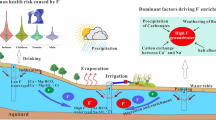
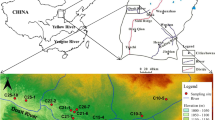
Abstract
Nitrate pollution in aquatic ecosystems has received growing concern, particularly in fragile karst basins. In this study, hydrochemical compositions, multiple stable isotopes (δ2H–H2O, δ18Ο–Η2Ο, δ15Ν–ΝΟ3−, and δ18Ο–ΝΟ3−), and Bayesian stable isotope mixing model (MixSIAR) were applied to elucidate nitrate pollution sources in groundwater of the Yangzhuang Basin. The Durov diagram identified the dominant groundwater chemical face as Ca–HCO3 type. The NO3− concentration ranged from 10.89 to 90.45 mg/L (average 47.34 mg/L), showing an increasing trend from the upstream forest and grassland to the downstream agricultural dominant area. It is worth noting that 47.2% of groundwater samples exceeded the NO3− threshold value of 50 mg/L for drinking water recommended by the World Health Organization. The relationship between NO3−/Cl− and Cl− ratios suggested that most groundwater samples were located in nitrate mixed endmember from agricultural input, soil organic nitrogen, and manure & sewage. The Self-Organizing Map (SOM) and Pearson correlations analysis further indicated that the application of calcium fertilizer, sodium fertilizer, and livestock and poultry excrement in farmland elevated NO3− level in groundwater. The output results of the MixSIAR model showed that the primary sources of NO3− in groundwater were soil organic nitrogen (55.3%), followed by chemical fertilizers (28.5%), sewage & manure (12.7%), and atmospheric deposition (3.4%). Microbial nitrification was a dominant nitrogen conversion pathway elevating NO3− levels in groundwater, while the denitrification can be neglectable across the study area. The human health risk assessment (HHRA) model identified that about 88.9%, 77.8%, 72.2%, and 50.0% of groundwater samples posing nitrate's non-carcinogenic health hazards (HQ > 1) through oral intake for infants, children, females, and males, respectively. The findings of this study can offer useful biogeochemical information on nitrogen pollution in karst groundwater to support sustainable groundwater management in similar human-affected karst regions.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Biddau, R., Dore, E., Da Pelo, S., Lorrai, M., Botti, P., Testa, M., & Cidu, R. (2023). Geochemistry, stable isotopes and statistic tools to estimate threshold and source of nitrate in groundwater (Sardinia, Italy). Water Research, 232, 119663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.119663
Casciotti, K. L., Sigman, D. M., Hastings, M. G., Böhlke, J. K., & Hilkert, A. (2002). Measurement of the oxygen isotopic composition of nitrate in seawater and freshwater using the Denitrifier method. Analytical Chemistry, 74, 4905–4912. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac020113w
Chen, J., Wang, S., Zhang, S., Bai, Y., Zhang, X., Chen, D., & Hu, J. (2023a). Identifying the hydrochemical features, driving factors, and associated human health risks of high-fluoride groundwater in a typical Yellow River floodplain, North China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 45, 8709–8733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01748-9
Chen, R., Hu, Q., Shen, W., Guo, J., Yang, L., Yuan, Q., Lu, X., & Wang, L. (2023b). Identification of nitrate sources of groundwater and rivers in complex urban environments based on isotopic and hydro-chemical evidence. Science of the Total Environment, 871, 162026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162026
Chen, X., Jiang, C., Zheng, L., Dong, X., Chen, Y., & Li, C. (2020). Identification of nitrate sources and transformations in basin using dual isotopes and hydrochemistry combined with a Bayesian mixing model: Application in a typical mining city. Environmental Pollution, 267, 115651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115651
Chen, X., Zheng, L., Zhu, M., Jiang, C., Dong, X., & Chen, Y. (2023c). Quantitative identification of nitrate and sulfate sources of a multiple land-use area impacted by mine drainage. Journal of Environmental Management, 325, 116551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116551
Cui, R., Fu, B., Mao, K., Chen, A., & Zhang, D. (2020). Identification of the sources and fate of NO3−-N in shallow groundwater around a plateau lake in southwest China using NO3− isotopes (δ15N and δ18O) and a Bayesian model. Journal of Environmental Management, 270, 110897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110897
Cui, R., Zhang, D., Hu, W., Zhao, X., Yan, H., Liu, G., & Chen, A. (2023). Nitrogen in soil, manure and sewage has become a major challenge in controlling nitrate pollution in groundwater around plateau lakes, Southwest China. Journal of Hydrology, 620, 129541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129541
Durov, S. A. (1948). Natural waters and graphic representation of their composition. In Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR (pp. 87–90).
