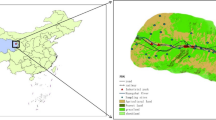
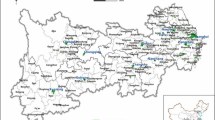
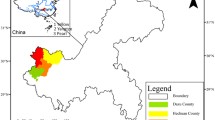
Abstract
This study analyzed the distribution and content of eight heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, Ni, Cr, As, Cd, and Hg) in 221 surface soil samples from the upper reaches of the Xiaowen River. Environmental geochemical baselines were established for the eight heavy metals, and the pollution status was assessed on the basis of these baselines and the soil background value of Weifang City. The calculation results of Nemerow pollution index and the potential ecological hazard index (PEHI)-Ri showed that the overall pollution degree and ecological hazard in the study area were at a slight level. 49% (calculated by baseline value) and 24% (calculated by background value of Weifang City) samples were at moderate or above pollution level. 9% (calculated by baseline value) and 42% (calculated by background value) samples were at the level of moderate potential ecological hazards or above. According to the calculation results of Igeo and PEHI-Ei, the main pollutant in the study area was Hg, followed by Cd. 3% (calculated by baseline value) and 12% (calculated by background value) of Hg samples were at moderate or above contamination levels. 5% (calculated by baseline value) and 38% (calculated by background value) of Hg samples were at the level of strong potential ecological hazard or above. The western, central, and eastern parts of the study area were mainly the primary areas of pollution and ecological hazards. The non-carcinogenic risk was at an acceptable level, the carcinogenic risk was at a tolerable level, and the main risk pathway was oral intake, with Cr being the main contributor. Source apportionment indicated that soil heavy metals primarily originate from soil parent material, transportation, agricultural fertilization, and industrial emissions (waste gas, waste water and solid waste).







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data will be shared on reasonable request to the corresponding author.
References
Amina, A., Ahmed, D., Mfopou, M. Y. C., Birang, M. R. C., Abdelmalek, D., & Souad, E. H. (2021). Determination of background values and assessment of pollution and ecological risk of heavy metals in urban agricultural soils of Yaoundé. Cameroon, Journal of Soils and Sediments, 21(3), 1437–1454.
Ana, V. D., Guillermo, A., Katja, D., Cyrus, K., Dante Daniel, C., & Adriana, N. (2021). The environmental geochemical baseline, background and sources of metal and metalloids present in urban, peri-urban and rural soils in the O´Higgins region, Chile. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 44(10), 3173–3189.
Dina, B., Dávid, T., Bianka, S., Béla, T., & Edina, S. (2023). Heavy metal pollution of soil in Vienna, Austria. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 234(4)
Chang, K. W., Shao, X., & Yang, T. (2023). Evaluation and source analysis of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil around a pyrite slag heap in Southern Sichuan Province. Journal of Sichuan University (Natural Science Edition), 60(3), 153–159. (in Chinese).
Chen, H., Zhao, X.Y., Chang, S., Song, Y.M., Lu, M.Q., Zhao, B., Chen, H.D., Gao, S., Wang, L.J., Cui, J.S., & Zhang, L.L. (2023). Source analysis and health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater of Shijiazhuang, a Typical City in North China Plain, Environmental Science, 1–17 (in Chinese)
Fan, J.N., He, X.M., & Du. W. (2021). Analysis and comparison of environmental baseline values of soil heavy metals based on standardized methods and statistical analysis, Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University 40(01), 160–167 (in Chinese)
Haque, M. M., Niloy, N. M., Nayna, O. K., Fatema, K. J., Quraishi, S. B., Park, J. H., Kim, K. W., & Tareq, S. M. (2020). Variability of water quality and metal pollution index in the Ganges River, Bangladesh. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(34), 42582–42599.
Li, J., Li, X., Li, K. M., Jiao, L., Tai, X.S., Zang, F, & Cao, S.Z. (2023). Characteristics and identification priority source of heavy metals pollution in farmland soils in the Yellow River Basin. Environmental Science, 1–20 (in Chinese)
Li, J., Li, X., Jiao, L., Tai, X. S., Zang, F., Chen, W., & Tuo, X.Y. (2023). Identification priority source of heavy metals pollution in greenspace soils based on source-specific ecological and human health risk analysis in the Yellow River Custom Tourist Line of Lanzhou, Environmental Science, 1–16 (Iin Chinese)
Liao, Z. Y., Li, J. Q., Shen, ,Z. J., Li, C. X., Luo, C. Z., Mei, N., Zhang, C., & Wang. D. Y. (2023). Assessment and source analysis of heavy metal pollution in arable land around an iron ore mining area in Chongqing. Environmental Science, 1–16 (in Chinese)
Liu, Y. J., Zhang, B. H., & Liu, Z. T. (2016). A study on distribution of soil heavy metal pollution in Weifang city based on geography information system. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 36(06), 150–154. (in Chinese).
