Abstract
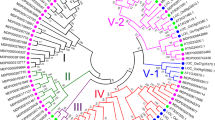
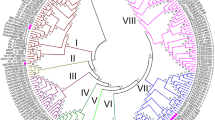
The WALL ASSOCIATED-KINASE - RECETOR-LIKE KINASE (WAK-RLK) gene family has been reported to act as a sensor for disease. Apple (Malus domestica) can be affected by multiple biotic stresses, such as fungal diseases from Valsa mali (Vm), Alternariaalternata Apple Pathotype (AaAP), and Pythium ultimum (Pu). However, there has been no report of WAK-RLK genes involved in apple biotic stress response. In this paper, we performed a comprehensive study including genome-wide annotation, characterization and gene expression analysis of WAK-RLKs in apple (MdWAK-RLKs). We found 44 members based on structural domain identification. The number of amino acids, molecular weight, and theoretical pI of these identified members ranged from 302 to 998, 33.63 to 110.35 kD, and 5.1 to 9.26, respectively. Members of the family were anchored to 16 out of 17 chromosomes and were classified into six phylogenetic groups. We found two phylogenetic groups specific to the apple genome. Synteny analysis revealed that 11 gene pairs arose from segmental duplications and 7 gene clusters resulted from tandem duplications. Cis-elements in the promoter region of MdWAK-RLKs were found mainly in response to circadian rhythm, hormones, and multiple stresses. The large number of members that showed high expression in multiple tissues and differential expressed in response to stress revealed that the different functional roles of MdWAK-RLKs under physiological or pathological conditions. Several genes, such as MDP0000278283, MDP0000153539, MDP0000170906, and MDP0000251865, were significantly influenced by multiple diseases. This study provides new insights into the potential function of WAK-RLKs in Malus and in Rosaceae and its contribution to disease resistance.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AaAP:
-
Alternaria alternata Apple Pathotype
- RLK:
-
Receptor Like Kinase
- WAK-RLKs :
-
The WALL-ASSOCIATED-KINASE - RECETOR-LIKE KINASE
- EGF:
-
Epidermal Growth Factor
- OGs:
-
Oligogalacturonides
- GDR:
-
Genome Database of Rosaceae species
- NCBI:
-
The National Center for Biotechnology Information
- TAIR:
-
The Arabidopsis Information Resources
- MdWAK-RLKs :
-
Malus domestica WAK-RLKs
- Pu :
-
Pythium ultimum
- qRT-PCR:
-
quantitative Reverse-Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Vm :
-
Valsa mali
References
Abe, K., Iwanami, H., Kotoda, N., Moriya, S., & Takahashi, S. (2010). Evaluation of apple genotypes and Malus species for resistance to Alternaria blotch caused by Alternaria alternata apple pathotype using detached-leaf method. Plant Breeding, 129(2), 208–218.
Baldo, A., Norelli, J. L., Farrell, R. E., Bassett, C. L., Aldwinckle, H. S., & Malnoy, M. (2010). Identification of genes differentially expressed during interaction of resistant and susceptible apple cultivars (Malus × domestica) with Erwinia amylovora. BMC Plant Biology, 10(1), 1–10.
Bassett, C. L., Baldo, A. M., Moore, J. T., Jenkins, R. M., Soffe, D. S., Wisniewski, M. E., Norelli, J. L., & Jr, R. E. F. (2014). Genes responding to water deficit in apple (malus x domestica borkh.) roots. BMC Plant Biology,14(1), 182.
Benschop, J. J., Mohammed, S., O'Flaherty, M., Heck, A. J., Slijper, M., & Menke, F. L. (2007). Quantitative phosphoproteomics of early elicitor signaling in Arabidopsis. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 6(7), 1198–1214.
Brutus, A., Sicilia, F., Macone, A., Cervone, F., & De Lorenzo, G. (2010). A domain swap approach reveals a role of the plant wall-associated kinase 1 (WAK1) as a receptor of oligogalacturonides. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(20), 9452–9457.