Egbi, C. D., Anornu, G. K., Ganyaglo, S. Y., Appiah-Adjei, E. K., Li, S.-L., & Dampare, S. B. (2020). Nitrate contamination of groundwater in the lower Volta River Basin of Ghana: Sources and related human health risks. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 191, 110227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110227
Feng, Y., Chen, H., Zhang, C., Guo, Y., Shi, F., & Tang, W. (2021). Research on hydrochemical characteristics and recharge sources in Yangzhuang Basin. Journal of China Hydrology, 41, 103–108+12. https://doi.org/10.19797/j.cnki.1000-0852.20194391
Ford, D., & Williams, P. (2007). Karst hydrogeology and geomorphology. West Sussex. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118684986
Fu, X. (2019). Optimization management of groundwater resources and modeling and remediation of nitrate pollution in YangZhuang Basin (Thesis). China University of Geosciences.
Fu, X., Tang, Z., Lv, W., Wang, X., & Yan, B. (2018). Exploitation potential of groundwater in Yangzhuang Basin, China under recharge enhancement. IJHT, 36, 483–493. https://doi.org/10.18280/ijht.360213
Gao, Y., Qian, H., Zhou, Y., Chen, J., Wang, H., Ren, W., & Qu, W. (2022). Cumulative health risk assessment of multiple chemicals in groundwater based on deterministic and Monte Carlo models in a large semiarid basin. Journal of Cleaner Production, 352, 131567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131567
Guo, Y., Zhang, C., Xiao, Q., & Bu, H. (2020). Hydrogeochemical characteristics of a closed karst groundwater basin in North China. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 325, 365–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07247-w
He, S., Li, P., Su, F., Wang, D., & Ren, X. (2022). Identification and apportionment of shallow groundwater nitrate pollution in Weining Plain, northwest China, using hydrochemical indices, nitrate stable isotopes, and the new Bayesian stable isotope mixing model (MixSIAR). Environmental Pollution, 298, 118852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.118852
Hou, L., Liu, Z., Zhai, B., Zhu, Y., & Xu, X. (2023). Contrasting water quality in response to long-term nitrogen fertilization in rainfed and irrigated apple-producing regions on China’s Loess Plateau. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 354, 108561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2023.108561
Hu, B., Song, X., Lu, Y., Liang, S., & Liu, G. (2022). Fluoride enrichment mechanisms and related health risks of groundwater in the transition zone of geomorphic units, northern China. Environmental Research, 212, 113588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113588
Huang, X., Jin, M., Ma, B., Liang, X., Cao, M., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., & Su, J. (2022). Identifying nitrate sources and transformation in groundwater in a large subtropical basin under a framework of groundwater flow systems. Journal of Hydrology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127943
Ji, X., Xie, R., Hao, Y., & Lu, J. (2017). Quantitative identification of nitrate pollution sources and uncertainty analysis based on dual isotope approach in an agricultural watershed. Environmental Pollution, 229, 586–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.06.100
Jiang, W., Liu, H., Sheng, Y., Ma, Z., Zhang, J., Liu, F., Chen, S., Meng, Q., & Bai, Y. (2022). Distribution, source apportionment, and health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater in a multi-mineral resource area, North China. Expo Health, 14, 807–827. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-021-00455-z
Kaown, D., Koh, D.-C., Mayer, B., & Lee, K.-K. (2009). Identification of nitrate and sulfate sources in groundwater using dual stable isotope approaches for an agricultural area with different land use (Chuncheon, mid-eastern Korea). Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 132, 223–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2009.04.004
Kendall, C., Elliott, E. M., & Wankel, S. D. (2007). Tracing anthropogenic inputs of nitrogen to ecosystems. Stable isotopes in ecology and environmental science (pp. 375–449). Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470691854.ch12
Kim, K.-H., Yun, S.-T., Mayer, B., Lee, J.-H., Kim, T.-S., & Kim, H.-K. (2015). Quantification of nitrate sources in groundwater using hydrochemical and dual isotopic data combined with a Bayesian mixing model. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 199, 369–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2014.10.014
Kohl, D. H., Shearer, G. B., & Commoner, B. (1971). Fertilizer nitrogen: Contribution to nitrate in surface water in a corn belt watershed. Science, 174, 1331–1334. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.174.4016.1331
Kohonen, T. (1982). Self-organized formation of topologically correct feature maps. Biological Cybernetics, 43, 59–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337288
Kou, X., Ding, J., Li, Y., Li, Q., Mao, L., Xu, C., Zheng, Q., & Zhuang, S. (2021). Tracing nitrate sources in the groundwater of an intensive agricultural region. Agricultural Water Management, 250, 106826.