Lu, X. Z., Kang, Z. J., Gu, A. Q., & Zhang, Y. W. (2018). Environmental geochemical baseline of soil metallic elements in agricultural soil. Advances in Geosciences, 8(4), 811–819.
Lv, J. S., & He, H. C. (2018). Identifying the origins and spatial distributions of heavy metals in the soils of the Jiangsu Coast. Environmental Science, 39(06), 2853–2864. (in Chinese).
Müller, G. (1969). Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal, 2, 108–118.
Pu, X. B., Feng, Q., Liao, C., Feng, Y. C., Liu, J. Q., & Wang, H. Z. (2022). Study on heavy metal pollution in highway soil based on principal component analysis. Journal of Safety and Environment, 22(4), 2241–2247. (in Chinese).
Qi, M. D., Wu, Y. J., Zhang, S., Li, G. Y., & An, T. C. (2023). Pollution profiles, source identification and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil near a non-ferrous metal smelting plant. International Journal of Environmental Research Public Health, 20(1004), 1004.
Shen, C., Wang, W.J., Sha, C.Y., Xie, Y.Q., Wang, M., & Wu, J. (2023). Distribution characteristics, source analysis and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the typical industries reclaimed soil. Environmental Science, 1–19 (in Chinese)
Sun, H. Y., Wei, X. F., Gan, F. W., Wang, H., He, Z. X., Jia, F. C., & Zhang, J. (2019). Determination of heavy metal geochemical baseline values and its accumulation in soils of the Luanhe River Basin, Chengde. Environmental Science, 40(08), 3753–3763. (in Chinese).
Sun, Y. Q., Xiao, K., Wang, X. D., Lv, Z. H., & Mao, M. (2021). Evaluating the distribution and potential ecological risks of heavy metal in coal gangue. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(15), 18604–18615.
USEPA. (2001). Supplemental guidance for developing soil screening levels for superfund sites. Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response (Washington DC).
Wang, J. H., Zhang, X., Yang, Q., Zhang, K., Zheng, Y., & Zhou, G. H. (2018). Pollution characteristics of atmospheric dustfall and heavy metals in a typical inland heavy industry city in China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 71(9), 283–291.
Wang, L., Du, W. Q., & Bai, J. J. (2022). Determination and influence of soil geochemical baseline values in Bayan Obo mining area. Chinese Rare Earths, 43(06), 44–57. (in Chinese).
Yan, T. T., Zhao, W. J., Yu, X. Y., Li, H. X., Gao, Z. K., Ding, M., & Yue, J. S. (2022). Evaluating heavy metal pollution and potential risk of soil around a coal mining region of Tai’an City, China. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 61(3), 2156–2165.
Zhang, X. F., Feng, S. H., Shang, T. T., Liu, J. S., & Meng, X. Z. (2023). Pollution characteristic and source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soil from a plain river network region. Journal of Agro-Environmental Science, 1–20 (in Chinese)
Zhao, X. F., Zhang, Y. S., Feng, A. P., Wang, Y. X., Xia, L. X., Wang, H. L., & Du, W. (2020). Geochemical characteristics and environmental assessment of heavy metal elements in agricultural soil of Anqiu area Shandong Province. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 44(06), 1446–1454. (In Chinese).
Zou, J. M., Liu, X. X., Dai, W., & Luan, Y. N. (2018). Pollution assessment of heavy metal accumulation in the farmland soils of Beijing’s suburbs. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(27), 27483–27492.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the reviewers who participated in the review, as well as MJEditor (www.mjeditor.com) for providing English editing services during the preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Geological Exploration and Scientific and Technological Innovation Project of Shandong Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources (Grant Number 202005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zongjun Gao contributed to formal analysis, methodology, and writing—original draft. Yiru Niu contributed to formal analysis, software, and writing—original draft. Yuqi Zhang contributed to supervision, conceptualization, writing—review & editing. Jiutan Liu contributed to software and methodology. Menghan Tan contributed to software. Bing Jiang contributed to investigation, resources, and software.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
We confirm that all authors of the paper consent to participate.
Consent for publication
This manuscript was approved for publication by all the authors.
Human or animal rights
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Z., Niu, Y., Zhang, Y. et al. Geochemical baseline establishment, pollution level and health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in the upper Xiaowen River Basin, Shandong Province, China. Environ Geochem Health 46, 124 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-024-01893-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-024-01893-9