Caillaud, M. C., Wirthmueller, L., Sklenar, J., Findlay, K., Piquerez, S. J., Jones, A. M., Robatzek, S., Jones, J. D. G., & Faulkner, C. (2014). The plasmodesmal protein PDLP1 localises to haustoria-associated membranes during downy mildew infection and regulates callose deposition. PLoS Pathogens, 10, e1004496.
Celton, J. M., Gaillard, S., Bruneau, M., Pelletier, S., Aubourg, S., Martin-Magniette, M. L., Navarro, L., Laurens, F., & Renou, J. P. (2014). Widespread anti-sense transcription in apple is correlated with siRNA production and indicates a large potential for transcriptional and/or post-transcriptional control. New Phytologist, 203(1), 287–299.
de Oliveira, L. F. V., Christoff, A. P., de Lima, J. C., de Ross, B. C. F., Sachetto-Martins, G., Margis-Pinheiro, M., & Margis, R. (2014). The Wall-associated Kinase gene family in rice genomes. Plant Science, 229(229), 181–192.
Depuydt, S., & Hardtke, C. S. (2011). Hormone signalling crosstalk in plant growth regulation. Current Biology, 21(9), R365–R373.
Diener, A. C., & Ausubel, F. M. (2005). Resistance to fusarium oxysproum 1, a dominant Arabidopsis disease-resistance gene, is not race specific. Genetics, 171(1), 305–321.
Finn, R.D., Bateman, A., Clements, J., Coggill, P., Eberhardt, R.Y., Eddy, S.R., Heger, A., Hetherington, K., Holm, L., Mistry, J., Sonnhammer, E.L.L., Tate, J., & Punta, M. (2014). Pfam: the protein families database. Nucleic acids research, 42(D1), 222–230.
Giorno, F., Guerriero, G., Baric, S., & Mariani, C. (2012). Heat shock transcriptional factors in Malus domestica: identification, classification and expression analysis. BMC Genomics,13, 639
Gendron, J. M., & Wang, Z. Y. (2007). Multiple mechanisms modulate brassinosteroid signaling. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 10(5), 436–441.
Hanada, K., Zou, C., Lehti-Shiu, M. D., Shinozaki, K., & Shiu, S. H. (2008). Importance of lineage-specific expansion of plant tandem duplicates in the adaptive response to environmental stimuli. Plant Physiology, 148(2), 993–1003.
Hou, X., Tong, H., Selby, J., DeWitt, J., Peng, X., & He, Z. H. (2005). Involvement of a cell wall-associated kinase, WAKL4, in Arabidopsis mineral responses. Plant Physiology, 139(4), 1704–1716.
Hu, B., Jin, J., Guo, A. Y., Zhang, H., Luo, J., Gao, G. 2015. GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics, 31(8), 1296–1297.
Hurni, S., Scheuermann, D., Krattinger, S. G., Kessel, B., Wicker, T., Herren, G., Fitze, M. N., Breen, J., Presterl, T., Ouzunova, M., & Keller, B. (2015). The maize disease resistance gene Htn1 against northern corn leaf blight encodes a wall-associated receptor-like kinase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(28), 8780–8785.
Kamber, T., Buchmann, J. P., Pothier, J. F., Smits, T. H., Wicker, T., & Duffy, B. (2016). Fire blight disease reactome: RNA-seq transcriptional profile of apple host plant defense responses to Erwinia amylovora pathogen infection. Scientific Reports, 6.
Kaur, R., Singh, K., & Singh, J. (2013). A root-specific wall-associated kinase gene, HvWAK1, regulates root growth and is highly divergent in barley and other cereals. Functional & Integrative Genomics, 13(2), 167–177.
Kohorn, B. D. (2001). WAKs; cell wall associated kinases. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 13(5), 529–533.
Kohorn, B. D., & Kohorn, S. L. (2012). The cell wall-associated kinases, WAKs, as pectin receptors. Frontiers in Plant Science, 3, 88.
