Abstract
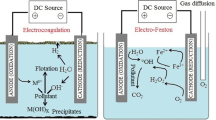
This study presents an environmentally sustainable method for minimizing sludge production in the textile effluent sector through the combined application of electrokinetic (EK) and electrooxidation (EO) processes. AAS and XRF analyses reveal that utilizing acidic electrolytes in the EK method successfully eliminates heavy metals (Cu, Mn, Zn, and Cr) from sludge, demonstrating superior efficiency compared to alkaline conditions. In addition, the total removal efficiency of COD contents was calculated following the order of EK-3 (60%), EK-1 (51%) and EK-2 (34%). Notably, EK-3, leveraging pH gradient fluctuations induced by anolyte in the catholyte reservoir, outperforms other EK systems in removing COD from sludge. The EK process is complemented by the EO process, leading to further degradation of dye and other organic components through the electrochemical generation of hypochlorite (940 ppm). At an alkaline pH of 10.0, the color and COD removal were effectively achieved at 98 and 70% in EO treatment, compared to other mediums. In addition, GC–MS identified N-derivative residues at the end of the EO. This study demonstrates an integrated approach that effectively eliminates heavy metals and COD from textile sludge, combining EK with EO techniques.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abilaji, S., Sathishkumar, K., Narenkumar, J., Alsalhi, M. S., Devanesan, S., Parthipan, P., Muthuraj, B., & Rajasekar, A. (2023). Sequential photo electro oxidation and biodegradation of textile effluent: Elucidation of degradation mechanism and bacterial diversity. Chemosphere, 331, 138816.
Annamalai, S., Santhanam, M., Sundaram, M., & Curras, M. P. (2014). Electrokinetic remediation of inorganic and organic pollutants in textile effluent contaminated agricultural soil. Chemosphere, 117, 673–678.
Annamalai, S., Selvaraj, S., Selvaraj, H., Santhanam, M., & Pazos, M. (2015). Electrokinetic remediation: Challenging and optimization of electrolyte for sulfate removal in textile effluent-contaminated farming soil. RSC Advances, 5(99), 81052–81058.
Annamalai, S., Sundaram, M., & Curras, M. P. (2017). Integrated approach of chemical and electrodialysis process in textile effluent contaminated groundwater for irrigation. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 5(4), 3190–3200.
Aravind, P., Devarajan, A., Solaiappan, A., Selvaraj, H., & Sundaram, M. (2019). Removal of BPA from thermal cash receipts via electro oxidation cum biodegradation: Evaluating its degradation mechanism and in silico toxicity analysis. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 31, 100849.
Aravind, P., Selvaraj, H., Ferro, S., & Sundaram, M. (2016). An integrated (electro-and bio-oxidation) approach for remediation of industrial wastewater containing azo-dyes: Understanding the degradation mechanism and toxicity assessment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 318, 203–215.
ASTM E1755-01. (2007). Standard test method for determination of ash in biomass. American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM).
ASTM E871-82(2019). (2006). Standard test method for moisture analysis of particulate wood fuels. American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM).
Azhar, U., Ahmad, H., Shafqat, H., Babar, M., Munir, H. M. S., Sagir, M., Arif, M., Hassan, A., Rachmadona, N., Rajendran, S., & Mubashir, M. (2022). Remediation techniques for elimination of heavy metal pollutants from soil: A review. Environmental research, 214, 113918.
Bidu, J. M., Van der Bruggen, B., Rwiza, M. J., & Njau, K. N. (2021). Current status of textile wastewater management practices and effluent characteristics in Tanzania. Water Science and Technology, 83(10), 2363–2376.
De Coster, J., Vanherck, W., Appels, L., & Dewil, R. (2017). Selective electrochemical degradation of 4-chlorophenol at a Ti/RuO2-IrO2 anode in chloride rich wastewater. Journal of Environmental Management, 190, 61–71.
Dhandapani, P., AlSalhi, M. S., Karthick, R., Chen, F., Devanesan, S., Kim, W., Rajasekar, A., Ahmed, M., & Aljaafreh, M. J. (2021). Biological mediated synthesis of RGO-ZnO composites with enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 409, 124661.
Dhandapani, P., Devanesan, S., Narenkumar, J., Maruthamuthu, S., AlSalhi, M. S., Rajasekar, A., & Ahamed, A. (2020). Novel synthesis of ZnO by Ice-cube method for photo-inactivation of E. coli. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 27(4), 1130–1138.
Dhandapani, P., MuraliKannan, M., Anandkumar, B., Maruthamuthu, S., & Manoharan, S. P. (2014). Electrochemistry of calcium precipitating bacteria in orthodontic wire. Oral Science International, 11(1), 22–29.
Dhandapani, P., Santhoshkumar, M., Narenkumar, J., AlSalhi, M. S., Kumar, P. A., Devanesan, S., Kokilaramani, S., & Rajasekar, A. (2022). Bio-approach: Preparation of RGO-AgNPs on cotton fabric and interface with sweat environment for antibacterial activity. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 45(11), 1825–1837.