Lei, Y., Liu, Y., Sun, Z., Zou, C., Ma, R., Yin, L., & Pan, H. (2023). Influences of paleoclimatic environment and hydrogeochemical evolution on groundwater salinity in an arid inland plain in northwestern China. Applied Geochemistry, 154, 105688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2023.105688
Li, J., Zhu, D., Zhang, S., Yang, G., Zhao, Y., Zhou, C., Lin, Y., & Zou, S. (2022). Application of the hydrochemistry, stable isotopes and MixSIAR model to identify nitrate sources and transformations in surface water and groundwater of an intensive agricultural karst wetland in Guilin, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 231, 113205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113205
Liu, F., Wang, S., Wang, L., Shi, L., Song, X., Yeh, T.-C.J., & Zhen, P. (2019). Coupling hydrochemistry and stable isotopes to identify the major factors affecting groundwater geochemical evolution in the Heilongdong Spring Basin, North China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 205, 106352.
Liu, F., Wang, S., Yeh, T. J., Zhen, P., Wang, L., & Shi, L. (2020). Using multivariate statistical techniques and geochemical modelling to identify factors controlling the evolution of groundwater chemistry in a typical transitional area between Taihang Mountains and North China Plain. Hydrological Processes, 34, 1888–1905. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13701
Liu, F., Zou, J., Liu, J., Zhang, J., & Zhen, P. (2022). Factors controlling groundwater chemical evolution with the impact of reduced exploitation. CATENA, 214, 106261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2022.106261
Liu, Q., Lin, Z., & Zhou, L. (2015). Spatio-temporal differentiation and environmental risk assessment of fertilization in Shandong Province, China. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 31, 208–214.
Mao, H., Wang, C., Qu, S., Liao, F., Wang, G., & Shi, Z. (2023). Source and evolution of sulfate in the multi-layer groundwater system in an abandoned mine—Insight from stable isotopes and Bayesian isotope mixing model. Science of the Total Environment, 859, 160368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160368
Mao, H., Wang, G., Rao, Z., Liao, F., Shi, Z., Huang, X., Chen, X., & Yang, Y. (2021). Deciphering spatial pattern of groundwater chemistry and nitrogen pollution in Poyang Lake Basin (eastern China) using self-organizing map and multivariate statistics. Journal of Cleaner Production, 329, 129697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129697
Mu, J., Ding, S., Liu, S. M., Song, G., Ning, X., Zhang, X., Xu, W., & Zhang, H. (2024). Multiple isotopes decipher the nitrogen cycle in the cascade reservoirs and downstream in the middle and lower Yellow River: Insight for reservoir drainage period. Science of the Total Environment, 918, 170625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.170625
Nawale, V. P., Malpe, D. B., Marghade, D., & Yenkie, R. (2021). Non-carcinogenic health risk assessment with source identification of nitrate and fluoride polluted groundwater of Wardha sub-basin, central India. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 208, 111548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111548
Pasupuleti, S., Singha, S. S., Singha, S., Kumar, S., Singh, R., & Dhada, I. (2022). Groundwater characterization and non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic health risk assessment of nitrate exposure in the Mahanadi River Basin of India. Journal of Environmental Management, 319, 115746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115746
Qi, S., Feng, Q., Zhu, M., Shu, H., Liu, W., Yang, L., Yin, Z., & Zhang, C. (2022). Source apportionment of nitrates in different aquifers in an arid region, northwestern China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 374, 133969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133969
Qu, X., Shi, L., & Han, J. (2022). Spatial evaluation of groundwater quality based on toxicological indexes and their effects on ecology and human health. Journal of Cleaner Production, 377, 134255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134255
Ren, X., Yue, F.-J., Tang, J., Li, C., & Li, S.-L. (2024). Nitrate transformation and source tracking of rivers draining into the Bohai Sea using a multi-tracer approach combined with an optimized Bayesian stable isotope mixing model. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 463, 132901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.132901
Rice, E. W., Baird, R. B., Eaton, A. D., & Clesceri, L. S. (2012). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association.