Kohorn, B. D., Kobayashi, M., Johansen, S., Riese, J., Huang, L. F., Koch, K., Fu, S., Dotson, A., & Byers, N. (2006). An Arabidopsis cell wall-associated kinase required for invertase activity and cell growth. The Plant Journal, 46(2), 307–316.
Lally, D., Ingmire, P., Tong, H. Y., & He, Z. H. (2001). Antisense expression of a cell wall–associated protein kinase, WAK4, inhibits cell elongation and alters morphology. The Plant Cell, 13(6), 1317–1332.
Larkin, M. A., Blackshields, G., Brown, N. P., Chenna, R., McGettigan, P. A., McWilliam, H., Valentin, F., Wallace, I. M., Wilm, A., Lopez, R., Thompson, J. D., Gibson, T. J., Higgins, D. G. 2007. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics, 23(21), 2947–2948
Lehti-Shiu, M. D., Zou, C., & Shiu, S. H. (2012). Origin, diversity, expansion history, and functional evolution of the plant Receptor-Like Kinase/Pelle family. In Receptor-Like Kinases in Plants (pp. 1–22). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer.
Leisso, R., Leisso, R., & Mazzola, M. (2016, December). Apple replant disease and the-omics: interaction of apple rootstock metabolome and the soil microbiome. In American Phytopathological Society Annual Meeting (Vol. 106, p. S4).
Lescot, M., Déhais, P., Thijs, G., Marchal, K., Moreau, Y., Peer, Y. V. D., Rouzé, P., & Rombauts, S. (2002). Plantcare, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 30(1), 325–327.
Li, H., Zhou, S. Y., Zhao, W. S., Su, S. C., & Peng, Y. L. (2009). A novel wall-associated receptor-like protein kinase gene, OsWAK1, plays important roles in rice blast disease resistance. Plant Molecular Biology, 69(3), 337–346.
Lim, C. W., Yang, S. H., Shin, K. H., Lee, S. C., & Kim, S. H. (2015). The AtLRK10L1. 2, Arabidopsis ortholog of wheat LRK10, is involved in ABA-mediated signaling and drought resistance. Plant Cell Reports, 34(3), 447–455.
Mangwanda, R., Myburg, A. A., & Naidoo, S. (2015). Transcriptome and hormone profiling reveals Eucalyptus grandis defence responses against Chrysoporthe austroafricana. BMC Genomics, 16(1), 319.
Matsubayashi, Y., Ogawa, M., Morita, A., & Sakagami, Y. (2002). An LRR receptor kinase involved in perception of a peptide plant hormone. phytosulfokine. Science, 296(5572), 1470–1472.
Meier, S., Ruzvidzo, O., Morse, M., Donaldson, L., Kwezi, L., & Gehring, C. (2010). The Arabidopsis wall associated kinase-like 10 gene encodes a functional guanylyl cyclase and is co-expressed with pathogen defense related genes. PLOS one, 5(1), e8904.
Nguyen, Q. N., Lee, Y. S., Cho, L. H., Jeong, H. J., An, G., & Jung, K. H. (2015). Genome-wide identification and analysis of Catharanthus roseus RLK1-like kinases in rice. Planta, 241(3), 603–613.
Osakabe, Y., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K., Shinozaki, K., & Tran, L. S. P. (2013). Sensing the environment: key roles of membrane-localized kinases in plant perception and response to abiotic stress. Journal of Experimental Botany, 64(2), 445–458.
Peleg, Z., & Blumwald, E. (2011). Hormone balance and abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 14(3), 290–295.
Rizzon, C., Ponger, L., & Gaut, B. S. (2006). Striking similarities in the genomic distribution of tandemly arrayed genes in Arabidopsis and rice. PLoS Computational Biology, 2(9), e115.
Robert-Seilaniantz, A., Grant, M., & Jones, J. D. (2011). Hormone crosstalk in plant disease and defense: more than just jasmonate-salicylate antagonism. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 49, 317–343.
