100017 on potato common scab and its impact on rhizosphere bacterial communities. Biological Control, 106, 89–98.
Dong, X. Z., & Cai, M. Y. (2001). Common bacterial system identification manual. Beijing: Science Press.
Fan, Z. Y., Miao, C. P., Qiao, X. G., Zheng, Y. K., Chen, H. H., Chen, Y. W., Xu, L. H., Zhao, L. X., & Guan, H. L. (2016). Diversity, distribution, and antagonistic activities of rhizobacteria of Panax notoginseng. Journal of Ginseng Research, 40(2), 97–104.
Fan, H. Y., Ru, J. J., Zhang, Y. Y., Wang, Q., & Li, Y. (2017). Fengycin produced by Bacillus subtilis 9407 plays a major role in the biocontrol of apple ring rot disease. Microbiological Research, 199, 89–97.
Fernando, W. D., Ramarathnam, R., Krishnamoorthy, A. S., & Savchuk, S. C. (2005). Identification and use of potential bacterial organic antifungal volatiles in biocontrol. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 37(5), 955–964.
Ferraz, L. P., da Cunha, T., da Silva, A. C., & Kupper, K. C. (2016). Biocontrol ability and putative mode of action of yeasts against Geotrichum citri-aurantii in citrus fruit. Microbiological Research, 188, 72–79.
Fu, D., Xiang, H., Yu, C., Zheng, X., & Yu, T. (2016). Colloidal chitin reduces disease incidence of wounded pear fruit inoculated by Penicillium expansum. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 111, 1–5.
Gudmewad, R. B., Khandagale, S. G., & Kumara, S. R. V. (2016). Correlation and path coefficient analysis of economically important traits in linseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) germplasm. Electronic Journal of Plant Breeding, 7(2), 427–433.
Guo, X., Chen, D. D., Peng, K. S., Cui, Z. W., Zhang, X. J., Li, S., & Zhang, Y. A. (2016). Identification and characterization of Bacillus subtilis from grass carp (Ctenopharynodon idellus) for use as probiotic additives in aquatic feed. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 52, 74–84.
He, J. Q., Wang, J. L., Tang, Y. B., & Wang, R. X. (2005). A technical study on flax seeds treatment with fungicides against Rhizoclonia solanikiikn. China’s Fiber and Products, 27(3), 146–148.
Heller, K., Sheng, Q. C., Guan, F., Alexopoulou, E., Hua, L. S., Wu, G. W., Jankauskienė, Z., & Fu, W. Y. (2015). A comparative study between Europe and China in crop management of two types of flax: Linseed and fibre flax. Industrial Crops and Products, 68, 24–31.
Jadhav, H. P., Shaikh, S. S., & Sayyed, R. Z. (2017). Role of hydrolytic enzymes of rhizoflora in biocontrol of fungal phytopathogens: An overview. In Rhizotrophs: plant growth promotion to bioremediation (pp. 183–203). Singapore: Springer.
Khedher, S. B., Kilani-Feki, O., Dammak, M., Jabnoun-Khiareddine, H., Daami-Remadi, M., & Tounsi, S. (2015). Efficacy of Bacillus subtilis V26 as a biological control agent against Rhizoctonia solani on potato. Comptes Rendus Biologies, 338(12), 784–792.
Kumar, K. V. K., Yellareddygari, S. K., Reddy, M. S., Kloepper, J. W., Lawrence, K. S., Zhou, X. G., Sudini, H., Groth, D. E., Raju, S. K., & Miller, M. E. (2012). Efficacy of Bacillus subtilis MBI 600 against sheath blight caused by Rhizoctonia solani and on growth and yield of rice. Rice Science, 19(1), 55–63.
Lane, D. J. (1991). 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In E. Stackebrandt & M. Goodfellow (Eds.), Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematices (pp. 115–175). Chichester: Wiley.
Liu, B., Huang, L. L., Buchenauer, H., & Kang, Z. S. (2010). Isolation and partial characterization of an antifungal protein from the endophytic Bacillus subtilis strain EDR4. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 98(2), 305–311.
Ma, X., Wang, X. B., Cheng, J., Nie, X., Yu, X. X., Zhao, Y. T., & Wang, W. (2015). Microencapsulation of Bacillus subtilis B99-2 and its biocontrol efficiency against Rhizoctonia solani in tomato. Biological Control, 90, 34–41.
Mu, J. J., Li, X. P., Jiao, J. G., Ji, G. N., Wu, J., Hu, F., & Li, H. X. (2017). Biocontrol potential of vermicompost through antifungal volatiles produced by indigenous bacteria. Biological Control, 112, 49–54.
Prasanna Kumar, M. K., Amruta, N., Manjula, C. P., Puneeth, M. E., & Teli, K. (2017). Characterisation, screening and selection of Bacillus subtilis isolates for its biocontrol efficiency against major rice diseases. Biocontrol Science and Technology, 27(4), 581–599.
Shi, J. F., & Sun, C. Q. (2017). Isolation, identification, and biocontrol of antagonistic bacterium against Botrytis cinerea after tomato harvest. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 48, 706–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjm.2017.03.002.