Elumalai, P., Kumar, A. S., Dhandapani, P., Cui, J., Gao, X., Prakash, A. A., Rajamohan, R., AlSalhi, M. S., Devanesan, S., Rajasekar, A., & Parthipan, P. (2023). Biodegradation of pyrene by bacterial consortia: Impact of natural surfactants and iron oxide nanoparticles. Environmental Research, 242, 117753.
Elumalai, P., Muthukumar, B., Dhandapani, P., Karthikeyan, O. P., & Huang, M. (2023). Role of bionanohybrids for pollutant removal in wastewater environment. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 35, 100504.
Erkan, H. S., & Engin, G. O. (2020). A comparative study of waste activated sludge disintegration by electrochemical pretreatment process combined with hydroxyl and sulfate radical based oxidants. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 8(4), 103918.
Fdez-Sanromán, A., Pazos, M., Rosales, E., & Sanromán, M. Á. (2021). Prospects on integrated electrokinetic systems for decontamination of soil polluted with organic contaminants. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 27, 100692.
Fitch, A., Balderas-Hernandez, P., & Ibanez, J. G. (2022). Electrochemical technologies combined with physical, biological, and chemical processes for the treatment of pollutants and wastes: A review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(3), 107810.
Geng, H., Xu, Y., Zheng, L., Gong, H., Dai, L., & Dai, X. (2020). An overview of removing heavy metals from sewage sludge: Achievements and perspectives. Environmental Pollution, 266, 115375.
Ghobadi, R., Altaee, A., Zhou, J. L., McLean, P., & Yadav, S. (2020). Copper removal from contaminated soil through electrokinetic process with reactive filter media. Chemosphere, 252, 126607.
Khadhar, S., Sdiri, A., Chekirben, A., Azouzi, R., & Charef, A. (2020). Integration of sequential extraction, chemical analysis and statistical tools for the availability risk assessment of heavy metals in sludge amended soils. Environmental Pollution, 263, 114543.
Li, J., Li, Y., Xiong, Z., Yao, G., & Lai, B. (2019). The electrochemical advanced oxidation processes coupling of oxidants for organic pollutants degradation: A mini-review. Chinese Chemical Letters, 30(12), 2139–2146.
Luna-Trujillo, M., Palma-Goyes, R., Vazquez-Arenas, J., & Manzo-Robledo, A. (2020). Formation of active chlorine species involving the higher oxide MOx+ 1 on active Ti/RuO2-IrO2 anodes: A DEMS analysis. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 878, 114661.
Martínez-Huitle, C. A., Rodrigo, M. A., Sirés, I., & Scialdone, O. (2023). A critical review on latest innovations and future challenges of electrochemical technology for the abatement of organics in water. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 328, 122430.
Meghlaoui, F. Z., Merouani, S., Hamdaoui, O., Bouhelassa, M., & Ashokkumar, M. (2019). Rapid catalytic degradation of refractory textile dyes in Fe (II)/chlorine system at near neutral pH: Radical mechanism involving chlorine radical anion (Cl2−)-mediated transformation pathways and impact of environmental matrices. Separation and Purification Technology, 227, 115685.
Moradi, M., Vasseghian, Y., Khataee, A., Kobya, M., Arabzade, H., & Dragoi, E. N. (2020). Service life and stability of electrodes applied in electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: A comprehensive review. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 87, 18–39.
Nair, G., Soni, B., & Shah, M. (2023). A comprehensive review on electro-oxidation and its types for wastewater treatment. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 23, 100980.
Okur, M. C., Akyol, A., Nayir, T. Y., Kara, S., Ozturk, D., & Civas, A. (2022). Performance of Ti/RuO2-IrO2 electrodes and comparison with BDD electrodes in the treatment of textile wastewater by electro-oxidation process. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 183, 398–410.
Prakash, A. A., Sathishkumar, K., AlSalhi, M. S., Devanesan, S., Mani, P., Kamala-Kannan, S., Vijayanand, S., & Rajasekar, A. (2022). Integrated approach of photo-assisted electrochemical oxidation and sequential biodegradation of textile effluent. Environmental Pollution, 307, 119412.
Rahmani, A. R., Godini, K., Nematollahi, D., & Azarian, G. (2015). Electrochemical oxidation of activated sludge by using direct and indirect anodic oxidation. Desalination and Water Treatment, 56(8), 2234–2245.
Rao, G., Rao, V. V. S. G., Ranganathan, K., Surinaidu, L., Mahesh, J., & Ramesh, G. (2011). Assessment of groundwater contamination from a hazardous dump site in Ranipet, Tamil Nadu, India. Hydrogeology Journal, 19(8), 1587.
Rodríguez-Narváez, O. M., Picos, A. R., Bravo-Yumi, N., Pacheco-Alvarez, M., Martínez-Huitle, C. A., & Peralta-Hernández, J. M. (2021). Electrochemical oxidation technology to treat textile wastewaters. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 29, 100806.
