Abstract
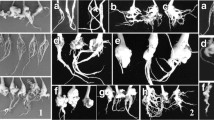
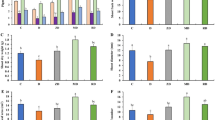
Clubroot, caused by Plasmodiophora brassicae, is a worldwide disease that can lead to significant yield losses in cruciferous crops. It causes root hypertrophy, hampering the uptake of nutrients and water. In the evaluation of resistance, small spheroid galls (SSGs), which are distinct from typical spindle galls, and are generally regarded as a host resistance reaction, were observed. In this study, the occurrence of SSGs was investigated when evaluating the host resistance of seven commercial clubroot-resistant (CR) Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa) cultivars inoculated with 12 P. brassicae populations collected from different infested fields in Chuanyu region of China. Results showed that while all seven CR Chinese cabbage cultivars exhibited high resistance levels to the major populations tested, SSGs occurred in host-population combinations contained either Chinese cabbage cultivar ‘T1–145’ or population ‘FL’. This indicated that some CR cultivars or P. brassicae populations might be more likely to produce SSGs than others. Thus, recording the occurrence of SSGs separately in the resistance evaluation might be useful in mitigating the potential for selection of SSG producing hosts. External morphology observations revealed that both fresh root weight and gall diameter of spindle galls were significantly higher than SSGs, and histological observations indicated that delayed pathogen development in cortical infection might contribute to the restricted development of SSGs. Additionally, the number of SSGs formed per root was low (2.2 in average). This observation further confirmed that some host-population combinations cannot form large numbers of SSGs on single roots.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buczacki, S. T., Toxopeus, H., Mattusch, P., Johnston, T. D., Dixon, G. R., & Hobolth, L. A. (1975). Study of physiological specialization in Plasmodiophora brassicae: proposals for attempted rationalization through an international approach. Transactions of British Mycological Society, 65, 295–303.
Chai, A. L., Xie, X. W., Shi, Y. X., & Li, B. J. (2014). Research status of clubroot (Plasmodiophora brassicae) on cruciferous crops in China. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology, 36, 142–153.
Donald, E. C., Cross, S. J., Lawrence, J. M., & Porter, I. J. (2006). Pathotypes of Plasmodiophora brassicae, the cause of clubroot, in Australia. Annals of Applied Biology, 148(3), 239–244.
Kageyama, K., & Asano, T. (2009). Life cycle of Plasmodiophora brassicae. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 28(3), 203–211.
Kobelt, P., Siemens, J., & Sacristán, M. D. (2000). Histological characterisation of the incompatible interaction between Arabidopsis thaliana and the obligate biotrophic pathogen Plasmodiophora brassicae. Mycological Research, 104(2), 220–225.
Kuginuki, Y., Yoshikawa, H., & Hirai, M. (1999). Variation in virulence of Plasmodiophora brassicae in Japan tested with clubroot-resistant cultivars of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). European Journal of Plant Pathol, 105(4), 327–332.
Larson, R. H. (1934). Wound infection and tissue invasion by Plasmodiophora brassicae. Journal of Agricultural Research, 49, 607–624.
Ludwig-Müller, J. (2014). Auxin homeostasis, signaling, and interaction with other growth hormones during the clubroot disease of Brassicaceae. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 9(3), e28593.
Ludwig-Müller, J., & Schuller, A. (2008). What can we learn from clubroots: alterations in host roots and hormone homeostasis caused by Plasmodiophora brassicae. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 121(3), 291–302.
Ludwig-Müller, J., Prinsen, E., Rolfe, S. A., & Scholes, J. D. (2009). Metabolism and plant hormone action during clubroot disease. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 28(3), 229–244.
McDonald, M. R., Sharma, K., Gossen, B. D., Deora, A., Feng, J., & Hwang, S. F. (2014). The role of primary and secondary infection in initiation of resistance to Plasmodiophora brassicae. Phytopathology, 104(10), 1078–1087.
Osaki, K., Tanaka, S., & Ito, S. (2008). Pathogenicity of Plasmodiophora brassicae populations from small, spheroid, resistant-type clubroot galls on roots of clubroot-resistant cultivars of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. subsp. pekinensis). Journal of General Plant Pathology, 74(3), 242–245.
Rennie, D. C., Manolii, V. P., Plishka, M., & Strelkov, S. E. (2013). Histological analysis of spindle and spheroid root galls caused by Plasmodiophora brassicae. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 135(4), 771–781.
Seaman, W. L., Walker, J. C., & Larson, R. H. (1963). A new race of Plasmodiophora brassicae affecting Badger Shipper cabbage. Phytopathology, 53, 1426–1429.
Somé, A., Manzanares, M. J., Laurens, F., Baron, F., Thomas, G., & Rouxel, F. (1996). Variation for virulence on Brassica napus L. amongst Plasmodiophora brassicae collections from France and derived single - spore isolates. Plant Pathology, 45(3), 432–439.
Tanaka, S., & Ito, S. (2013). Pathogenic and genetic diversity in Plasmodiophora brassicae (clubroot) from Japan. Journal of General Plant Pathology, 79(5), 297–306.
Wang, J., Huang, Y., Li, X. L., & Li, H. Z. (2011). Research progress in clubroot of crucifers. Plant Protection, 37(6), 153–158.
Willliams, P. H. (1966). A system for the determination of races of Plasmodiophora brassicae that infect Cabbage and Rutabaga. Phytopathology, 56(6), 624–626.
Xiao, C. G., & Guo, X. H. (2002). Biological characteristic of Plasmodiophora brassicae. Mycosystema, 21(4), 597–603.
Xue, S., Cao, T., Howard, R. J., Hwang, S. F., & Strelkov, S. E. (2008). Isolation and variation in virulence of single-spore isolates of Plasmodiophora brassicae from Canada. Plant Disease, 92(3), 456–462.
Acknowledgments
This study is financially supported by the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (201003029) and National Nature Science Foundation of China (31470098).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Y., Huang, Y., Ye, L. et al. Occurrence and morphology of small spheroid galls on clubroot-resistant Chinese cabbage. Eur J Plant Pathol 145, 591–599 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-016-0925-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-016-0925-7