Abstract
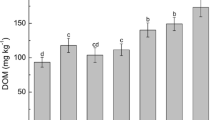
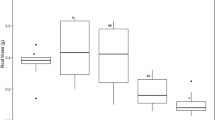
This study was conducted to investigate the impact of supplementing blue and red light on the biomass yield, metal uptake, contaminant purification, and the alleviation of leaching risks by Noccaea caerulescens, a well-known hyperaccumulator of Cd and Zn. As previously reported for the closely related Thlaspi arvense, N. caerulescens retarded the leaching of Cd and Zn but aggravated the leaching of Pb and Cu, because the species mobilized all metals in soil but only extracted Cd and Zn. Monochromic red light reduced the leaching of Pb and Cu by 13.8% and 1.3%, respectively, but simultaneously weakened Cd phytoremediation by reducing shoot biomass. Our results demonstrated that a small proportion of blue light (10%) could eliminate the negative effect of monochromatic red light on plant shoot growth. However, root biomass decreased by 14.3%, 26.2%, 21.4%, and 61.9% as the percentage of blue light increased from 10 to 100%. Noccaea caerulescens generated the most biomass and accumulated the highest metal concentrations, except for Pb, when the ratio of red to blue light was 1:1. In addition, leachate volume was significantly reduced under the 10% and 50% blue light treatments compared to other light treatments. Therefore, light supplementation with a suitable proportion of blue light can enhance metal purification by N. caerulescens and alleviate potential leaching risk during phytoremediation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data and materials availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Ali, H., Khan, E., & Sajad, M. A. (2013). Phytoremediation of heavy metals-concepts and applications. Chemosphere, 91, 869–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.075
Brady, J. P., Ayoko, G. A., Martens, W. N., & Goonetilleke, A. (2015). Weak acid extractable metals in bramble bay, Queensland, Australia: Temporal behaviour, enrichment and source apportionment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 91, 380–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.11.048
Chen, Y., Song, X., Zhang, Z., Shi, P., & Tao, F. (2015). Simulating the impact of flooding events on non-point source pollution and the effects of filter strips in an intensive agricultural watershed in China. Limnology, 16, 91–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-014-0443-2
Dinh, N. T., Vu, D. T., Mulligan, D., & Nguyen, A. V. (2015). Accumulation and distribution of zinc in the leaves and roots of the hyperaccumulator Noccaea caerulescens. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 110, 85–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2014.10.001
Dong, C., Fu, Y., Liu, G., & Liu, H. (2014). Growth, photosynthetic characteristics, antioxidant capacity and biomass yield and quality of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) exposed to LED light sources with different spectra combinations. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 200, 219–230. https://doi.org/10.1111/jac.12059
Ghane, A., Mazaheri, M., & Samani, J. M. V. (2016). Location and release time identification of pollution point source in river networks based on the backward probability method. Journal of Environmental Management, 180, 164–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.05.015
Godo, T., Fujiwara, K., Guan, K., & Miyoshi, K. (2011). Effects of wavelength of LED-light on in vitro asymbiotic germination and seedling growth of Bletilla ochracea schltr. (Orchidaceae). Plant Biotechnology., 28, 397–400. https://doi.org/10.5511/plantbiotechnology.11.0524a
Ho, C. P., Hseu, Z. Y., Chen, N. C., & Tsai, C. C. (2013). Evaluating heavy metal concentration of plants on a serpentine site for phytoremediation applications. Environment and Earth Science, 70, 191–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-2115-z
Hogewoning, S. W., Trouwborst, G., Maljaars, H., Poorter, H., van Ieperen, W., & Harbinson, J. (2010). Blue light dose-responses of leaf photosynthesis, morphology, and chemical composition of Cucumis sativus grown under different combinations of red and blue light. Journal of Experimental Botany, 61, 3107–3117. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq132
Ibrahim, M. M., Alsahli, A. A., & El-Gaaly, G. (2013). Evaluation of phytoremediation potential of six wild plants for metal in a site polluted by industrial wastes: A field study in Riyadh Saudi Arabia. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 45, 571–576.
