Abstract
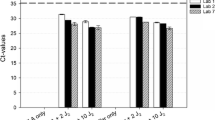
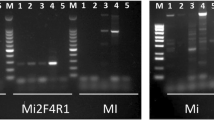
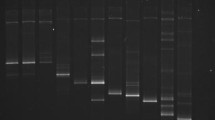
Several conventional PCR tests have been developed for the identification of the European quarantine root-knot nematodes Meloidogyne chitwoodi and M. fallax but data are lacking for the evaluation of their performance in terms of sensitivity, repeatability, reproducibility and specificity against a large range of populations. This study evaluated the performance criteria of three conventional PCR tests recommended by the consensus diagnostic protocol for Meloidogyne chitwoodi and Meloidogyne fallax published by the European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization (EPPO): a species-specific PCR (IGS target), a SCAR PCR, and a rDNA ITS PCR-RFLP. Evaluation was carried out with DNA extracts from juveniles, males and females according to EPPO recommendations for test validation. A minimum of 34 populations of target and non target nematode species were tested to check the specificity of these three PCR assays. The three PCR tests were ranked according to their specificity (with regard to cross reaction with other nematodes species or genus) and their sensitivity (detection of a single juvenile or mixed with other species). The species-specific PCR proved to be more sensitive but less specific than the SCAR PCR. The PCR-RFLP enables the identification of several Meloidogyne species but profile analysis can be difficult when several species are present in the mixture. Specific PCR products and RFLP profiles were also observed for M. arenaria and M. enterolobii, and described for M. minor and M. artiellia.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam, M. A. M., Phillips, M. S., & Blok, V. C. (2007). Molecular diagnostic key for identification of single juveniles of seven common and economically important species of root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp). Plant Pathology, 56, 190–197.
Esbenshade, P. R., & Triantaphyllou, A. C. (1985). Use of enzyme phenotypes for identification of Meloidogyne species. Journal of Nematology, 17(1), 6–20.
Golden, A. M., O’Bannon, J. H., Santo, G. S., & Finley, A. M. (1980). Description and SEM observations of Meloidogyne chitwoodi n. sp. (Meloidogynidae). A root knot nematode on potato in the Pacific Northwest. Journal of Nematology, 12(4), 319–327.
Humphreys-Pereira, D. A., & Elling, A. A. (2013). Intraspecific variability and genetic structure in Meloidogyne chitwoodi from the USA. Nematology, 15(3), 315–327.
Ibrahim, S. K., Perry, R. N., Burrows, P. R., & Hooper, D. J. (1994). Differentiation of species and populations of Aphelenchoides and of Ditylenchus angustus using a fragment of ribosomal DNA. Journal of Nematology, 26(4), 412–421.
Karssen, G. (1996). Description of Meloidogyne fallax n. sp. (Nematoda: Heteroderidae), a root-knot nematode from the Netherlands. Fundamental and Applied Nematology, 19(6), 593–599.
Karssen, G., Van Hoenselaar, T., Verkerk-Bakker, B., & Janssen, R. (1995). Species identification of cyst and root-knot nematodes from potato by electrophoresis of individual females. Electrophoresis, 16, 105–109.
Karssen, G., Bolk, R. J., Van Aelst, A. C., Van Den Beld, I., Kox, L. F. F., Korthals, G., Molendijk, L., Zijlstra, C., Van Hoof, R., & Cook, R. (2004). Description of Meloidogyne minor n. sp. (Nematoda : Meloidogynidae), a root-knot nematode associated with yellow patch disease in golf courses. Nematology, 6(1), 59–72.
OEPP/EPPO. (2009). EPPO Standard PM 7/41 (2). Meloidogyne chitwoodi and Meloidogyne fallax. Bulletin OEPP/EPPO, Bulletin, 39, 5–17.
OEPP/EPPO. (2010). EPPO standard PM 7/98. Specific requirements for laboratories preparing accreditation for a plant pest diagnostic activity. Bulletin OEPP/EPPO, Bulletin, 40, 5–22.
Perry, R. N., Moens, M., & Starr, J. L. (2009). Root-knot nematodes. Wallingford UK: CABI Publishing. 488 pp.
Petersen, D. J., & Vrain, T. C. (1996). Rapid identification of Meloidogyne chitwoodi, M. hapla, and M. fallax using PCR primers to amplify their ribosomal intergenic spacer. Fundamental and Applied Nematology, 19(6), 601–605.
Petersen, D. J., Zijlstra, C., Wishart, J., Blok, V., & Vrain, T. C. (1997). Specific probes efficiently distinguish root-knot nematode species using signature sequences in the ribosomal intergenic spacer. Fundamental and Applied Nematology, 20(6), 619–626.
Powers, T. O., & Harris, T. S. (1993). A polymerase chain reaction method for identification of five major Meloidogyne species. Journal of Nematology, 25(1), 1–6.
Stanton, J., Hugall, A., & Moritz, C. (1997). Nucleotide polymorphisms and an improved PCR-based mtDNA diagnostic for parthenogenetic root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.). Fundamental and Applied Nematology, 20(3), 261–268.
Van Meggelen, J. C., Karssen, G., Janssen, G. J. W., Verkerk-Bakker, B., & Janssen, R. (1994). A new race of Meloidogyne chitwoodi. Fundamental and Applied Nematology, 17(1), 93.
Vrain, T. C., Wakarchuk, D. A., Levesque, A. C., & Hamilton, R. I. (1992). Intraspecific rDNA restriction fragment length polymorphism in the Xiphinema americanun group. Fundamental and Applied Nematology, 15(6), 563–573.
Wishart, J., Phillips, M. S., & Blok, V. C. (2002). Ribosomal intergenic spacer: a polymerase chain reaction diagnostic for Meloidogyne chitwoodi, M. fallax, and M. hapla. Phytopathology, 92(8), 884–892.
Zijlstra, C. (2000). Identification of Meloidogyne chitwoodi, M. fallax and M. hapla based on SCAR-PCR: a powerful way of enabling reliable identification of populations or individuals that share common traits. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 106, 283–290.
Zijlstra, C., & Van Hoof, R. A. (2006). A multiplex real-time polymerase chain reaction (TaqMan) assay for the simultaneous detection of Meloidogyne chitwoodi and M. fallax. Nematology, 96(11), 1255–1262.
Zijlstra, C., Lever, A. E. M., Uenk, B. J., & Van Silfhout, C. H. (1995). Differences between ITS regions of isolates of root-knot nematodes Meloidogyne hapla and M. chitwoodi. Phytopathology, 85(10), 1231–1237.
Zijlstra, C., Uenk, B. J., & Van Silfhout, C. H. (1997). A reliable, precise method to differentiate species of root-knot nematodes in mixtures on the basis of ITS-RFLPs. Fundamental and Applied Nematology, 20(1), 59–63.
Acknowledgments
This assessment study was both funded by the French Federation of Seed Potato Growers (FN3PT) and the French Ministry in charge of agriculture. We would like to thank the French National Institute for Agricultural Research (INRA) unit 1303 based in Sophia Antipolis (France), the Oregon State University, the University of Idaho in Florida or Florida Department of Agriculture & Consumer Services and the Belgian Institute for Agricultural and Fisheries Research for providing us with nematode populations or DNA solutions used in this study. The authors also wish to thank Dr R. Ioos and Dr E. Grenier for their helpful review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gamel, S., Huchet, E., Le Roux-Nio, AC. et al. Assessment of PCR-based tools for the specific identification of some temperate Meloidogyne species including M. chitwoodi, M. fallax and M. minor . Eur J Plant Pathol 138, 807–817 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-013-0355-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-013-0355-8