Saka, D., Adu-Gyamfi, J., Skrzypek, G., Antwi, E. O., Heng, L., & Torres-Martínez, J. A. (2023). Disentangling nitrate pollution sources and apportionment in a tropical agricultural ecosystem using a multi-stable isotope model. Environmental Pollution, 328, 121589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121589
Sheng, D., Meng, X., Wen, X., Wu, J., Yu, H., Wu, M., & Zhou, T. (2023). Hydrochemical characteristics, quality and health risk assessment of nitrate enriched coastal groundwater in northern China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 403, 136872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136872
Su, C., Jiang, J., Xie, X., Han, Z., Wang, M., Li, J., & Shi, H. (2023a). Sources and cycling processes of nitrogen revealed by stable isotopes and hydrochemistry in a typical agricultural lake basin. Applied Geochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2023.105662
Su, C., Wang, M., Xie, X., Han, Z., Jiang, J., Wang, Z., & Xiao, D. (2023b). Natural and anthropogenic factors regulating fluoride enrichment in groundwater of the Nansi Lake Basin, Northern China. Science of the Total Environment, 904, 166699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166699
Su, H., Kang, W., Li, Y., & Li, Z. (2021). Fluoride and nitrate contamination of groundwater in the Loess Plateau, China: Sources and related human health risks. Environmental Pollution, 286, 117287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117287
Subba Rao, N. (2021). Spatial distribution of quality of groundwater and probabilistic non-carcinogenic risk from a rural dry climatic region of South India. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 43, 971–993. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00621-3
Sun, L., Liang, X., Jin, M., & Zhang, X. (2022). Sources and fate of excessive ammonium in the Quaternary sediments on the Dongting Plain, China. Science of the Total Environment, 806, 150479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150479
Torres-Martínez, J. A. (2021). Estimation of nitrate pollution sources and transformations in groundwater of an intensive livestock-agricultural area (Comarca Lagunera), combining major ions, stable isotopes and MixSIAR model. Environmental Pollution. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115445
Torres-Martínez, J. A., Mora, A., Mahlknecht, J., Kaown, D., & Barceló, D. (2021). Determining nitrate and sulfate pollution sources and transformations in a coastal aquifer impacted by seawater intrusion—A multi-isotopic approach combined with self-organizing maps and a Bayesian mixing model. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 417, 126103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126103
Tran, T. Q., Banning, A., Heinze, T., & Wohnlich, S. (2022). Integration of self-organizing maps, statistical analysis, and hydrogeochemical modeling methods to identify spatio-seasonal variations in mine water quality. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 233, 106908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2021.106908
USEPA. (2004). Risk assessment guidance for superfund volume I: Human health evaluation manual (Part E). Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, U.S.
Wang, D., Li, P., Yang, N., Yang, C., Zhou, Y., & Li, J. (2023a). Distribution, sources and main controlling factors of nitrate in a typical intensive agricultural region, northwestern China: Vertical profile perspectives. Environmental Research, 237, 116911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.116911
Wang, S., Chen, J., Jiang, W., Zhang, S., Jing, R., & Yang, S. (2023b). Identifying the geochemical evolution and controlling factors of the shallow groundwater in a high fluoride area, Feng County, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30, 20277–20296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23516-5
Wang, S., Chen, J., Zhang, S., Zhang, X., Chen, D., & Zhou, J. (2023c). Hydrochemical evolution characteristics, controlling factors, and high nitrate hazards of shallow groundwater in a typical agricultural area of Nansi Lake Basin, North China. Environmental Research, 223, 115430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115430
Wang, Y., Peng, J., Cao, X., Xu, Y., Yu, H., Duan, G., & Qu, J. (2020). Isotopic and chemical evidence for nitrate sources and transformation processes in a plateau lake basin in Southwest China. Science of the Total Environment, 711, 134856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134856
Wu, Y., Ju, H., Jiang, H., Zhang, G., Qi, P., & Li, Z. (2023). Identifying nitrate sources and transformations in an agricultural watershed in Northeast China: Insights from multiple isotopes. Journal of Environmental Management, 340, 118023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118023
Xiao, Y., Liu, K., Hao, Q., Xiao, D., Zhu, Y., Yin, S., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Hydrogeochemical insights into the signatures, genesis and sustainable perspective of nitrate enriched groundwater in the piedmont of Hutuo watershed, China. CATENA, 212, 106020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2022.106020
Xue, D., Botte, J., De Baets, B., Accoe, F., Nestler, A., Taylor, P., Van Cleemput, O., Berglund, M., & Boeckx, P. (2009). Present limitations and future prospects of stable isotope methods for nitrate source identification in surface- and groundwater. Water Research, 43, 1159–1170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.12.048