Jacobs, A., De Brabandere, L., Drouet, T., Sterckeman, T., & Noret, N. (2018). Phytoextraction of Cd and Zn with Noccaea caerulescens for urban soil remediation: Influence of nitrogen fertilization and planting density. Ecological Engineering, 116, 178–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2018.03.007
Jacobs, A., Drouet, T., Sterckeman, T., & Noret, N. (2017). Phytoremediation of urban soils contaminated with trace metals using Noccaea caerulescens: Comparing non-metallicolous populations to the metallicolous ‘Ganges’ in field trials. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 8176–8188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8504-9
Johkan, M., Shoji, K., Goto, F., Hahida, S., & Yoshihara, T. (2012). Effect of green light wavelength and intensity on photomorphogenesis and photosynthesis in Lactuca sativa. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 75, 128–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2011.08.010
Kwon, H. K., Jeon, J. Y., & Oh, S. J. (2017). Potential for heavy metal (copper and zinc) removal from contaminated marine sediments using microalgae and light emitting diodes. Ocean Science Journal, 52, 57–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-017-0001-z
Li, H., Xu, Z., & Tang, C. (2010). Effect of light-emitting diodes on growth and morphogenesis of upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) plantlets in vitro. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture, 103, 155–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9763-z
Lin, K. H., Huang, M. Y., Huang, W. D., Hsu, M. H., Yang, Z. W., & Yang, C. M. (2013). The effects of red, blue, and white light-emitting diodes on the growth, development, and edible quality of hydroponically grown lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. var. Capitata). Scientia Horticulture, 150, 86–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2012.10.002
Liza, R., Fenton, G. A., Lake, C. B., & Griffiths, D. V. (2017). An analytical approach to assess quality control sample sizes of cement-based “solidification/stabilization.” Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 54, 419–427. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2016-0218
Luo, J., Cao, M., Zhang, C. M., Wu, J., & Gu, X. W. (2020). The influence of light combination on the physicochemical characteristics and enzymatic activity of soil with multi-metal pollution in phytoremediation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 393, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122406
Ma, P., Bai, T. H., Wang, X. Q., & Ma, F. W. (2015). Effects of light intensity on photosynthesis and photoprotective mechanisms in apple under progressive drought. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 14, 1755–1766. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(15)61148-0
Martínez-Alcalá, I., Hernández, L. E., Esteban, E., Walker, D. J., & Bernal, M. P. (2013). Responses of Noccaea caerulescens and Lupinus albus in trace elements-contaminated soils. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 66, 47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.01.017
Mastropasqua, L., Borraccino, G., Bianco, L., & Paciolla, C. (2012). Light qualities and dose influence ascorbate pool size in detached oat leaves. Plant Science, 183, 57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.11.009
Meers, E., Ruttens, A., Geebelen, W., Vangronsveld, J., Samson, R., Vanbroekhoven, K., Vandegehuchte, M., Diels, L., & Tack, F. M. G. (2005a). Potential use of the plant antioxidant network for environmental assessment of heavy metals in soils. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 120, 243–267.
Meers, E., Ruttens, A., Hopgood, M. J., Samson, D., & Tack, F. M. G. (2005b). Comparison of EDTA and EDDS as potential soil amendments for enhanced phytoextraction of heavy metals. Chemosphere, 58, 1011–1022.
Olivares, A. R., Carrillo-González, R., González-Chávez, M. D. C. A., & Hernández, R. M. S. (2013). Potential of castor bean (Ricinus communis L.) for phytoremediation of mine tailings and oil production. Journal of Environmental Management, 114, 316–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.10.023
Ortakci, S., Yesil, H., & Tugtas, A. E. (2019). Ammonia removal from chicken manure digestate through vapor pressure membrane contactor (VPMC) and phytoremediation. Waste Management, 85, 186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.12.033
Pilon-Smits, E. (2005). Phytoremediation. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 56, 15–39. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.56.032604.144214
Poerschmann, J., & Schultze-Nobre, L. (2015). Rapid screening of phytoremediation effluents by off-line tetramethylammonium hydroxide assisted thermochemolysis. Science of the Total Environment, 518–519, 371–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.099
Pulford, I. D., & Watson, C. (2003). Phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated land by trees - a review. Environment International, 29, 529–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00152-6
R, Li., Huang, W., Wang, X., Liu, X., & Xu, Z. (2018). Effects of yellow, green, and different blue spectra on growth of potato plantlets in vitro. HortScience, 53, 541–546. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI12848-18
Rascio, N., & Navari-Izzo, F. (2011). Heavy metal hyperaccumulating plants: How and why do they do it? And what makes them so interesting? Plant Science, 180, 169–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.08.016
Salt, D. E., Blaylock, M., Kumar, N., Dushenkov, V., Ensley, B., Chet, I., & Raskin, I. (1995). Phytoremediation-a novel strategy for the removal of toxic metals from the environment using plants. Bio-Technology, 13, 468–474. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0595-468
