Abstract
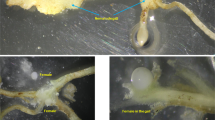
Seven root-knot nematodes (RKN), including Meloidogyne exigua, M. incognita, M. paranaensis, M. enterolobii, M. arabicida, M. izalcoensis and M. arenaria are major pathogens of coffee crop in the Americas. Species-specific primers for their identification have been developed for five of them and constitute a fast and reliable method of identification. Here we report a PCR-based assay for specific detection of M. arabicida and M. izalcoensis. Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA fragments specific for these two species were converted into sequence characterized amplified region (SCAR) markers. PCR amplification using the SCAR primers produced a specific fragment of 300 bp and 670 bp for M. arabicida and M. izalcoensis, respectively, which were absent in other coffee-associated Meloidogyne spp. tested. SCAR primers also allowed successful amplification of DNA from single second-stage juveniles (J2), males and females. In addition, these primers were able to unambiguously detect the target species in nematode suspensions extracted from soil and roots samples, in different isolates of the same species or when used in multiplex PCR reactions containing mixtures of species. These results demonstrated the effectiveness of these SCAR markers and their multiplex use with those previously developed for M. exigua, M. incognita, M. paranaensis, M. enterolobii and M. arenaria constitute an essential detection tool. This diagnostic kit will contribute for specific J2 identification of the major RKN infecting coffee from field samples in the Americas.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbosa, D. H. S. G., Viera, H. D., Souza, R. M., Vianaand, A. P., & Silca, C. P. (2004). Field estimates of coffee yield losses and damage threshold by Meloidogyne exigua. Nematologia Brasileira, 28, 49–54.
Berry, S. D., Fargette, M., Spaull, V. W., Morand, S., & Cadet, P. (2008). Detection and quantification of root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne javanica), lesion nematode (Pratylenchus zeae) and dagger nematode (Xiphinema elongatum) parasites of sugarcane using real-time PCR. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 22, 168–176.
Blok, V. C., & Powers, O. (2009). Biochemical and molecular identification. In R. Perry, M. Moens, & J. L. Starr (Eds.), Root knot nematodes (pp. 98–118). Cambridge: CABI International.
Campos, V. P., & Villain, L. (2005). Nematode parasites of coffee and cocoa. In M. Luc, R. Sikora, & J. Bridge (Eds.), Plant parasitic nematodes in subtropical and tropical agriculture (pp. 529–579). Wallingford: CABI International.
Campos, V. P., Sivapalan, P., & Gnanapragasam, N. C. (1990). Nematode parasites of coffee, cocoa and tea. In M. Luc, R. A. Sikora, & J. Bridge (Eds.), Plant parasitic nematodes in subtropical and tropical agriculture (pp. 387–430). Wallingford: CABI International.
Carneiro, R. M. D. G., & Almeida, M. R. A. (2001). Técnica de eletroforese usada no estudo de enzimas dos nematoides de galhas para identificação de espécies. Nematologia Brasileira, 25, 555–560.
Carneiro, R. M. D. G., & Cofcewicz, E. T. (2008). The taxonomy of coffee-parasitic root-knot nematodes Meloidogyne spp. In R. M. Souza (Ed.), Plant parasitic nematodes of coffee (pp. 87–122). Dordrecht: Springer.
Carneiro, R. M. D. G., Carneiro, R. G., Abrantes, I. M. O., Santos, M. S. N. A., & Almeida, M. R. A. (1996a). Meloidogyne paranaensis n. sp. (Nemata: Meloidogynidae), a root-knot nematode parasitizing coffee in Brazil. Journal of Nematology, 28, 177–189.
Carneiro, R. M. D. G., Almeida, M. R. A., & Carneiro, R. G. (1996b). Enzyme phenotypes of Brazilian isolates of Meloidogyne spp. Fundamental and Applied Nematology, 19, 555–560.
Carneiro, R. M. D. G., Almeida, M. R. A., & Quénéhervé, P. (2000). Enzyme phenotypes of Meloidogyne spp. isolates. Nematology, 2, 645–654.
Carneiro, R. M. D. G., Tigano, M. S., Randig, O., Almeida, M. R. A., & Sarah, J. L. (2004). Identification and genetic diversity of Meloidogyne spp. (Tylenchida: Meloidogynidae) on coffee from Brazil, Central America and Hawaii. Nematology, 6, 287–298.
Carneiro, R. M. D. G., Almeida, M. R. A., Gomes, A. C. M. M., & Hernandez, A. (2005a). Meloidogyne izalcoensis n.sp. (Nematoda: Meloidogynidae), a root-knot nematode parasitizing coffea in El Salvador. Nematology, 7, 819–832.
Carneiro, R. M. D. G., Randig, O., Almeida, M. R. A., & Gonçalves, W. (2005b). Identificação e caracterização de espécies de Meloidogyne em cafeeiros nos Estados de São Paulo e Minas Gerais através dos fenótipos de esterase e SCAR-multiplex PCR. Nematologia Brasileira, 29, 233–241.
Cenis, J. L. (1993). Identification of four major Meloidogyne spp. by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD-PCR). Phytopathology, 83, 76–80.