Scheer, J. M., & Ryan, C. A. (2002). The systemin receptor SR160 from Lycopersicon peruvianum is a member of the LRR receptor kinase family. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99(14), 9585–9590.
Schultz, J., Milpetz, F., Bork, P., Ponting, C. P. (1998). SMART, a simple modular architecture research tool: identification of signaling domains. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 95(11), 5857–5864.
Shin, S., Lv, J., Fazio, G., Mazzola, M., & Zhu, Y. (2014). Transcriptional regulation of ethylene and jasmonate mediated defense response in apple (Malus domestica) root during Pythium ultimum infection. Horticulture research, 1, 14053.
Shin, S., Zheng, P., Fazio, G., Mazzola, M., Main, D., & Zhu, Y. (2016a). Transcriptome changes specifically associated with apple (Malus domestica) root defense response during Pythium ultimum infection. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 94, 16–26.
Shin, K. H., Yang, S. H., Lee, J. Y., Lim, C. W., Lee, S. C., Brown, J. W., & Kim, S. H. (2015). Alternative splicing of mini-exons in the arabidopsis leaf rust receptor-like kinase lrk10 genes affects subcellular localisation. Plant Cell Reports, 34(3), 495–505.
Shin, S. Y., Chung, H., Kim, S. Y., & Nam, K. H. (2016b). BRI1-EMS-suppressor 1 gain-of-function mutant shows higher susceptibility to necrotrophic fungal infection. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 470(4), 864–869.
Shiu, S. H., Karlowski, W. M., Pan, R., Tzeng, Y. H., Mayer, K. F., & Li, W. H. (2004). Comparative analysis of the receptor-like kinase family in Arabidopsis and rice. The Plant Cell, 16(5), 1220–1234.
Sivaguru, M., Ezaki, B., He, Z. H., Tong, H., Osawa, H., Baluška, F., Volkmann, D., & Matsumoto, H. (2003). Aluminum-induced gene expression and protein localization of a cell wall-associated receptor kinase in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 132(4), 2256–2266.
Tamura, K., Peterson, D., Peterson, N., Stecher, G., Nei, M., Kumar, S. 2011. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28(10), 2731–2739.
Velasco, R., Zharkikh, A., Affourtit, J., Dhingra, A., Cestaro, A., Kalyanaraman, A., Fontana, P., Bhatnagar, S. K., Troggio, M., Pruss, D., Salvi, S., Pindo, M., Baldi, P., Castelletti, S., Cavaiuolo, M., Coppola, G., Costa, F., Cova, V., Ri, A. D., Goremykin, V., Komjanc, M., Longhi, S., Magnago, P., Malacarne, G., Malnoy, M., Micheletti, D., Moretto, M., Perazzolli, M., Si-Ammour, A., Vezzulli, S., Zini, E., Eldredge, G., Fitzgerald, L. M., Gutin, N., Lanchbury, J., Macalma, T., Mitchell, J. T., Reid, J., Wardell, B., Kodira, C., Chen, Z., Desany, B., Niazi, F., Palmer, M., Koepke, T., Jiwan, D., Schaeffer, S., Krishnan, V., Wu, C., Chu, V. T., King, S. T., Vick, J., Tao, Q., Mraz, A., Stormo, A., Stormo, K., Bogden, R., Ederle, D., Stella, A., Vecchietti, A., Kater, M. M., Masiero, S., Lasserre, P., Lespinasse, Y., Allan, A. C., Bus, V., Chagné, D., Crowhurst, R. N., Gleave, A. P., Lavezzo, E., Fawcett, J. A., Proost, S., Rouzé, P., Sterck, L., Toppo, S., Lazzari, B., Hellens, R. P., Durel, C., Gutin, A., Bumgarner, R. E., Gardiner, S. E., Skolnick, M., Egholm, M., Peer, Y. V., & Salamin, F. (2010). The genome of the domesticated apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.). Nature Genetics, 42(10), 833–839.