Salt, D. E., Smith, R. D., & Raskin, I. (1998). Phytoremediation. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 49, 643–668. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.49.1.643
Seregin, I. V., Kozhevnikova, A. D., Zhukovskaya, N. V., & Schat, H. (2015). Cadmium tolerance and accumulation in excluder Thlaspi arvense and various accessions of hyperaccumulator Noccaea caerulescens. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 62, 837–846. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443715050131
Shah, K., & Nongkynrih, J. M. (2007). Metal hyperaccumulation and bioremediation. Biologia Plantarum, 51, 618–634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-007-0134-5
Shukla, O. P., Juwarkar, A. A., Singh, S. K., Khan, S., & Rai, U. N. (2011). Growth responses and metal accumulation capabilities of woody plants during the phytoremediation of tannery sludge. Waste Management, 31, 115–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2010.08.022
Spadoni, M., Voltaggio, M., Carcea, M., Coni, E., Raggi, A., & Cubadda, F. (2007). Bioaccessible selenium in Italian agricultural soils: Comparison of the biogeochemical approach with a regression model based on geochemical and pedoclimatic variables. Science of the Total Environment, 376, 160–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.01.066
Sterckeman, T., Cazes, Y., Gonneau, C., & Sirguey, C. (2017). Phenotyping 60 populations of Noccaea caerulescens provides a broader knowledge of variation in traits of interest for phytoextraction. Plant and Soil, 418, 523–540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3311-0
Tőzsér, D., Magura, T., & Simon, E. (2017). Heavy metal uptake by plant parts of willow species: A meta-analysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 336, 101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.03.068
Tume, P., González, E., King, R. W., Cuitiño, L., Roca, N., & Bech, J. (2018). Distinguishing between natural and anthropogenic sources for potentially toxic elements in urban soils of Talcahuano, Chile. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 18, 2335–2349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1750-0
Vaistij, F. E., Barros-Galvão, T., Cole, A. F., Gilday, A. D., He, Z., Li, Y., Harvey, D., Larson, T. R., & Graham, I. A. (2018). MOTHER-OF-FT-AND-TFL1 represses seed germination under far-red light by modulating phytohormone responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1806460115
Vocciante, M., Caretta, A., Bua, L., Bagatin, R., & Ferro, S. (2016). Enhancements in electrokinetic remediation technology: environmental assessment in comparison with other configurations and consolidated solutions. Chemical Engineering Journal, 289, 123–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.12.065
Wan, X., Lei, M., Chen, T., Tan, Y., & Yang, J. (2017). Safe utilization of heavy-metal-contaminated farmland by mulberry tree cultivation and silk production. Science of the Total Environment, 599, 1867–1873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.150
Yekeen, T. A., Xu, X., Zhang, Y., Wu, Y., Kim, S., Reponen, T., Dietrich, K. N., & HoChenHuo, S. M. A. X. (2016). Assessment of health risk of trace metal pollution in surface soil and road dust from e-waste recycling area in China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23, 17511–17524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6896-6
Zhou, W. L., Liu, W. K., & Yang, Q. C. (2012). Quality changes in hydroponic lettuce grown under pre-harvest short-duration continuous light of different intensities. The Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology, 87, 429–434. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2012.11512890
Zhu, Z., Han, Z., Bi, X., & Yang, W. (2012). The relationship between magnetic parameters and heavy metal contents of indoor dust in e-waste recycling impacted area Southeast China. Science of the Total Environment, 433, 302–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.06.067
Funding
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Ministry of Natural Resources of China Geological Survey (Project Nos. 21876014 and DD20230480) for financial support to carry out this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HG involved in formal analysis and writing—original draft; XH involved in formal analysis and writing—review and editing; JZ involved in investigation and writing—original draft; LD involved in formal analysis and funding acquisition; CH involved in writing—review and editing; JL involved in conceptualization, methodology, validation, writing—review and editing, supervision, and funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Human and animal rights
This work did not describe experiments with animals, human subjects, or human tissue samples.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The manuscript entitled “Effect of red and blue light supplementation on the efficacy of Noccaea caerulescens in decontaminating metals and alleviating leaching risk” is prepared in accordance with the Guide for authors available on the journal’s website and it has not been published elsewhere in part or in its entirety. All authors attest to the validity of its contents, and agree to its submission in Environmental Geochemistry and Health.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, H., Hu, X., Zhang, J. et al. Effect of red and blue light supplementation on the efficacy of Noccaea caerulescens in decontaminating metals and alleviating leaching risk. Environ Geochem Health 46, 48 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01837-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01837-9