Abstract
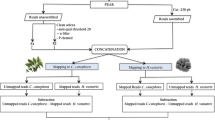
One of the phytosanitary problems of coffee cultivation in Brazil is Coffee Leaf Scorch (CLS) disease, caused by the phytopathogenic bacterium Xylella fastidiosa. Due to the economic importance of coffee to Brazil and the losses caused by X. fastidiosa, a cDNA library (RX1) was constructed using infected coffee stems. This library is one of the 37 coffee EST libraries constructed using different organs and tissues and biological conditions (Coffee Genome Project-CafEST). The objective of this study was to identify genes potentially involved in defence processes in response to X. fastidiosa infection by in silico analysis of the transcripts from the RX1 library as well as compare the coffee ESTs to citrus Xylella-infected ESTs. Clustering analysis of the RX1 library grouped a total of 7,501 sequences into 3,248 contigs, 19 of which were not found in the other 36 libraries. Additionally, 119 contigs were considered differentially expressed in comparison with the other libraries and according to statistical criteria. The global analysis of these contigs showed several genes involved in dehydration and photosynthesis. A total of 2,235 singlets were also obtained in the RX1 library and several of these genes are classically involved in defence processes. The comparison to a Xylella-infected citrus EST library revealed several genes similarly modulated in both species, indicating common defence mechanisms in both host plants in response to X. fastidiosa. The results obtained showed that water deprivation and response to osmotic and oxidative stress were expressed in a similar way in both coffee and citrus libraries. This is the first study to propose a common mechanism shared by citrus and coffee plants in response to the same pathogen.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe, H., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K., Urao, T., Iwasaki, T., Hosokawa, D., & Shinozaki, K. (1997). Role of Arabidopsis MYC and MYB homologs in drought-and abscisic acid-regulated gene expression. The Plant Cell, 9, 1859–1868.
Almeida, R. P., Nascimento, F. E., Chau, J., Prado, S. S., Tsai, C. W., Lopes, S. A., et al. (2008). Genetic structure and biology of Xylella fastidiosa strains causing disease in citrus and coffee in Brazil. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74, 3690–3701.
Altschul, S., Madden, T., Schaffer, A., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Mille, W., et al. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST, A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 3389–3402.
Ashburner, M., Ball, C. A., Blake, J. A., Botstein, D., Butler, H., Cherry, J. M., et al. (2000). Gene Ontology, tool for the unification of biology. Nature Genetics, 25, 25–29.
Audic, S., & Claverie, J. M. (1997). The significance of digital gene expression profiles. Genome Research, 7, 986–995.
Baiges, I., Schaffner, A. R., Affenzeller, M. J., & Mas, A. (2002). Plant aquaporins. Plant Physiology, 115, 175–182.
Balaji, V., Gibly, A., Debbie, P., & Sessa, G. (2007). Transcriptional analysis of the tomato resistance response triggered by recognition of the Xanthomonas type III effector AvrXv3. Functional & Integrative Genomics, 4, 305–316.
Biemelt, S., & Sonnewald, U. (2006). Plant-microbe interactions to probe regulation of plant carbon metabolism. Journal of Plant Physiology, 163, 307–318.
Bohnert, H. J., Nelson, D. E., & Jensen, R. G. (1995). Adaptations to environmental stresses. The Plant Cell, 7, 1099–1111.
Bonfig, K. B., Schreiber, U., Gabler, A., Roitsch, T., & Berger, S. (2006). Infection with virulent and avirulent P. syringae strains differentially affects photosynthesis and sink metabolism in Arabidopsis leaves. Planta, 225, 1–12.
Chen, H., & Vierling, R. A. (2000). Molecular cloning and characterization of soybean peroxidase gene families. Plant Science, 150, 129–137.
Chen, S., Vaghchhipawala, Z., Li, W., Asard, H., & Dickman, M. B. (2004). Tomato phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase inhibits cell death induced by bax and oxidative stresses in yeast and plants. Plant Physiology, 135, 1630–1641.
Collinge, D. B., Kragh, K. M., Mikkelsen, J. D., Nielsen, K. K., Rasmussen, U., & Vad, K. (1993). Plant chitinases. The Plant Journal, 3, 31–40.
Coupland, G., & Prat Monguio, S. (2005). Cell signalling and gene regulation signalling mechanisms in plants, examples from the present and the future. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 8, 457–461.
D’Souza, C. A., Chopra, V., Varhol, R., Xie, Y. Y., Bohacec, S., Zhao, Y., et al. (2008). Identification of a set of genes showing regionally enriched expression in the mouse brain. BMC Neuroscience, 9, 66–80.
De Negri, J. D. (1990). Clorose variegada dos citros, Nova anomalia afetando pomares em São Paulo e Minas Gerais. Comunicado Técnico n° 82, CATI Campinas, 6p.
De Souza, A. A., Takita, M. A., Coletta-Filho, H. D., Targon, M. L. P. N., Carlos, F. E., Locali-Fabris, E. C., et al. (2007). Analysis of expressed sequence tags from Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck infected with Xylella fastidiosa. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 30, 957–964.
