Abstract
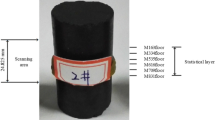
In order to study the influence of water–rock interaction on the mass time-varying characteristics of coal rocks, coal was selected as the research object and subjected to chemical immersion tests with different pH aqueous solutions for 12 days. By experiment, the time-varying patterns of mass change fraction in coal samples, pH value in solution, and ions concentration of calcium and magnesium were obtained. Based on the gray correlation theory, the correlation degree between the mass change fraction and four influencing factors was analyzed. The gray prediction models for the mass time-varying characteristics of coal rocks have been established. The research shows that: (1) the influence ways and degree of different pH aqueous solutions on the mass changes of coal rocks are different, (2) during the process of water–rock interaction, the change law of pH value, ions concentration of calcium and magnesium in solution are obvious, (3) the multiple regression models can be used to predict the mass change of coal rocks accurately under water–rock interaction.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- m 0 :
-
Initial mass(g)
- m d :
-
Instant mass(g)
- ρ 0 :
-
Density(kg·m−3)
- v 0 :
-
Initial sound velocity(m·s−1)
- t :
-
Soaking days
- h :
-
Height (mm)
- d :
-
Hiameter (mm)
- a :
-
Instant pH value
- η :
-
Mass change fraction
- b 2, b 3, b 4, b 5, a :
-
Parameters to be determined
- c 1 :
-
Instant calcium ions concentration (mol·L−1)
- c 2 :
-
Instant magnesium ions concentration (mol·L−1)
- R :
-
Correlation coefficient
- P :
-
Probability value that the correlation coefficient is zero
References
An, Q. Y., Zhang, L. W., Zhang, X., & Zhang, Q. S. (2023). Experiment on no-flow and flow CO2-water-rock interaction: A kinetics calculation method for rock pore evolution. Chemical Engineering Journal, 464, 14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.142754
An, T. X., Yu, B. S., Wang, Y. S., Ruan, Z., Meng, W., & Feng, Y. L. (2021). Water-rock interactions and origin of formation water in the Bohai Bay Basin: A case study of the Cenozoic Formation in Bonan Sag. Interpretation-a Journal of Subsurface Characterization, 9(2), T475–T493. https://doi.org/10.1190/int-2020-0181.1
Chen, G. B., Li, Y., Li, T., & Zhang, G. H. (2022). Deterioration law of intermittent jointed sandstone mechanical properties under water-rock interaction. Acta Geophysica, 70(4), 1923–1935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-022-00832-5
Chen, G. B., Li, Y., Li, T., & Zhang, G. H. (2023). Experimental study on the mechanical properties of intermittent jointed sandstone considering water-rock interaction and confining pressure effect. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 82(4), 15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03156-w
Chen, Q. Y., & Wang, F. (2021). Mathematical modeling and numerical simulation of water-rock interaction in shale under fracturing-fluid flowback conditions. Water Resources Research, 57(8), 20. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020wr029537
Dong, F. X., Peng, Z., Sun, W. B., Zhou, S. L., & Kong, L. J. (2021). Experimental research on the effect of water-rock interaction in filling media of fault structure. Geomechanics and Engineering, 24(5), 471–478. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2021.24.5.471
Guo, C., Qin, Y., Ma, D. M., Yang, Z. B., & Lu, L. L. (2020). Prediction of geotemperatures in coal-bearing strata and implications for coal bed methane accumulation in the Bide-Santang basin, western Guizhou, China. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 30(2), 235–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2018.07.008
Hu, Z. M., & Liu, C. (2021). An improved nonequidistant grey model based on simpson formula and its application. Complexity, 2021, 11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6654324
Huang, T. M., Li, Z. B., Long, Y., Zhang, F., & Pang, Z. H. (2022). Role of desorption-adsorption and ion exchange in isotopic and chemical (Li, B, and Sr) evolution of water following water-rock interaction. Journal of Hydrology, 610, 13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127800
Jia, C., Li, S., Fan, C. J., Luo, M. K., Zhou, L. J., Pu, Z., & Yang, L. (2022). Bolt-cable-mesh integrated support technology for water drenching roadway in thick coal seam. ACS Omega, 7(50), 46682–46692. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c05650
Jiang, J., Hou, Z. M., Hou, K. P., Lu, Y. F., Sun, H. F., & Niu, X. D. (2022). The damage constitutive model of sandstone under water-rock coupling. Geofluids, 2022, 12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1731254
Li, E. Q., Wei, Y. Q., Chen, Z. Y., Archbold, P., & Mullarney, B. (2023). Experimental study on tensile characteristics of layered carbonaceous slate subject to water-rock interaction and weathering. Sustainability, 15(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010885
Li, Z., Liu, S. G., Ren, W. T., Fang, J. J., Zhu, Q. H., & Dun, Z. L. (2020). Multiscale laboratory study and numerical analysis of water-weakening effect on shale. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5263431
Liu, H. Y., Li, Z. Y., Zhang, Y. S., & Wang, D. D. (2020a). The weakening mechanisms of the rock mechanics of marlite bank slopes under water-rock interaction conditions. Carbonates and Evaporites, 35(2), 11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00595-4
Liu, Q., Sun, Y. J., & Li, J. (2020b). Experimental study on seepage characteristics of jurassic weakly cemented sandstone under water-rock interaction. Geofluids, 2020, 12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8543687
Liu, S. Y., Zhang, K., Gao, J., Yang, Y. M., Bai, L., & Yan, J. Y. (2023). Research on temporal patterns of water-rock interaction in the coal mine underground reservoir based on the dynamic simulation test. ACS Omega, 8(15), 13819–13832. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c08145
