Abstract
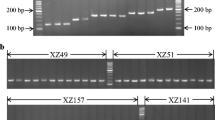
The chorismate mutase gene is widely distributed in both cyst and root-knot nematode species and believed to play a critical role in nematode parasitism. In this study, we cloned a new chorismate mutase gene (Gt-cm-1) from Globodera tabacum and further characterized the gene structure in both G. tabacum and G. pallida, a closely related species of G. rostochiensis. The genomic clones of chorismate mutase genes from these two species were found to contain three introns with the second intron having unusual 5’ and 3’ splice sites. A previous study revealed that the chorismate mutase gene from G. rostochiensis is subject to alternative splicing through retention of intron 2, a process that allows for the generation of multiple mRNA transcripts from a single gene. As expected, we discovered that alternative splicing of the chorismate mutase gene is a conserved event in three Globodera species, supporting an important role of alternative splicing in regulating chorismate mutase gene function in plant parasitism by these nematodes. In addition to the potential suboptimal 5’ and 3’ splice sites and the small size of intron 2, detailed sequence analysis also identified candidate cis-acting elements that might be responsible for regulating intron retention of Globodera chorismate mutase genes. Based on genomic sequence variations observed, we developed TaqMan qPCR assays that provided a highly specific and sensitive identification of each Globodera species, revealing a new application of using the chorismate mutase gene as a valuable diagnostic marker for plant-parasitic nematodes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AS:
-
alternative splicing
- CM :
-
chorismate mutase
- ESE:
-
exonic splicing enhancer
- Gr-cm-1 :
-
Globodera rostochiensis chorismate mutase gene
- Gp-cm-1 :
-
Globodera pallida chorismate mutase gene
- Gt-cm-1 :
-
Globodera tabacum chorismate mutase gene
- LNA:
-
locked nucleic acids
- PCN:
-
potato cyst nematode
- qPCR:
-
quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- TCN:
-
tobacco cyst nematode
References
Bates, J. A., Taylor, E. J. A., Gans, P. T., & Thomas, J. E. (2002). Determination of relative proportions of Globodera species in mixed populations of potato cyst nematodes using PCR product melting peak analysis. Molecular Plant Pathology, 3, 153–161.
Bélair, G., & Miller, S. (2006). First report of Globodera tabacum infecting tobacco plants in Quebec, Canada. Plant Disease, 90, 527.
Blencowe, B. J. (2006). Alternative splicing: new insights from global analyses. Cell, 126, 37–47.
Blumenthal, T., & Steward, K. (1997). RNA processing and gene structure. In D. L. Riddle, T. Blumenthal, B. J. Meyer, & J. R. Priess (Eds.), C. ELEGANS II (pp. 117–145). New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Bulman, S. R., & Marshall, J. W. (1997). Differentiation of Australasian potato cyst nematode (PCN) populations using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). New Zealand Journal of Crop and Horticultural Science, 25, 123–129.
Cartegni, L., Wang, J., Zhu, Z., Zhang, M. Q., & Krainer, A. R. (2003). ESEfinder: a web resource to identify exonic splicing enhancers. Nucleic Acids Research, 31, 3568–3571.
Davis, E. L., Hussey, R. S., & Baum, T. J. (2004). Getting to the roots of parasitism by nematodes. Trends in Parasitology, 20, 134–141.
Doyle, E. A., & Lambert, K. N. (2003). Meloidogyne javanica chorismate mutase 1 alters plant cell development. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 16, 123–131.
Dye, B. T., Buvoli, M., Mayer, S. A., Lin, C.-H., & Patton, J. G. (1998). Enhancer elements activate the weak 3’ splice site of α-tropomyosin exon 2. RNA, 4, 1523–1536.
Grenier, E., Bossis, M., Fouville, D., Renault, L., & Mugniéry, D. (2001). Molecular approaches to the taxonomic position of Peruvian potato cyst nematodes and gene pool similarities in indigenous and important populations of Globodera. Heredity, 86, 277–290.
Jones, J. T., Furlanetto, C., Bakker, E., Banks, B., Blok, V., Chen, Q., et al. (2003). Characterization of a chorismate mutase from the potato cyst nematode Globodera pallida. Molecular Plant Pathology, 4, 43–50.
Kabat, J. L., Barberan-Soler, S., McKenna, P., Clawson, H., Farrer, T., & Zahler, A. M. (2006). Intronic alternative splicing regulators identified by comparative genomics in nematodes. PLoS Computational Biology, 2, e86.
Kim, E., Magen, A., & Ast, G. (2007). Different levels of alternative splicing among eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Research, 35, 125–131.