De Souza, A. A., Takita, M. A., Coletta-Filho, H. D., Campos, M. A., Teixeira, E. C. J., Targon, M. L. P. N., et al. (2007). Comparative analysis of differentially expressed sequence tags of sweet orange and mandarin infected with Xylella fastidiosa. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 30, 965–971.
Dietz, K. J., Jacob, S., Oelze, M. L., Laxa, M., Tognetti, V., de Miranda, S. M., et al. (2006). The function of peroxiredoxins in plant organelle redox metabolism. Journal of Experimental Botany, 57, 1697–1709.
Espinoza, C., Vega, A., Medina, C., Schlauch, K., Cramer, G., & Arce-Johnson, P. (2007). Gene expression associated with compatible viral diseases in grapevine cultivars. Functional & Integrative Genomics, 7, 95–110.
Fung, R. W., Gonzalo, M., Fekete, C., Kovacs, L. G., He, Y., Marsh, E., et al. (2008). Powdery mildew induces defense-oriented reprogramming of the transcriptome in a susceptible but not in a resistant grapevine. Plant Physiology, 146, 236–249.
Gibly, A., Bonshtien, A., Balaji, V., Debbie, P., Martin, G. B., & Sessa, G. (2004). Identification and expression profiling of tomato genes differentially regulated during a resistance response to Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 17, 1212–1222.
Gomes, M. M. A., Lagôa, A. M. M. A., Machado, E. C., & Medina, C. L. (2003). Abscisic acid and indole-3-acetic acid contents in orange trees infected by Xylella fastidiosa and submitted to cycles of water stress. Plant Growth Regulation, 39, 263–270.
Guidetti-Gonzalez, S., Freitas-Astúa, J., do Amaral, A. M., Martins, N. F., Mehta, A., Silva, M. S., et al. (2007). Genes associated with hypersensitive response (HR) in the citrus EST (CitEST) database. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 30, 943–956.
Han, J. Y., Park, T. S., Kim, J. N., Kim, M. A., Lim, D., Lim, J. M., et al. (2006). Gene expression profiling of chicken primordial germ cell ESTs. BMC Genomics, 7, 220–226.
Jelitto-Van Dooren, E. P., Vidal, S., & Denecke, J. (1999). Anticipating endoplasmic reticulum stress. A novel early response before pathogenesis-related gene induction. Plant Cell, 11, 1935–1944.
Jones, J. D. G., & Dangl, J. L. (2006). The plant immune system. Nature, 444, 323–329.
Kieselbach, T., Bystedt, M., Hynds, P., Robinson, C., & Schroder, W. P. (2000). A peroxidase homologue and novel plastocyanin located by proteomics to the Arabidopsis chloroplast thylakoid lumen. FEBS Letters, 480, 271–276.
Kong, L., Ohm, H. W., & Anderson, J. M. (2007). Expression analysis of defense-related genes in wheat in response to infection by Fusarium graminearum. Genome, 50, 1038–1048.
Li, W. B., Pria, W. D., Teixeira, D. C., Miranda, V. S., Ayres, A. J., Franco, C. F., et al. (2001). Coffee leaf scorch caused by a strain of Xylella fastidiosa from citrus. Plant Disease, 85, 501–505.
Liavonchanka, A., & Feussnerm, I. (2006). Lipoxygenases, Occurrence, functions and catalysis. Journal of Plant Physiology, 163, 348–357.
Lima, J. E. O., de Miranda, V. S., Coutinho, A., Roberto, S. R., & Carlos, E. F. (1996). Distribuição de Xylella fastidiosa no cafeeiro nas regiões cafeeiras, e seu isolamento in vitro. Fitopatologia Brasileira, 21, 392–393.
Martin, D., Brun, C., Remy, E., Mouren, P., Thieffry, D., & Jacq, B. (2004). GOToolBox, functional analysis of gene datasets based on Gene Ontology. Genome Biology, 5, R101.
Matiello, J. B., Miranda, V. S., Almeida, S. R., & Manfio, G. P. (1998). “Amarelinho” ou requeima das folhas do cafeeiro, conheça e tome cuidado. Boletim Informativo Fund. André Tosello-CTC/Fundecitrus.
Melillo, M. T., Leonetti, P., Bongiovanni, M., Castagnone-Sereno, P., & Bleve-Zacheo, T. (2006). Modulation of reactive oxygen species activities and H2O2 accumulation during compatible and incompatible tomato–root-knot nematode interactions. The New Phytologist, 170, 501–512.
Milhomem, A. V. & Teixeira, S. M. (2001). Competitividade dos sistemas produtivos de cafés no Brasil. Simpósio Brasileiro de Pesquisa dos Cafés do Brasil (Vitória, ES). Anais. Brasília, D.F. Embrapa Café (CD-ROM), 2136–2144.
Mondego, J. M., Vidal, R. O., Carazzolle, M. F., Tokuda, E. K., Parizzi, L. P., Costa, G. G., et al. (2011). An EST-based analysis identifies new genes and reveals distinctive gene expression features of Coffea arabica and Coffea canephora. BMC Plant Biology, 11. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-11-30.