Luo, Z. S., Zhu, Z. X., Li, J. L., Wang, L. H., Jiang, Q., Zhang, J. Y., & Deng, H. F. (2021). Study on the creep constitutive model of a sandstone rock under the water-rock interaction. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2021, 10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6648421
Qu, H. Y., Peng, Y., Pan, Z. J., Xu, X. D., & Zhou, F. J. (2023). Numerical study on the impact of water-rock interactions on the propagation of water-flooding induced fracture. Frontiers in Earth Science, 11, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2023.1129913
Shang, D. L., Zhao, Z. H., Dou, Z. H., & Yang, Q. (2020). Shear behaviors of granite fractures immersed in chemical solutions. Engineering Geology, 279, 14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105869
Sun, Q., Zhang, H., Hu, J. J., Geng, J. S., & Zhou, S. T. (2023). Damage mechanism of granite under subcritical water-rock interaction. Environmental Earth Sciences, 82(5), 13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-10827-0
Wang, Q. M., Hu, Q. H., Larsen, C., Zhao, C., Sun, M. D., Zhang, Y. X., & Zhang, T. (2021). Microfracture-pore structure characterization and water-rock interaction in three lithofacies of the lower eagle ford formation. Engineering Geology, 292, 12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106276
Wang, W. A., Yao, Q. L., Xu, Q., Chen, X. Y., Liu, H. Y., & Li, X. H. (2022). Experimental study on the evolution law of coal mine underground reservoir water storage space under the disturbance and water-rock interaction effect. Minerals, 12(12), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121491
Wang, Y., Shi, L. Q., Wang, M., & Liu, T. H. (2020). Hydrochemical analysis and discrimination of mine water source of the Jiaojia gold mine area, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 79(6), 14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-8856-1
Xiao, Y., Deng, H. F., Li, G. Y., Peng, M., Xu, P. F., Assefa, E., & Liu, L. P. (2022). Pore structure characteristics of an underground limestone chamber in the three Gorges reservoir area. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 81(9), 14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02863-0
Xu, Q., Tian, A. R., Luo, X. Y., Liao, X., & Tang, Q. (2022). Chemical damage constitutive model establishment and the energy analysis of rocks under water-rock interaction. Energies, 15(24), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15249386
Yan, B. Q., Guo, Q. F., Ren, F. H., & Cai, M. F. (2020). Modified Nishihara model and experimental verification of deep rock mass under the water-rock interaction. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 128, 10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104250
Yao, Q. L., Zheng, C. K., Tang, C. J., Xu, Q., Chong, Z. H., & Li, X. H. (2020). Experimental investigation of the mechanical failure behavior of coal specimens with water intrusion. Frontiers in Earth Science, 7, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2019.00348
Yao, W. M., Li, C. D., Ke, Q. R., Fan, Y. B., Li, B. C., Zhan, H. B., & Criss, R. E. (2023). Multi-scale deterioration of physical and mechanical properties of argillaceous siltstone under cyclic wetting-drying of Yangtze River water. Engineering Geology, 312, 14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106925
Zhang, C., Bai, Q. S., & Han, P. H. (2023). A review of water rock interaction in underground coal mining: Problems and analysis. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 82(5), 22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03142-2
Zhang, H., Hu, Z. Q., Ma, B., & Chen, X. Z. (2021). Stability analysis of a red bed slope reservoir bank considering water-rock interaction characteristics. Desalination and Water Treatment, 239, 289–300. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2021.27801
Zhang, K., Deng, X., Gao, J., Liu, S. Y., Wang, F. Y., & Han, J. L. (2022a). Insight into the process and mechanism of water-rock interaction in underground coal mine reservoirs based on indoor static simulation experiments. ACS Omega, 7(41), 36387–36402. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c04161
Zhang, S. G., Yun, X., Song, Y., Liu, W. B., & Yang, L. (2022b). Fluid-structure coupling creep characteristics of red-bed soft rock in south China. Water, 14(24), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14244088
Zhao, Z. H., Liu, H., Gao, X. J., & Feng, Y. H. (2023). Meso-macro damage deterioration of weakly cemented red sandstone under the coupling effect of high-humidity and uniaxial loading. Engineering Failure Analysis, 143, 13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106911
Zhao, Z. H., Liu, H., Lyu, X. Z., Wang, L., Tian, Z. X., & Sun, J. C. (2021). Experimental study on the damage and deterioration behaviour of deep soft rock under water-rock interaction. Geofluids, 2021, 11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8811110
Zhou, K. Y., Dou, L. M., Gong, S. Y., Chai, Y. J., Li, J. Z., Ma, X. T., & Song, S. K. (2022). Mechanical behavior of sandstones under water-rock interactions. Geomechanics and Engineering, 29(6), 627–643. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2022.29.6.627
Zhou, M. L., Li, J. L., Luo, Z. S., Sun, J. B., Xu, F., Jiang, Q., & Deng, H. F. (2021). Impact of water-rock interaction on the pore structures of red-bed soft rock. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86815-w
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (52034007), the Open Fund Project of the State Key Laboratory of Coal Resources and Safe Mining, CUMT (SKLCRSM19KF013), and the National Undergraduate Practice and Innovation Training Program (202110320013Z).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by ZY, SL, YL, and NZ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by ZY and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Li, S., Liu, Y. et al. Experimental study on the influence of water–rock interaction on the time-varying characteristics of coal rock mass. Environ Geochem Health 46, 45 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01832-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01832-0