Lejeune, F., Cavaloc, Y., & Stevenin, J. (2001). Alternative splicing of intron 3 of the serine/arginine-rich protein 9G8 gene. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 7850–7858.
Lu, S.-W., Tian, D., Borchardt-Wier, H. B., & Wang, X. (2008). Alternative splicing: A novel mechanism of regulation identified in the chorismate mutase gene of the potato cyst nematode Globodera rostochiensis. Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology, 162, 1–15.
Madani, M., Ward, L. J., & De Boer, S. H. (2008). Multiplex real-time polymerase chain reaction for identifying potato cyst nematodes, Globodera pallida and Globodera rostochiensis, and the tobacco cyst nematode, Globodera tabacum. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology, 30, 554–564.
Marché, L., Valette, S., Grenier, E., & Mugniéry, D. (2001). Intraspecies DNA polymorphism in the tobacco cyst-nematode complex (Globodera tabacum) using AFLP. Genome, 44, 941–946.
Mercado, P. A., Ayala, Y. M., Romano, M., Buratti, E., & Baralle, F. E. (2005). Depletion of TDP 43 overrides the need for exonic and intronic splicing enhancers in the human apoA-II gene. Nucleic Acids Research, 33, 6000–6010.
Nielsen, H., Engelbrecht, J., Brunak, S., & von Heijne, G. (1997). Identification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic signal peptides and prediction of their cleavage sites. Protein Engineering, 10, 1–6.
Powers, T. O., Todd, T. C., Burnell, A. M., Murray, P. C. B., Fleming, C. C., Szalanski, A. L., et al. (1997). The rDNA internal transcribed spacer region as a taxonomic marker for nematodes. Journal of Nematology, 29, 441–450.
Sakabe, N. J., & de Souza, S. J. (2007). Sequence features responsible for intron retention in human. BMC Genomics, 8, 59.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., & Maniatis, T. (Eds.). (1989). Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Skantar, A. M., Handoo, Z. A., Carta, L. K., & Chitwood, D. J. (2007). Morphological and molecular identification of Globodera pallida associated with potato in Idaho. Journal of Nematology, 39, 133–144.
Soller, M. (2006). Pre-messenger RNA processing and its regulation: a genomic perspective. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 63, 796–819.
Sun, F., Miller, S., Wood, S., & Côté, M.-J. (2007). Occurance of potato cyst nematode, Globodera rostochiensis, on potato in the Saint-Amable region, Quebec, Canada. Plant Disease, 91, 908.
Syracuse, A. J., Johnson, C. S., Eisenback, J. D., Nessler, C. L., & Smith, E. P. (2004). Intraspecific variability within Globodera tabacum solanacearum using random amplified polymorphic DNA. Journal of Nematology, 36, 433–439.
Thiéry, M., & Mugniéry, D. (1996). Interspecific rDNA restriction fragment length polymorphism in Globodera species, parasites of Solanaceous plants. Fundamental and Applied Nematology, 19, 471–479.
Voelker, R. B., & Berglund, A. J. (2010). A comprehensive computational characterization of conserved mammalian intronic sequences reveals conserved motifs associated with constitutive and alternative splicing. Genome Research, 17, 1023–1033.
Wang, B. B., & Brendel, V. (2006). Genomewide comparative analysis of alternative splicing in plants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences in the United States of America, 103, 7175–7180.
Wang, X., Allen, R., Ding, X., Goellner, M., Maier, T., de Boer, J. M., et al. (2001). Signal peptide-selection of cDNA cloned directly from the esophageal gland cells of the soybean cyst nematode Heterodera glycines. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 14, 536–544.
Zahler, A.M. (2005). Alternative splicing in C. elegans. The C. elegans Research Community. WormBook. doi/10.1895/wormbook.1.31.1. http//www.wormbook.org.
Acknowledgements
We thank Melissa G. Mitchum for providing TCN and for critical review of this manuscript. We thank Eric Grenier for providing DNA from G. pallida populations originated from South Peru, Switzerland and UK, Geert Smant for providing DNA from PCN populations originated from the Netherlands, Guy Bélair for providing DNA from G. rostochiensis populations originated from St.-Amable, Canada, Solke De Boer for providing DNA from PCN populations originated from Newfoundland, Canada, Robert Zemetra for providing G. pallida cysts originated from Idaho, U.S.A., and Eric Davis for providing Heterodera glycines and a second TCN population from North Carolina, U.S.A. This study was supported in part by funding from USDA-ARS and USDA-APHIS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Chronis, D., Lu, S. et al. Chorismate mutase: an alternatively spliced parasitism gene and a diagnostic marker for three important Globodera nematode species. Eur J Plant Pathol 129, 89–102 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-010-9695-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-010-9695-9