Santhanam, M., Selvaraj, R., Annamalai, S., & Sundaram, M. (2017). Combined electrochemical, sunlight-induced oxidation and biological process for the treatment of chloride containing textile effluent. Chemosphere, 186, 1026–1032.
Sathishkumar, K., AlSalhi, M. S., Sanganyado, E., Devanesan, S., Arulprakash, A., & Rajasekar, A. (2019). Sequential electrochemical oxidation and bio-treatment of the azo dye congo red and textile effluent. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology b: Biology, 200, 111655.
Scialdone, O., Proietto, F., & Galia, A. (2021). Electrochemical production and use of chlorinated oxidants for the treatment of wastewater contaminated by organic pollutants and disinfection. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 27, 100682.
Seibert, D., Zorzo, C. F., Borba, F. H., de Souza, R. M., Quesada, H. B., Bergamasco, R., Baptista, A. T., & Inticher, J. J. (2020). Occurrence, statutory guideline values and removal of contaminants of emerging concern by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 748, 141527.
Selvi, A., & Aruliah, R. (2018). A statistical approach of zinc remediation using acidophilic bacterium via an integrated approach of bioleaching enhanced electrokinetic remediation (BEER) technology. Chemosphere, 207, 753–763.
Selvi, A., Rajasekar, A., Theerthagiri, J., Ananthaselvam, A., Sathishkumar, K., Madhavan, J., & Rahman, P. K. (2019). Integrated remediation processes toward heavy metal removal/recovery from various environments-a review. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 7, 66.
Srinivasan, S., Bankole, P. O., & Sadasivam, S. K. (2022). Biodecolorization and degradation of textile azo dyes using Lysinibacillussphaericus MTCC 9523. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10, 990855.
Standard method for the examination of water and wastewater (1999) (twentieth ed.), American Public Healt Association.
Tang, J., He, J., Tang, H., Wang, H., Sima, W., Liang, C., & Qiu, Z. (2020). Heavy metal removal effectiveness, flow direction and speciation variations in the sludge during the biosurfactant-enhanced electrokinetic remediation. Separation and Purification Technology, 246, 116918.
Tang, J., Qiu, Z., Tang, H., Wang, H., Sima, W., Liang, C., Liao, Y., Li, Z., Wan, S., & Dong, J. (2021). Coupled with EDDS and approaching anode technique enhanced electrokinetic remediation removal heavy metal from sludge. Environmental Pollution, 272, 115975.
Uddin, F. (2021). Environmental hazard in textile dyeing wastewater from local textile industry. Cellulose, 28(17), 10715–10739.
Vocciante, M., Dovì, V. G., & Ferro, S. (2021). Sustainability in ElectroKinetic Remediation processes: A critical analysis. Sustainability, 13(2), 770.
Wang, J., & Wang, S. (2020). Reactive species in advanced oxidation processes: Formation, identification and reaction mechanism. Chemical Engineering Journal, 401, 126158.
Wang, Y., Li, A., & Cui, C. (2021). Remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils by electrokinetic technology: Mechanisms and applicability. Chemosphere, 265, 129071.
Xu, X., Yang, Y., Wang, G., Zhang, S., Cheng, Z., Li, T., Yang, Z., Xian, J., Yang, Y., & Zhou, W. (2020). Removal of heavy metals from industrial sludge with new plant–based washing agents. Chemosphere, 246, 125816.
Zeng, Q., Huang, H., Tan, Y., Chen, G., & Hao, T. (2022). Emerging electrochemistry-based process for sludge treatment and resources recovery: A review. Water Research, 209, 117939.
Zhu, X., Hu, W., Feng, C., Chen, N., Chen, H., Kuang, P., Deng, Y., & Ma, L. (2021). Electrochemical oxidation of aniline using Ti/RuO2-SnO2 and Ti/RuO2-IrO2 as anode. Chemosphere, 269, 128734.
Acknowledgements
The authors express their sincere appreciation to the Researchers Supporting Project Number (RSP2024R68) King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. A. Rajasekar was supported by TANSCHE-RGP project (RGP/2019-20/TVU/HECP-0059). Dr Dhandapani. P. thanks to D.S. Kothari postdoctoral Fellowship (Normal) (File.No.F.4-2/2006 (BSR) BL/17-18/0343) by University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PD was contributed to experimental work, field collection, writing—original draft. VS was contributed to experimental work, field collection; PP was contributed to validation, result Interpretation. MSA was contributed to validation, formal analysis, funding. SD was contributed to writing—review and editing, validation; JN was contributed to validation, result interpretation; RR was contributed to validation; VE was contributed to validation; AR was contributed to project administration, supervision, validation, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dhandapani, P., Srinivasan, V., Parthipan, P. et al. Development of an environmentally sustainable technique to minimize the sludge production in the textile effluent sector through an electrokinetic (EK) coupled with electrooxidation (EO) approach. Environ Geochem Health 46, 81 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01847-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01847-7