Esbenshade, P. R., & Triantaphyllou, A. C. (1985). Identification of major Meloidogyne species employing enzyme phenotypes as differentiating characters. In J. N. Sasser & C. C. Carter (Eds.), An advanced treatise on Meloidogyne (Biology and control, Vol. I, pp. 135–140). Raleigh: North Carolina State University Graphics.
Esbenshade, P. R., & Triantaphyllou, A. C. (1990). Isozyme phenotypes for the identification of Meloidogyne species. Journal of Nematology, 22, 10–15.
Harris, T. S., Sandal, L. J., & Power, T. O. (1990). Identification of single Meloidogyne juveniles by polymerase chain reaction amplification of mitochondrial DNA. Journal of Nematology, 22, 518–524.
Hernandez, A., Fargette, M., & Sarah, J. L. (2004). Characterization of Meloidogyne spp. (Tylenchida: Meloidogynidae) from coffee plantations in Central America and Brazil. Nematology, 6, 193–204.
Holterman, M., Van Der Wurff, A., Van Den Elsen, S., Van Megen, H., Bongers, T., Holovachov, O., et al. (2006). Phylum-wide analysis of SSU rDNA reveals deep phylogenetic relationships among nematodes and accelerated evolution toward crown clades. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 23, 1792–1800.
Lopez, R., & Salazar, L. (1989). Meloidogyne arabicida sp. n. (Nemata: Heteroderidae) nativo de Costa Rica: um nuevo y severo patógeno del cafeto. Turrialba, 39, 313–323.
McClure, M., Kruk, T. H., & Migashi, I. (1973). A method for obtaining quantities of clear Meloidogyne eggs. Journal of Nematology, 5, 230.
Meng, Q. P., Long, H., & Xu, J. H. (2004). PCR assays for rapid and sensitive identification of three major root-knot nematodes, Meloidogyne incognita, M. javanica and M. arenaria. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 34, 204–210.
Randig, O., Bongiovanni, M., Carneiro, R. M. D. G., & Castagnone-Sereno, P. (2002). Genetic diversity of root-knot nematodes from Brazil and development of SCAR markers specific for the coffee-damaging species. Genome, 45, 862–870.
Randig, O., Carneiro, R. M. D. G., & Castagnone-Sereno, P. (2004). Identificação das principais especies de Meloidogyne parasitas do cafeeiro no Brasil com marcadores SCAR-CAFÉ em Multiplex-PCR. Nematologia Brasileira, 28, 1–10.
Rodriguez, M. G., Rodriguez, I., & Sanchez, L. (1995). Especies del genero Meloidogyne que parasitan el cafeto en Cuba. Distribucion geografica y sintomatologia. Revista de Proteccion Vegetal, 10, 123–128.
Rozen, S., & Skaletsky, H. J. (2000). Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In S. Krawetz & S. Misener (Eds.), Bioinformatics methods and protocols: methods in molecular biology (pp. 365–386). Totowa: Humana Press.
Skantar, A. M., & Carta, L. K. (2005). Multiple displacement amplification (MDA) of total genomic DNA from Meloidogyne spp. and comparison to crude DNA extracts in PCR of ITS1, 28S D2-D3 rDNA and Hsp90. Nematology, 7, 285–293.
Tautz, D., Arctander, P., Minelli, A., Thomas, R. H., & Vogler, A. P. (2003). A plea for DNA taxonomy. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 18, 70–74.
Tigano, M. S., Carneiro, R. M. D. G., Jeyaprakash, A., Dickson, D. W., & Adams, B. J. (2005). Phylogeny of Meloidogyne spp. based on 18S rDNA and the intergenic region of mitocrondrial DNA sequences. Nematology, 7, 851–862.
Tigano, M. S., Siqueira, K., Castagnone-Sereno, P., Mulet, K., Queiroz, P., Santos, M., et al. (2010). Genetic diversity of the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne enterolobii and development for SCAR marker for this guava-damaging species. Plant Pathology, 59, 1054–1061.
Villain, L., Hernandez, A., & Anzueto, F. (2008). Central America. In R. M. Souza (Ed.), Plant parasitic nematodes of coffee (pp. 261–275). Dordrecht: Springer.
Yang, B., & Eisenback, J. D. (1983). Meloidogyne enterolobii n. sp. (Meloidogynidae), a root-knot nematode parasitizing pacara earpod tree in China. Journal of Nematology, 15, 381–391.
Zijlstra, C. (2000). Identification of Meloidogyne chitwoodi, M. fallax and M. hapla based on SCAR–PCR: a powerful way of enabling reliable identification of populations or individuals that share common traits. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 106, 283–290.
Zijlstra, C., Donkers-Venne, D. T. H. M., & Fargette, M. (2000). Identification of Meloidogyne incognita, M. javanica and M. arenaria using sequence characterized amplified regions (SCAR) based PCR assays. Nematology, 2, 847–853.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Brazilian agencies Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and EMBRAPA—Recursos Genéticos e Biotecnologia. V.R. Correa and M.F.A. Santos thank CAPES for their scholarships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Valdir Ribeiro Correa and Marcilene Fernandes Almeida dos Santos contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Correa, V.R., dos Santos, M.F.A., Almeida, M.R.A. et al. Species-specific DNA markers for identification of two root-knot nematodes of coffee: Meloidogyne arabicida and M. izalcoensis . Eur J Plant Pathol 137, 305–313 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-013-0242-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-013-0242-3