Yang, F., Jia, C., Yang, X., Yang, H., & Chang, W. (2022). Probabilistic potential health risk quantification, hydrochemistry, driving forces of groundwater nitrate and fluoride in a typical irrigation district, Northern China. Journal of Environmental Management, 323, 116171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116171
Yang, H., Xiao, Y., Hao, Q., Wang, L., Zhang, Y., Liu, K., Zhu, Y., Liu, G., Yin, S., & Xie, Z. (2023). Geochemical characteristics, mechanisms and suitability for sustainable municipal and agricultural water supply of confined groundwater in central North China Plain. Urban Climate, 49, 101459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2023.101459
Yang, P., Wang, Y., Wu, X., Chang, L., Ham, B., Song, L., & Groves, C. (2020). Nitrate sources and biogeochemical processes in karst underground rivers impacted by different anthropogenic input characteristics. Environmental Pollution, 265, 114835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114835
Yoshihara, N., Matsumoto, S., Machida, I., & Uchida, Y. (2023). Deciphering natural and anthropogenic effects on the groundwater chemistry of Nago City, Okinawa Island, Japan. Environmental Pollution, 318, 120917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120917
Zaryab, A., Nassery, H. R., Knoeller, K., Alijani, F., & Minet, E. (2022). Determining nitrate pollution sources in the Kabul Plain aquifer (Afghanistan) using stable isotopes and Bayesian stable isotope mixing model. Science of the Total Environment, 823, 153749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153749
Zhang, C., Rao, W., Wu, Z., Zheng, F., Li, T., Li, C., Lei, X., Xie, H., & Chu, X. (2024a). Anthropogenic impacts and quantitative sources of nitrate in a rural-urban canal using a combined PMF, δ15N/δ18O–NO3-, and MixSIAR approach. Environmental Research, 251, 118587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2024.118587
Zhang, H., Xu, Y., Cheng, S., Li, Q., & Yu, H. (2020). Application of the dual-isotope approach and Bayesian isotope mixing model to identify nitrate in groundwater of a multiple land-use area in Chengdu Plain, China. Science of the Total Environment, 717, 137134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137134
Zhang, J., Cao, M., Jin, M., Huang, X., Zhang, Z., & Kang, F. (2022a). Identifying the source and transformation of riverine nitrates in a karst watershed, North China: Comprehensive use of major ions, multiple isotopes and a Bayesian model. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 246, 103957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2022.103957
Zhang, P., Wang, X.-D., Yue, F.-J., Chen, S.-N., Liu, Z.-H., Lu, M., & Shi, Z.-Y. (2023). Dynamic characteristics of nitrogen transport in various land use in a typical karst catchment during rainfall events. Environment and Earth Science, 82, 332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-10980-6
Zhang, Q., Shu, W., Li, F., Li, M., Zhou, J., Tian, C., Liu, S., Ren, F., & Chen, G. (2022b). Nitrate source apportionment and risk assessment: A study in the largest ion-adsorption rare earth mine in China. Environmental Pollution, 302, 119052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119052
Zhang, Q., Wang, H., Liu, L., Zhai, T., & Zhang, X. (2024b). Multiple isotopes reveal the driving mechanism of high NO3– level and key processes of nitrogen cycling in the lower reaches of Yellow River. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 138, 597–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2023.05.001
Zhao, Z., Zhang, M., Chen, Y., Ti, C., Tian, J., He, X., Yu, K., Zhu, W., Yan, X., & Wang, Y. (2022). Traceability of nitrate polluted hotspots in plain river networks of the Yangtze River delta by nitrogen and oxygen isotopes coupling bayesian model. Environmental Pollution, 315, 120438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120438
Zheng, H. (2019). Study on dynamic prediction of groundwater in Yangzhuang Basin (Thesis). Shandong University of Science and Technology.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFD0900703); the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX23_0737) and the Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2208085US09). Special thanks to the editor and anonymous reviewers for their critical comments and valuable suggestions in the present form.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shou Wang: Investigation, Sample collection, Data curation, Writing-original draft, Conceptualization. Jing Chen: Resources, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Project administration. Shuxuan Zhang: Writing-original draft, Methodology, Software, Investigation, Sample collection. Yanjie Bai: Software, Visualization. Xiaoyan Zhang: Investigation, Sample collection. Dan Chen: Investigation. Jiahong Hu: Data collection, Formal analysis. All authors read and approved the final draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Chen, J., Zhang, S. et al. Groundwater hydrochemical signatures, nitrate sources, and potential health risks in a typical karst catchment of North China using hydrochemistry and multiple stable isotopes. Environ Geochem Health 46, 173 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-024-01964-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-024-01964-x