Montero-Astua, M., Hartung, J. S., Aguilar, E., Chacon, C., Li, W., Albertazzi, F., et al. (2008). Genetic diversity of Xylella fastidiosa isolates from Costa Rica, Sao Paulo and the United States of America. Phytopathology, 97, 1338–1347.
Moy, P., Qutob, D., Chapman, B. P., Atkinson, I., & Gijzen, M. (2004). Patterns of gene expression upon infection of soybean plants by Phytophthora sojae. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 17, 1051–1062.
Murray, D., Doran, P., MacMathuna, P., & Moss, A. C. (2007). In silico gene expression analysis – an overview. Molecular Cancer, 6, 50–60.
Okubo, K., Hori, N., Matoba, R., Nuyama, T., Fukushima, A., Kojima, Y., et al. (1992). Large scale cDNA sequencing for analysis of quantitative and qualitative aspects of gene expression. Nature Genetics, 2, 173–179.
Paradela Filho, O., Sugimori, M. H., Ribeiro, I. J. A., Machado, M. A., Laranjeira, F. F., Garcia Júnior, A., et al. (1995). Primeira constatação em cafeeiro no Brasil da Xylella fastidiosa causadora da clorose variegada dos citrus. Laranja, 16, 127–134.
Preston, G. M., Carroll, T. P., Guggino, W. B., & Agree, P. (1992). Appearance of water channels in Xenopus oocytes expressing red cell CHIP28 protein. Science, 256, 385–387.
Rehman, S., Postma, W., Tytgat, T., Prins, P., Qin, L., Overmars, H., et al. (2009). A secreted SPRY domain-containing protein (SPRYSEC) from the plant-parasitic nematode Globodera rostochiensis interacts with a CC-NB-LRR protein from a susceptible tomato. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 22, 330–340.
Restrepo, S., Myers, K. L., del Pozo, O., Martin, G. B., Hart, A. L., Buell, C. R., et al. (2005). Gene profiling of a compatible interaction between Phytophthora infestans and Solanum tuberosum suggests a role for carbonic anhydrase. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 18, 913–922.
Rossetti, V., Garnier, M. B., Bove, J. M., Beretta, M. J. G., Teixeira, A. R. R., Quaggio, J. Á., et al. (1990). Présence de bactéries dans le xyléme d’orangers atteints de chlorose variégée une nouvelle maladie des agrumes au Brésil. Les Comptes Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences Paris, 310, 345–349.
Sagi, M., & Fluhr, R. (2006). Production of reactive oxygen species by plant NADPH oxidases. Plant Physiology, 141, 336–340.
Scholes, J. D., Lee, P. J., Horton, P., & Lewis, D. H. (1994). Invertase, understanding changes in the photosynthetic and carbohydrate metabolism of barley leaves with powdery mildew. The New Phytologist, 126, 213–222.
Shao, H. B., Chu, L. Y., Shao, M. A., Jaleel, C. A., & Mi, H. M. (2008). Higher plant antioxidants and redox signaling under environmental stresses. Comptes Rendus Biologies, 331, 433–441.
Siefritz, F., Tyree, M. T., Lovisolo, C., Schubert, A., & Kaldenhoff, R. (2002). PIP1 plasma membrane aquaporins in tobacco, from cellular effects to function in plants. The Plant Cell, 14, 869–876.
Simpson, A. J., Reinach, F. C., Arruda, P., et al. (2000). The genome sequence of the plant pathogen Xylella fastidiosa. The Xylella fastidiosa Consortium of the organization for nucleotide sequencing and analysis. Nature, 406, 151–157.
Targon, M. L. P. N., Takita, M. A., Amaral, A. M., Souza, A. A., Locali, E. C., Dorta, S. O., et al. (2007). CITEST libraries. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 30, 1019–1023.
Tyerman, S. D., Niemietz, C. M., & Bramley, H. (2002). Plant aquaporins, multifunctional water and solute channels with expanding roles. Plant, Cell & Environment, 25, 173–194.
Ueno, B., & Leite, J. R. P. (1996). Estudo da variabilidade de isolados de Xylella fastidiosa obtidos de cafeeiro e citros através da análise de proteínas totais. Fitopatologia Brasileira, 21, 341.
Vieira, L., Andrade, A., Colombo, C., Moraes, A., Mehta, A., et al. (2006). Brazilian coffee genome project, an EST-based genomic resource. Brazilian Journal of Plant Physiology, 18, 95–108.
Yamada, S., Komori, T., Myers, P. N., Kuwata, S., Kubo, T., & Imaseki, H. (1997). Expression of plasma membrane water channel genes under water stress in Nicotiana excelsior. Plant & Cell Physiology, 38, 1226–1231.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Table 1
Differentially expressed genes of the RX1 library, when compared (XLS 48 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carazzolle, M.F., Rabello, F.R., Martins, N.F. et al. Identification of defence-related genes expressed in coffee and citrus during infection by Xylella fastidiosa . Eur J Plant Pathol 130, 529–540 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-011-9775-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-011-9775-5