Sun, G. Z., Yao, T., Feng, C. J., Chen, L., Li, J. H., & Wang, L. D. (2017). Identification and biocontrol potential of antagonistic bacteria strains against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and their growth-promoting effects on Brassica napus. Biological Control, 104, 35–43.
Velusamy, P., Immanuel, J. E., & Gnanamanickam, S. S. (2013). Rhizosphere bacteria for biocontrol of bacterial blight and growth promotion of rice. Rice Science, 20(5), 356–362.
Vida, C., Cazorla, F. M., & de Vicente, A. (2017). Characterization of biocontrol bacterial strains isolated from a suppressiveness-induced soil after amendment with composted almond shells. Research in Microbiology, 168(6), 583–593.
Xue, L., Xue, Q. H., Chen, Q., Lin, C. F., Shen, G. H., & Zhao, J. (2013). Isolation and evaluation of rhizosphere actinomycetes with potential application for biocontrol of Verticillium wilt of cotton. Crop Protection, 43, 231–240.
Yánez-Mendizábal, V., Usall, J., Viñas, I., Casals, C., Marín, S., Solsona, C., & Teixidó, N. (2011). Potential of a new strain of Bacillus subtilis CPA-8 to control the major postharvest diseases of fruit. Biocontrol Science and Technology, 21(4), 409–426.
Yang, X., Liu, L. Y., Guang, F. Z., Li, Z. G., Wu, G. W., Wang, X., Lu, Y., & Chen, H. (2009). Identification of flax Rhizoctonia solani pathogen and medicament selection. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences in China, 2009(4), 67–68.
Youssef, S. A., Tartoura, K. A., & Abdelraouf, G. A. (2016). Evaluation of Trichoderma harzianum and Serratia proteamaculans effect on disease suppression, stimulation of ROS-scavenging enzymes and improving tomato growth infected by Rhizoctonia solani. Biological Control, 100, 79–86.
Yu, X. M., Ai, C. X., Xin, L., & Zhou, G. F. (2011). The siderophore-producing bacterium, Bacillus subtilis CAS15, has a biocontrol effect on fusarium wilt and promotes the growth of pepper. European Journal of Soil Biology, 47(2), 138–145.
Yu, Y. Y., Jiang, C. H., Wang, C., Chen, L. J., Li, H. Y., Xu, Q., & Guo, J. H. (2017). An improved strategy for stable biocontrol agents selecting to control rice sheath blight caused by Rhizoctonia solani. Microbiological Research, 203, 1–9.
Zhang, M. J., Li, J. L., Shen, A. R., Tan, S. Y., Yan, Z., Yu, Y. T., Xue, Z. D., Tan, T. M., & Zeng, L. B. (2016). Isolation and identification of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens IBFCBF-1 with potential for biological control of Phytophthora blight and growth promotion of pepper. Journal of Phytopathology, 164(11–12), 1012–1021.
Zhang, X., Zhou, Y. Y., Li, Y., Fu, X. C., & Wang, Q. (2017). Screening and characterization of endophytic Bacillus for biocontrol of grapevine downy mildew. Crop Protection, 96, 173–179.
Zhang, B., Wang, J. N., Ning, S. Q., Yuan, Q., Chen, X. N., Zhang, Y. Y., & Fan, J. F. (2018). Peptides derived from tryptic hydrolysate of Bacillus subtilis culture suppress fungal spoilage of table grapes. Food Chemistry, 239, 520–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.06.153.
Zhao, S., Li, J. Y., Liu, F., Yang, W. X., Zhang, N., & Liu, D. Q. (2015). Antagonism of Paenibacillus polymyxa Z-X-225 against pathogen of pricklyash peel ear blight disease. Journal of Plant Protection in China, 42(5), 863–864.
Zheng, Y., Xue, Q. Y., Xu, L. L., Xu, Q., Lu, S., Gu, C., & Guo, J. H. (2011). A screening strategy of fungal biocontrol agents towards Verticillium wilt of cotton. Biological Control, 56(3), 209–216.
Zhu, X., Yang, G. A., Wang, X. M., Chen, X. Y., Sun, C. H., Yang, J. Q., Dong, L. M., Chen, G. H., Sheng, J. B., Tian, C. L., & Yang, W. G. (2010). Control efficacy of several agrochemicals to flax Rhizoctonia solani in field. Plant Fiber Sciences in China, 32(6), 323–326.
Zouari, I., Jlaiel, L., Tounsi, S., & Trigui, M. (2016). Biocontrol activity of the endophytic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain CEIZ-11 against Pythium aphanidermatum and purification of its bioactive compounds. Biological Control, 100, 54–62.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-ASTIP-2015- IBFC), the Major Scientific and Technological Projects of Hunan Province (2016NK1001), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFD0200900) and the project for Monitoring and Prevention of Crop Pests, Disease, and Mice from the Ministry of Agriculture (S158).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The work complies to the ethical standards of this journal. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This research did not involve human and/or animal participants. The manuscript was only submitted to EJPP and not previously published. All authors contributed and agreed to submission to EJPP.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, T., Zhu, J., Shen, A. et al. Isolation and identification of a Bacillus subtilis HZ-72 exhibiting biocontrol activity against flax seedling blight. Eur J Plant Pathol 153, 825–836 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-018-1595-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-018-1595-4