Verica, J. A., & He, Z. H. (2002). The Cell Wall-Associated Kinase (WAK) and WAK-Like Kinase Gene Family. Plant Physiology, 129(2), 455–459.
Wagner, T. A., & Kohorn, B. D. (2001). Wall-associated kinases are expressed throughout plant development and are required for cell expansion. The Plant Cell, 13(2), 303–318.
Wang, W., Barnaby, J. Y., Tada, Y., Li, H., Tör, M., Caldelari, D., Lee, D., Fu, X., & Dong, X. (2011). Timing of plant immune responses by a central circadian regulator. Nature, 470(7332), 110–114.
Wang, Y., Tang, H., DeBarry, J. D., Tan, X., Li, J., Wang, X., Lee, T., Jin, H., Marler, B., Guo, H., Kissinger, J. C., & Paterson, A. H. (2012). MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Research, 40(7), e49–e49.
Wang, S., Hu, T., Wang, Y., Luo, Y., Michailides, T. J., & Cao, K. (2016). New understanding on infection processes of Valsa canker of apple in China. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 146(3), 531–540.
Weigel, D., Ahn, J. H., Blázquez, M. A., Borevitz, J. O., Christensen, S. K., Fankhauser, C., Ferrándiz, C., Kardailsky, I., Malancharuvil, E. J., Neff, M. M., Nguyen, J. T., Sato, S., Wang, Z. Y., Xia, Y., Dixon, R. A., Harrison, M. J., Lamb, C. J., Yanofsky, M. F., & Chory, J. (2000). Activation tagging in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 122(4), 1003–1014.
Wu, T., Wang, Y., Zheng, Y., Fei, Z., Dandekar, A. M., Xu, K., Han, Z., & Cheng, L. (2015). Suppressing sorbitol synthesis substantially alters the global expression profile of stress response genes in apple (Malus domestica) leaves. Plant and Cell Physiology, 56(9), 1748–1761.
Yin, Z., Ke, X., Kang, Z., & Huang, L. (2016). Apple resistance responses against Valsa mali revealed by transcriptomics analyses. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 93, 85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2016.01.004.
Zhang, S., Chen, C., Li, L., Meng, L., Singh, J., Jiang, N., Deng, X., He, Z., & Lemaux, P. G. (2005). Evolutionary expansion, gene structure, and expression of the rice wall-associated kinase gene family. Plant Physiology, 139(3), 1107–1124.
Zhang, K. X., Tian, W. E. N., Jun, D. O. N. G., BAI, T. H., Kun, W. A. N. G., & LI, C. Y. (2016). Comprehensive evaluation of tolerance to alkali stress by 17 genotypes of apple rootstocks. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 15(7), 1499–1509.
Zhu, J. K. (2003). Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 6(5), 441–445.
Zhu, L., Ni, W., Liu, S., Cai, B., Xing, H., & Wang, S. (2017). Transcriptomics Analysis of Apple Leaves in Response to Alternaria alternata Apple Pathotype Infection. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8.
Zuo, W., Chao, Q., Zhang, N., Ye, J., Tan, G., Li, B., Xing, Y., Zhang, B., Liu, H., Fengler, K. A., Zhao, J., Zhao, X., Chen, Y., Lai, J., Yan, J., & Xu, M. (2015). A maize wall-associated kinase confers quantitative resistance to head smut. Nature Genetics, 47(2), 151–157.
Funding
This study was funded by the Talent introduction Project of Gansu Agricultural University (GSAU-RCZX201712) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31501728) and the Ministry of Agriculture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All authors have received research grants from Gansu Agricultural University. All authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, C., Liu, Y., Guo, Z. et al. Genome-wide annotation and expression responses to biotic stresses of the WALL-ASSOCIATED KINASE - RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE (WAK-RLK) gene family in Apple (Malus domestica). Eur J Plant Pathol 153, 771–785 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-018-1591-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-018-1591-8